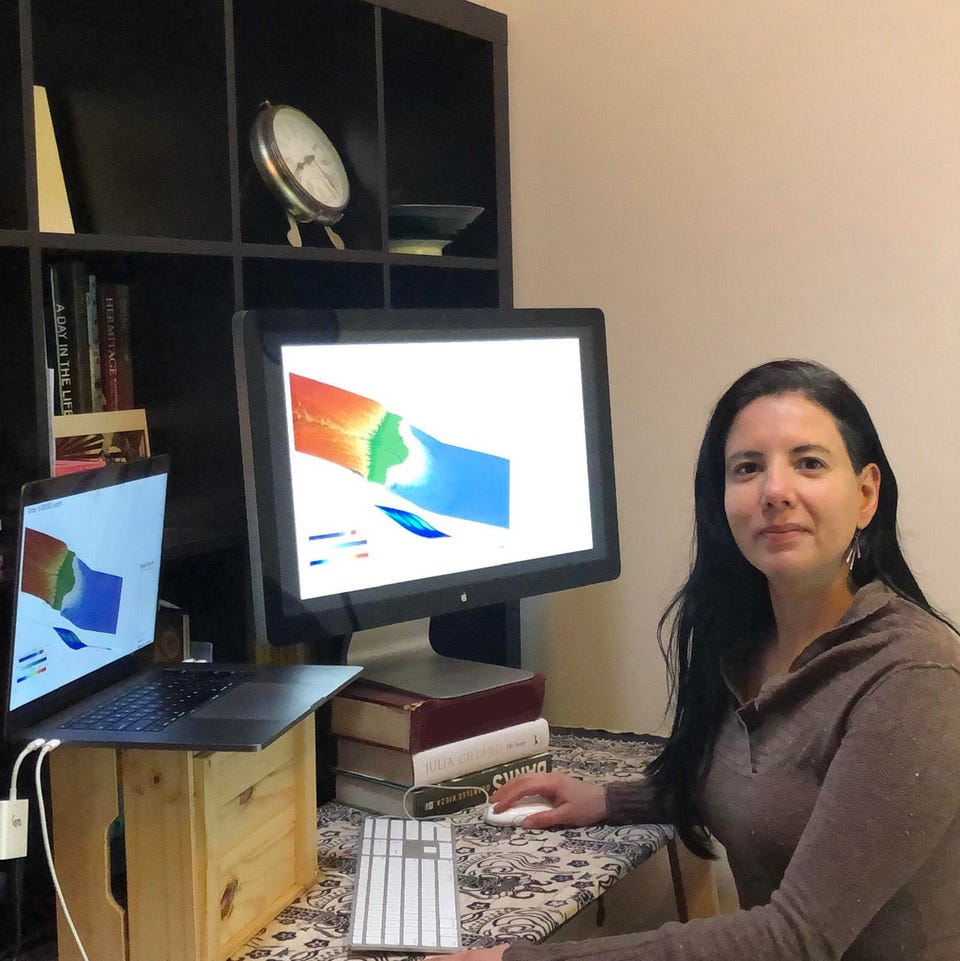
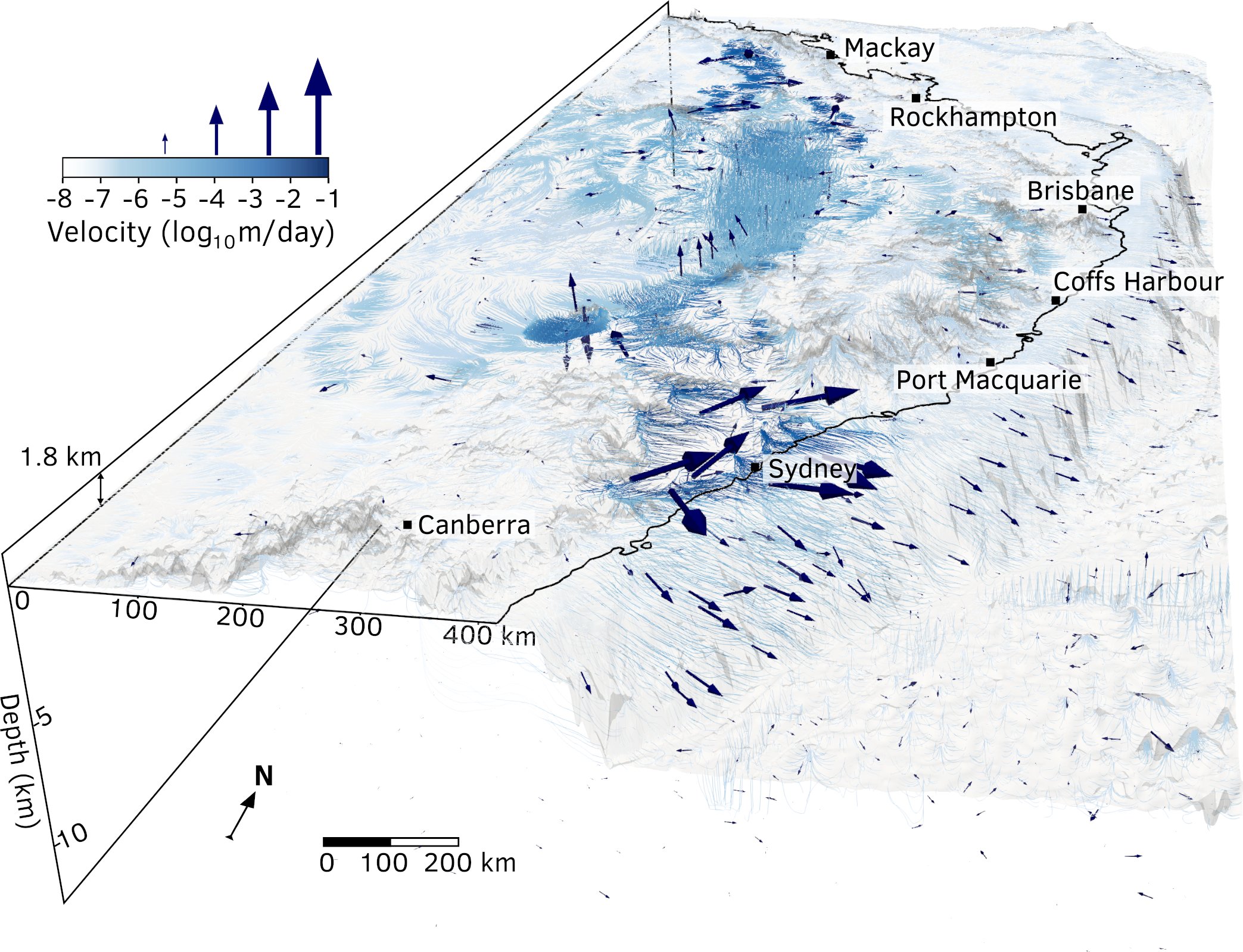
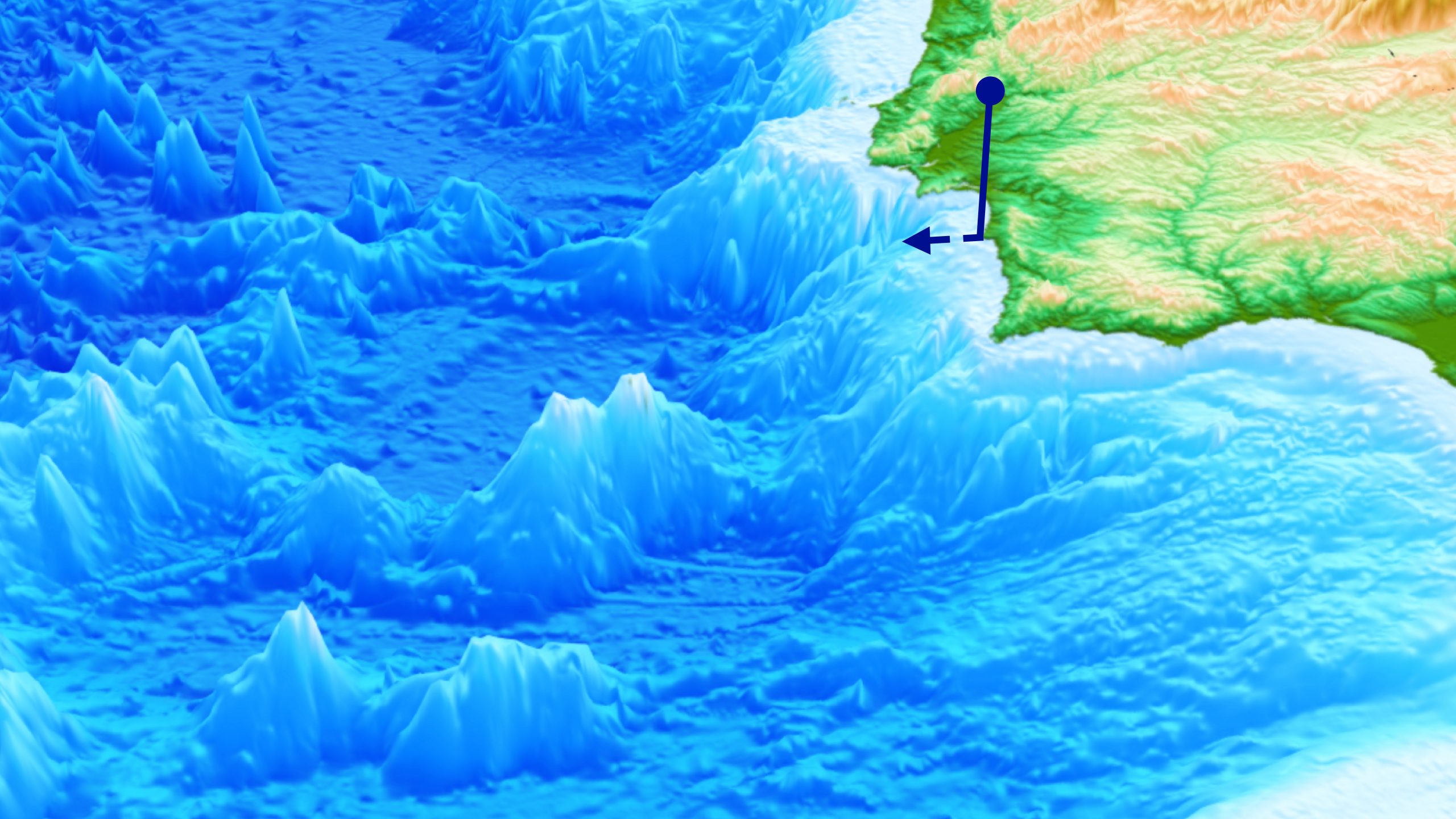
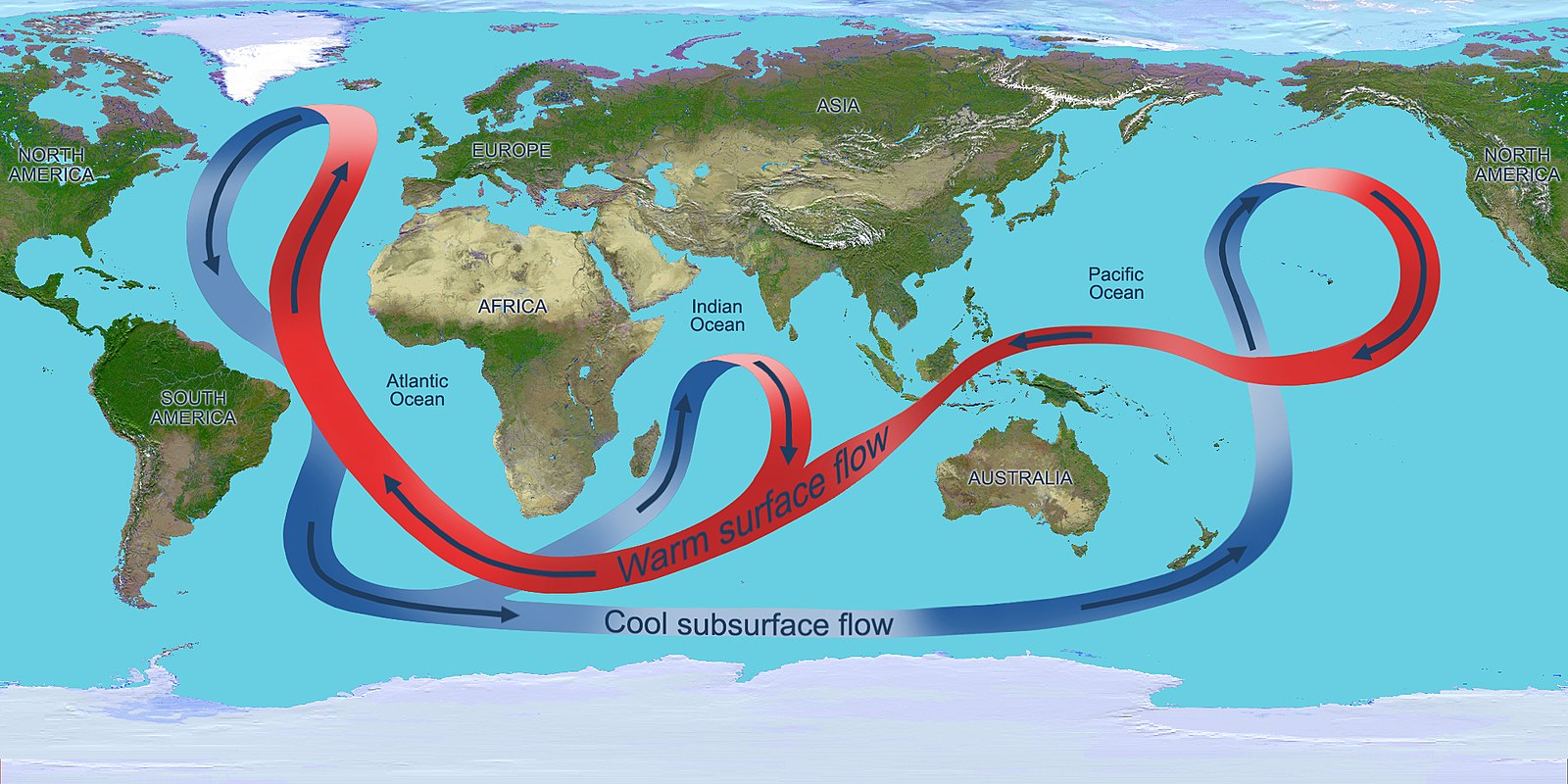
