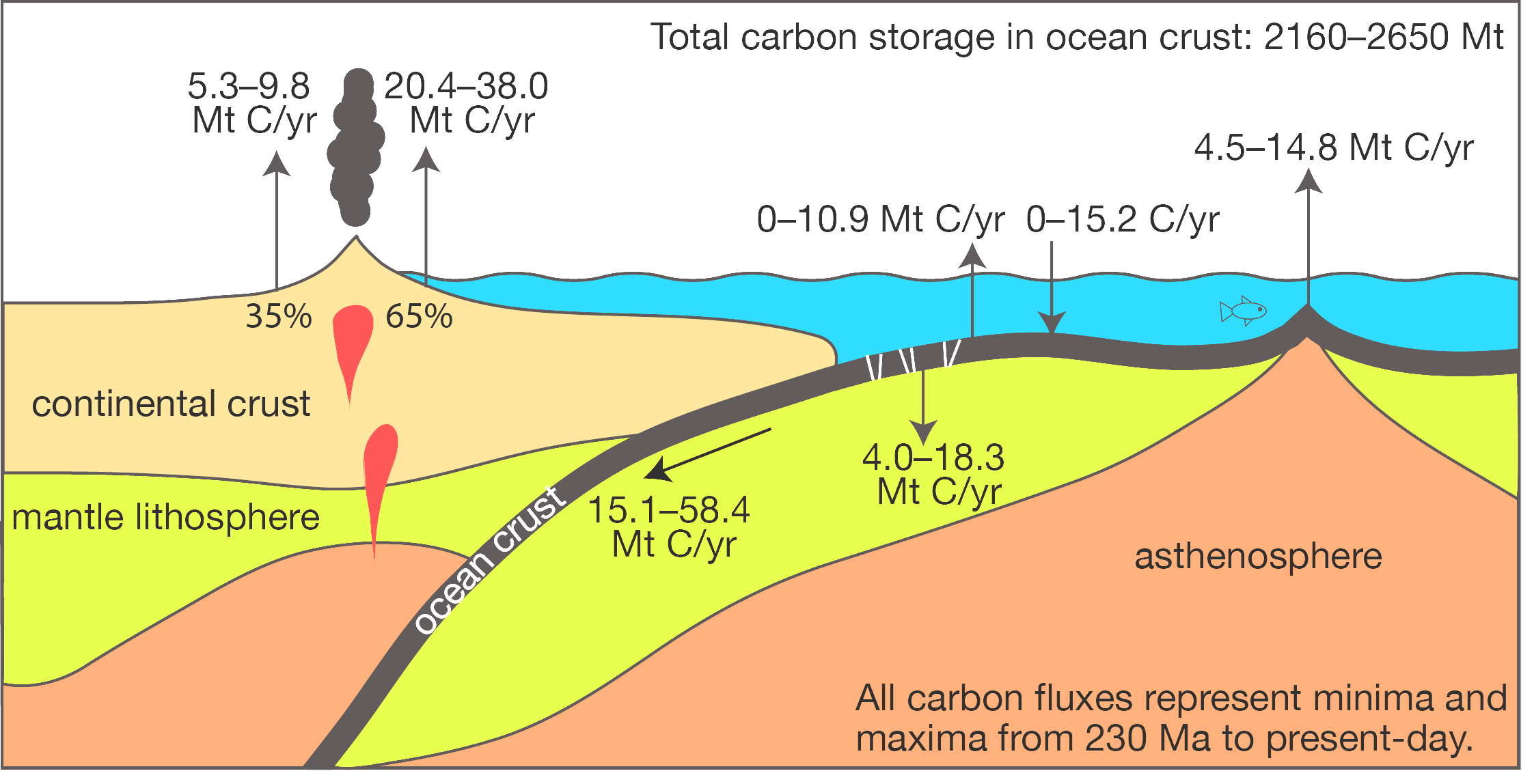
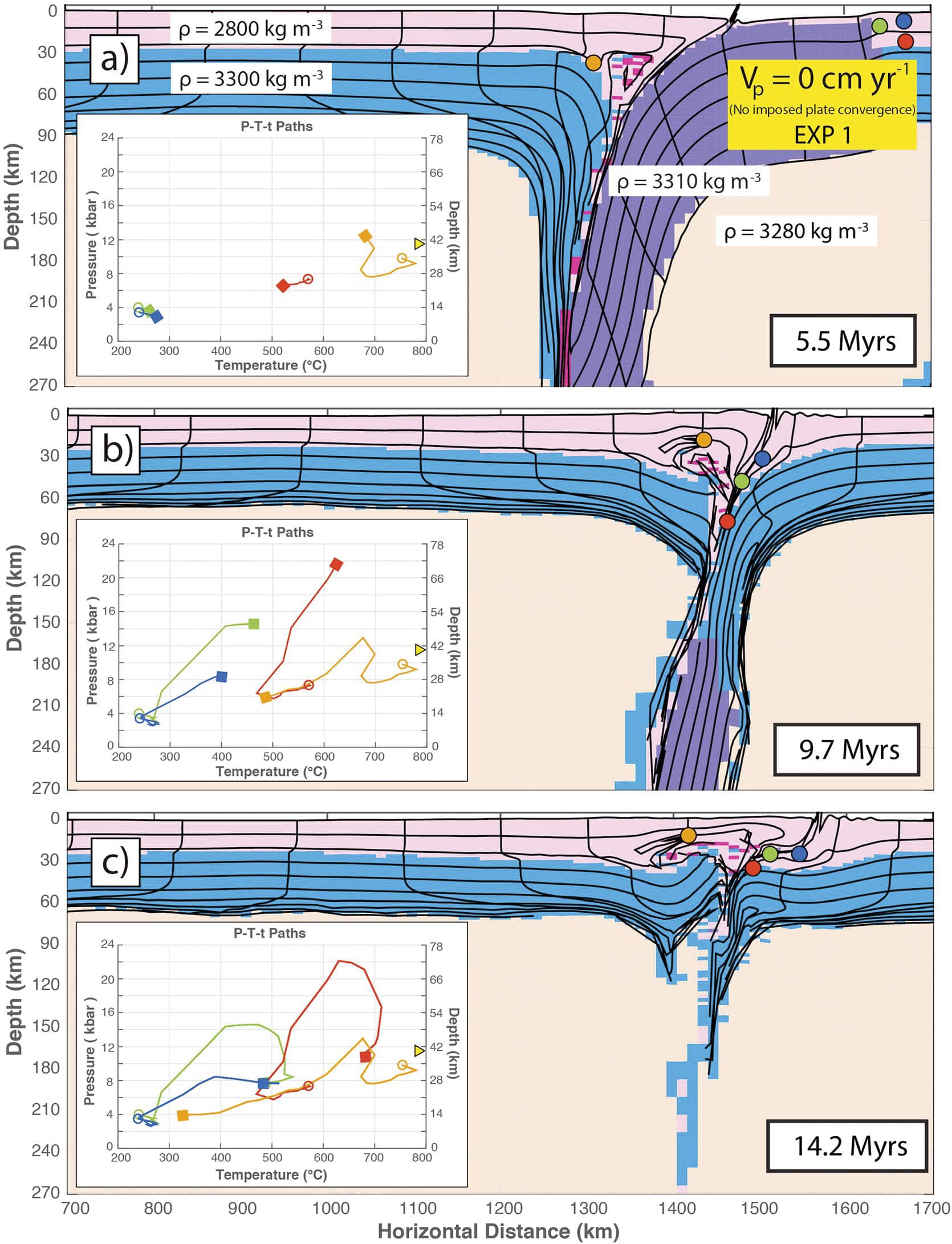
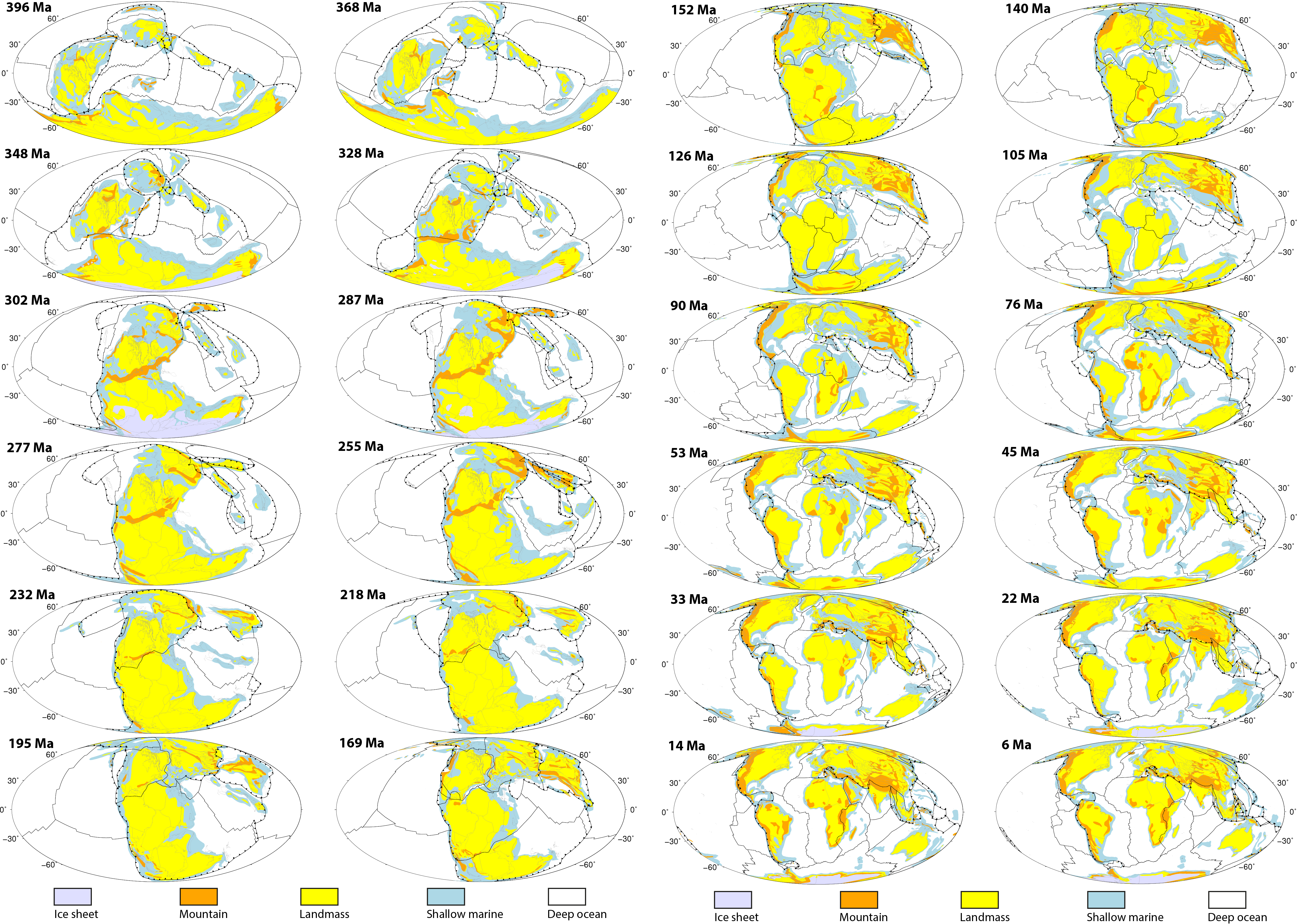
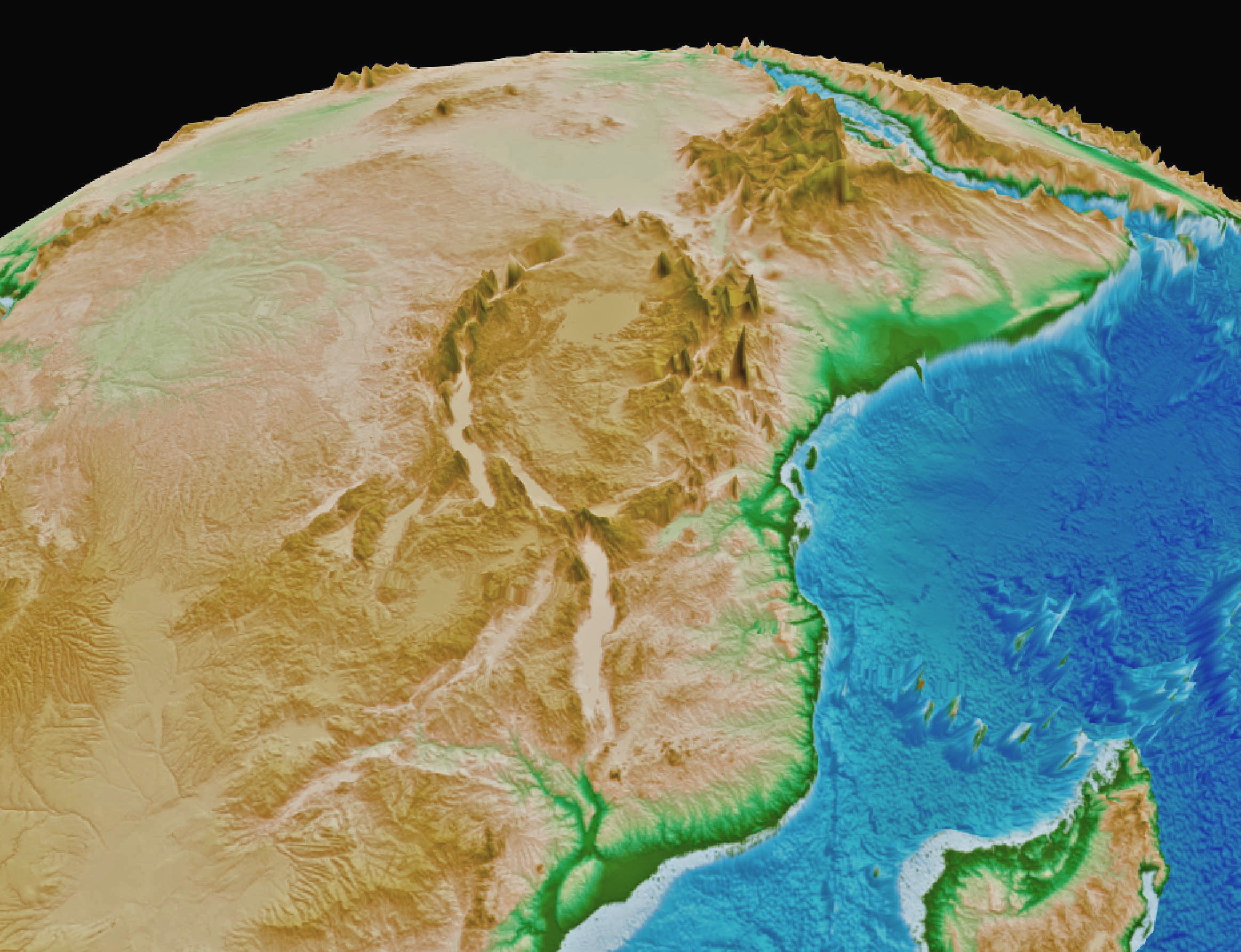