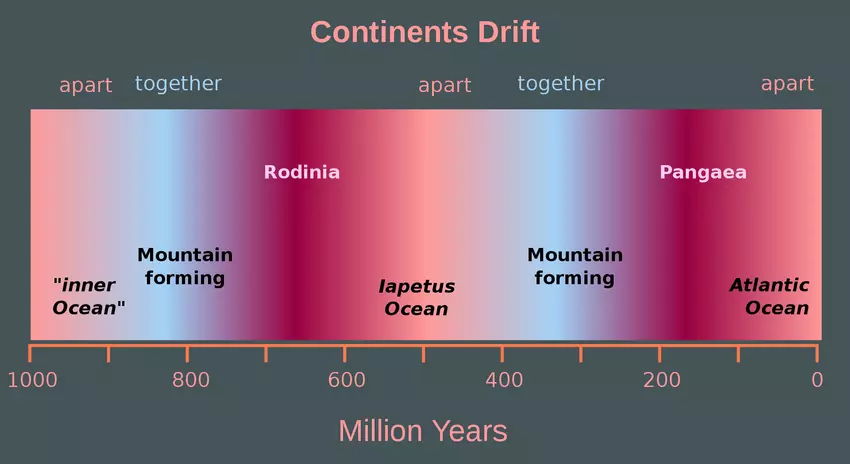
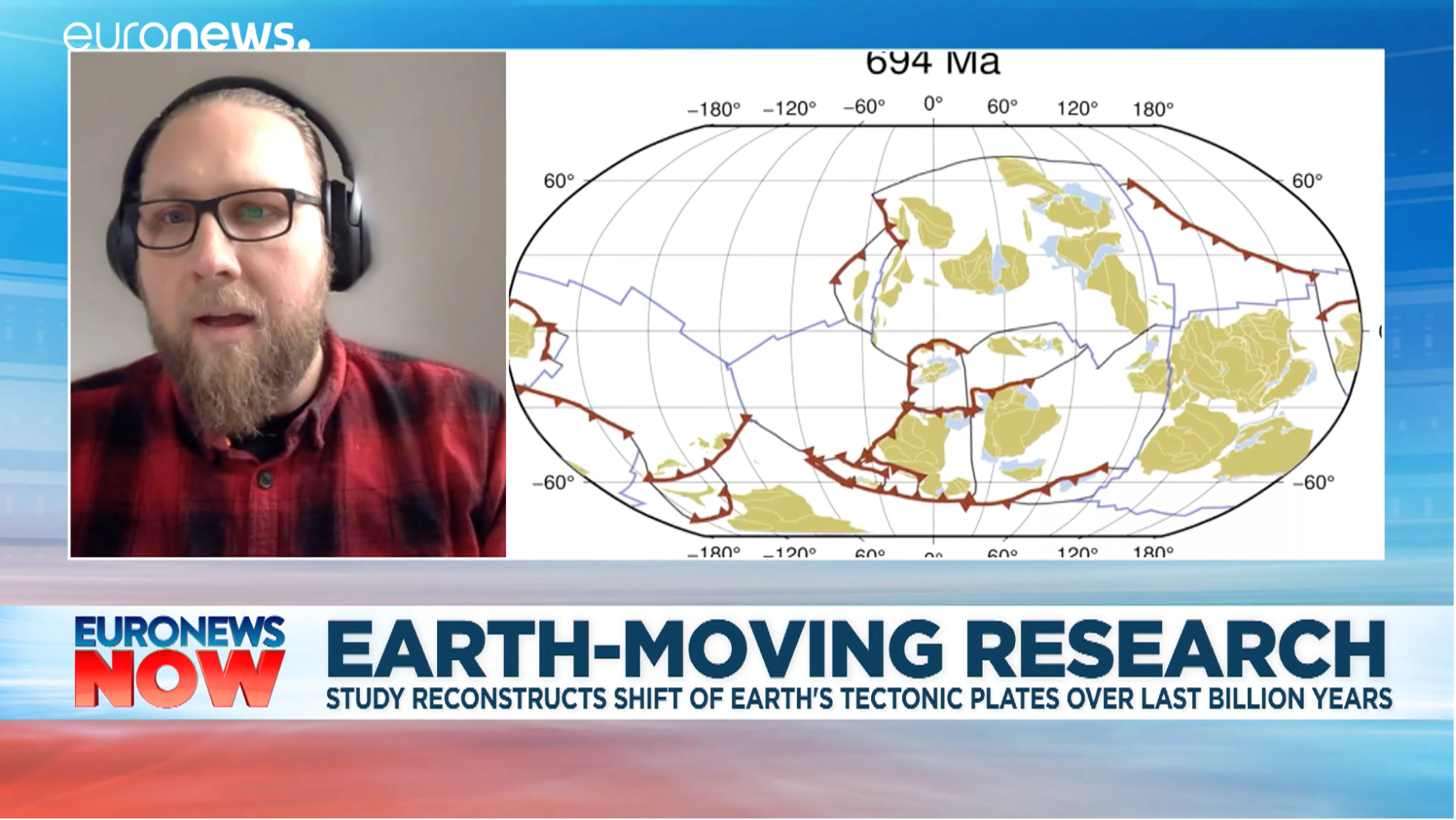
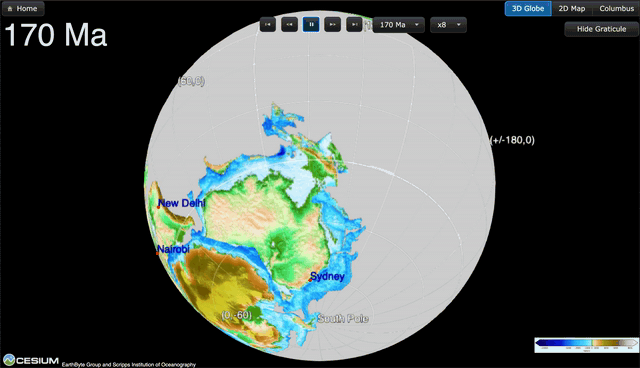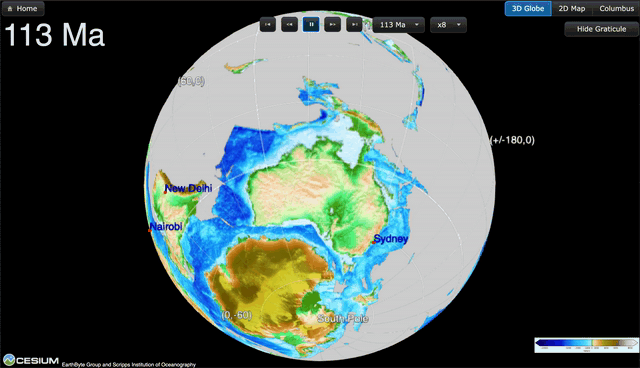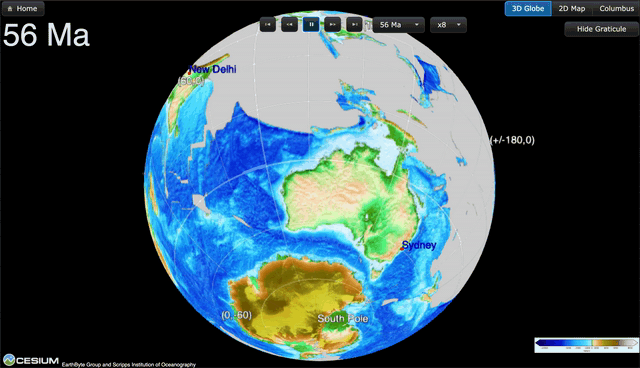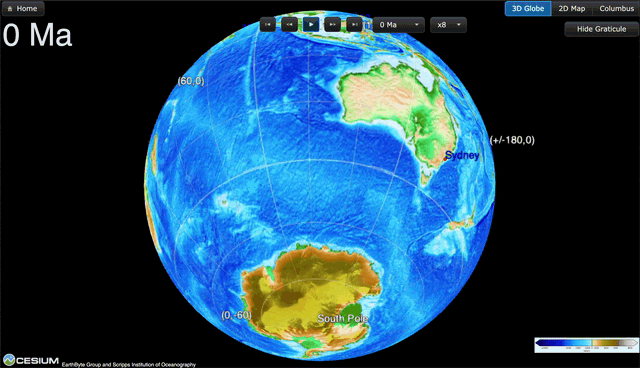
A New View of Deep Earth’s Carbon Emissions