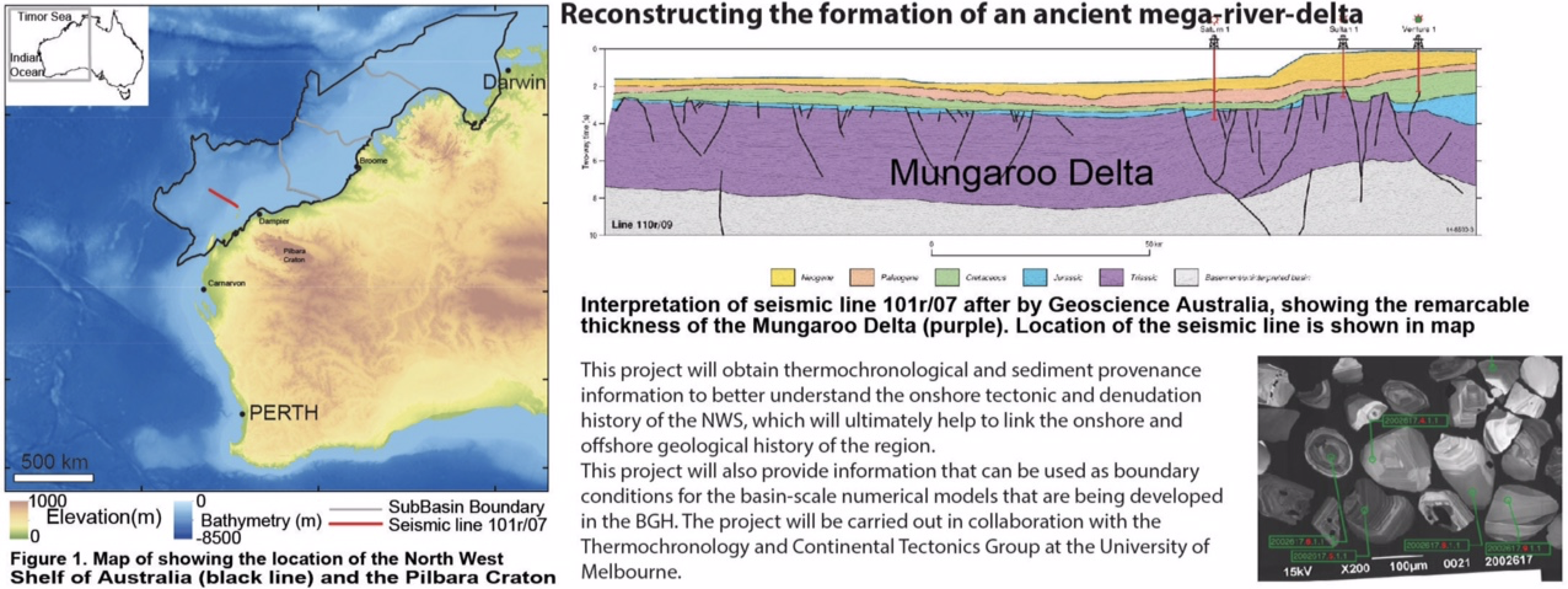
Aftershocks hit Papua New Guinea as it recovers from a remote major earthquake
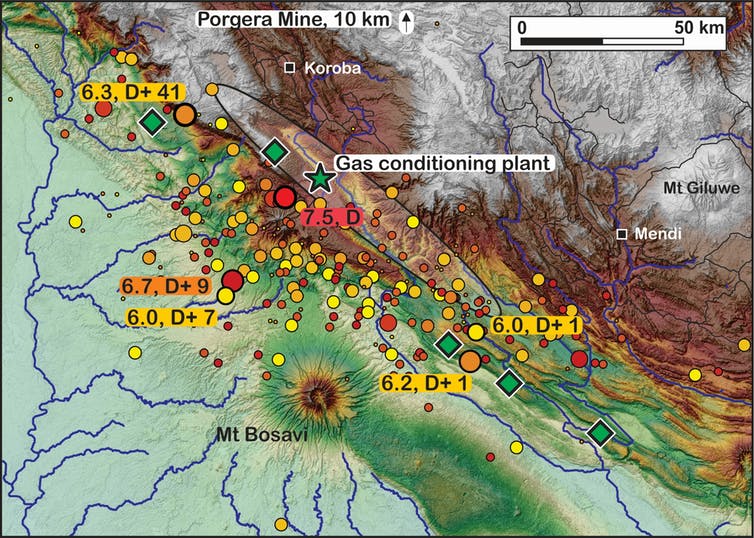
Another powerful aftershock hit Papua New Guinea this weekend as the recovery effort continues following February’s deadly magnitude 7.5 earthquake, with many thousands of people dependent on humanitarian aid. Aid organisations such as CARE Australia and UNICEF are still seeking donations. The Australian government has sent medical staff and other support to help. Some have criticised the PNG government’s efforts as “too slow”. But the … Read more…