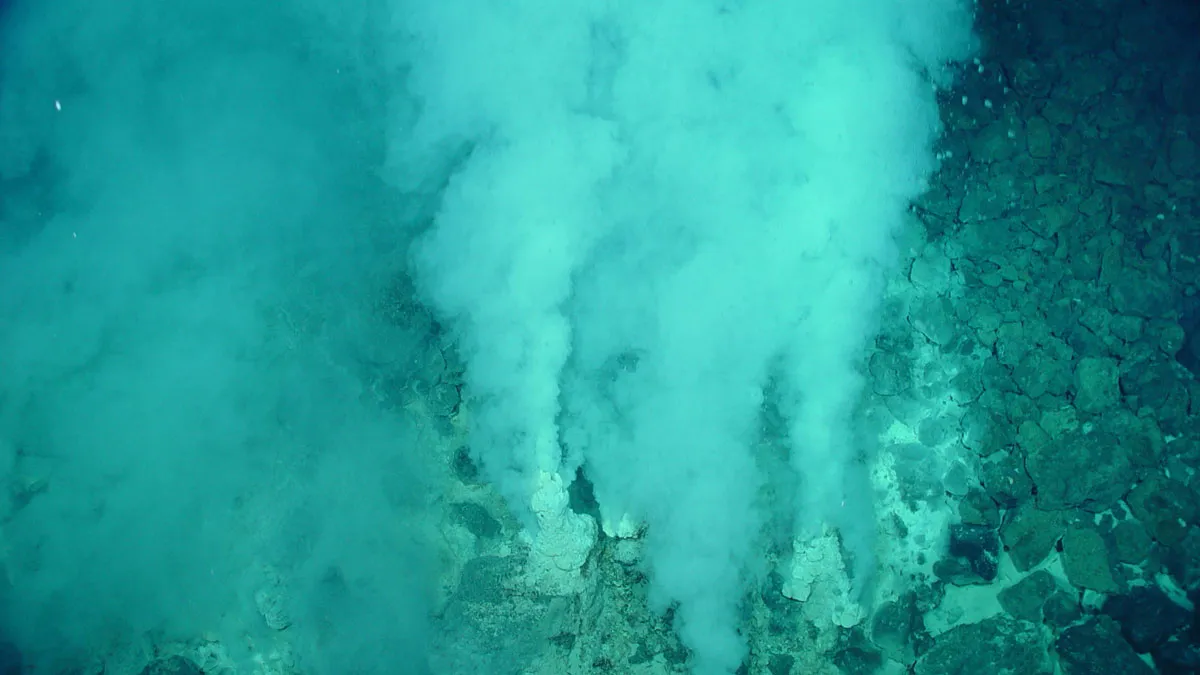
EOS: Advances in plate tectonics research allow a deeper understanding of how greenhouse gases escape from within the planet. by Saima May Sidik7 November 2024 Gases escape from the deep-sea Champagne Vents in the Northern Marianas region of the Pacific, where tectonic plates are colliding. Credit: Submarine Ring of Fire 2014 – Ironman, NOAA/PMEL, NSF Source: Geochemistry, Geophysics, … Read more…