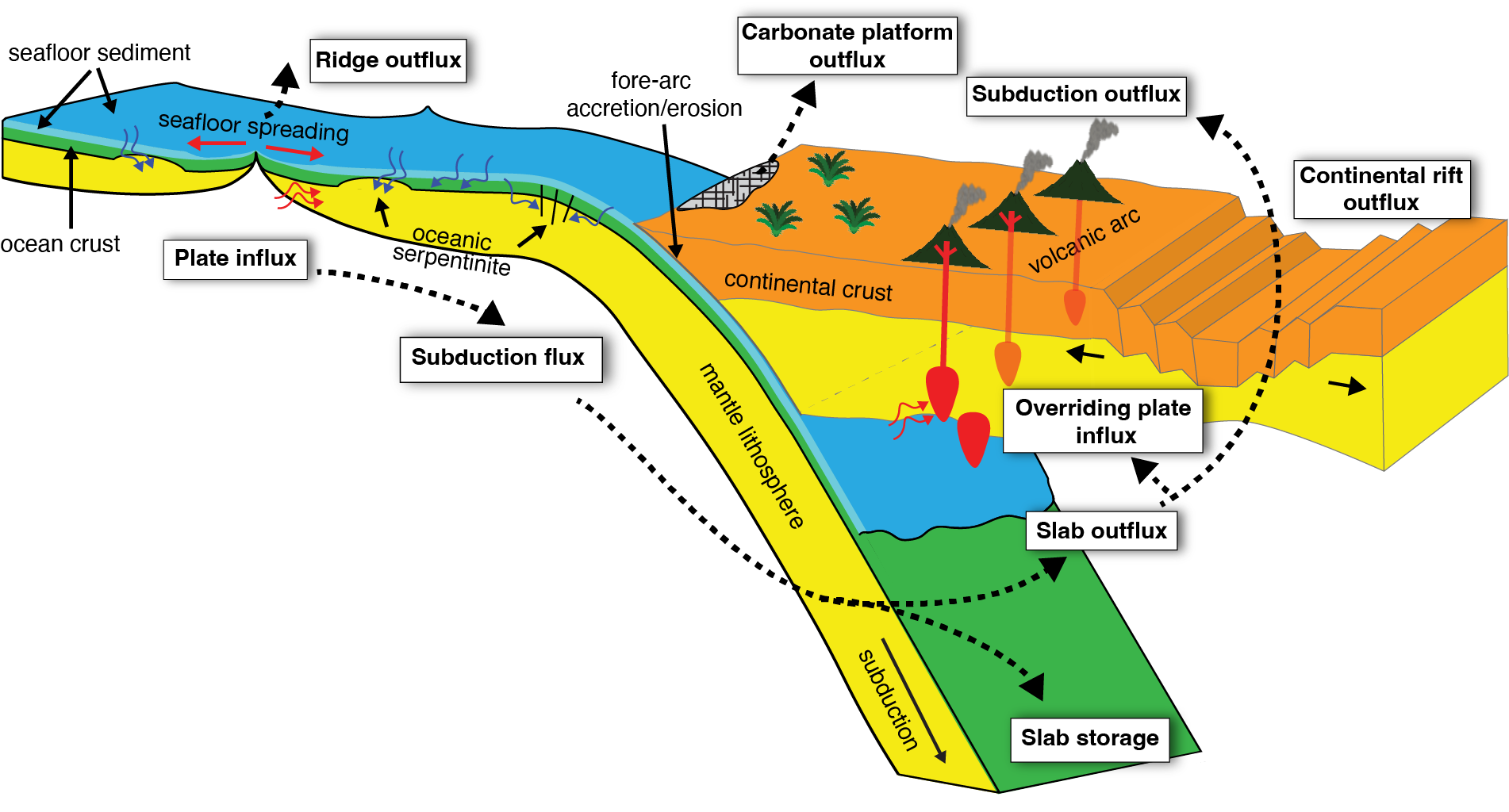
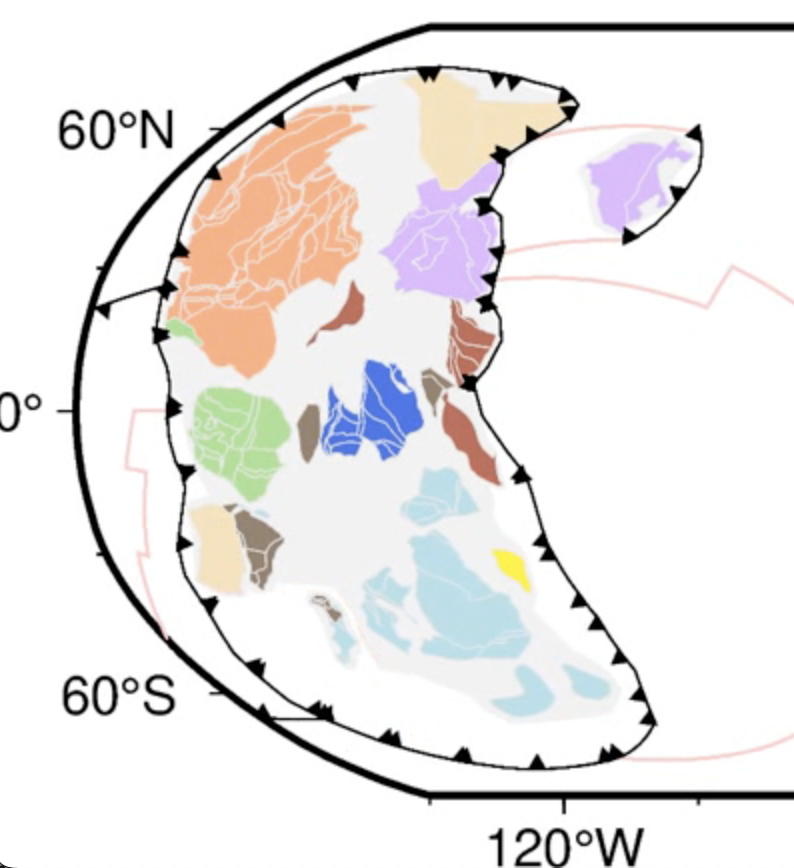
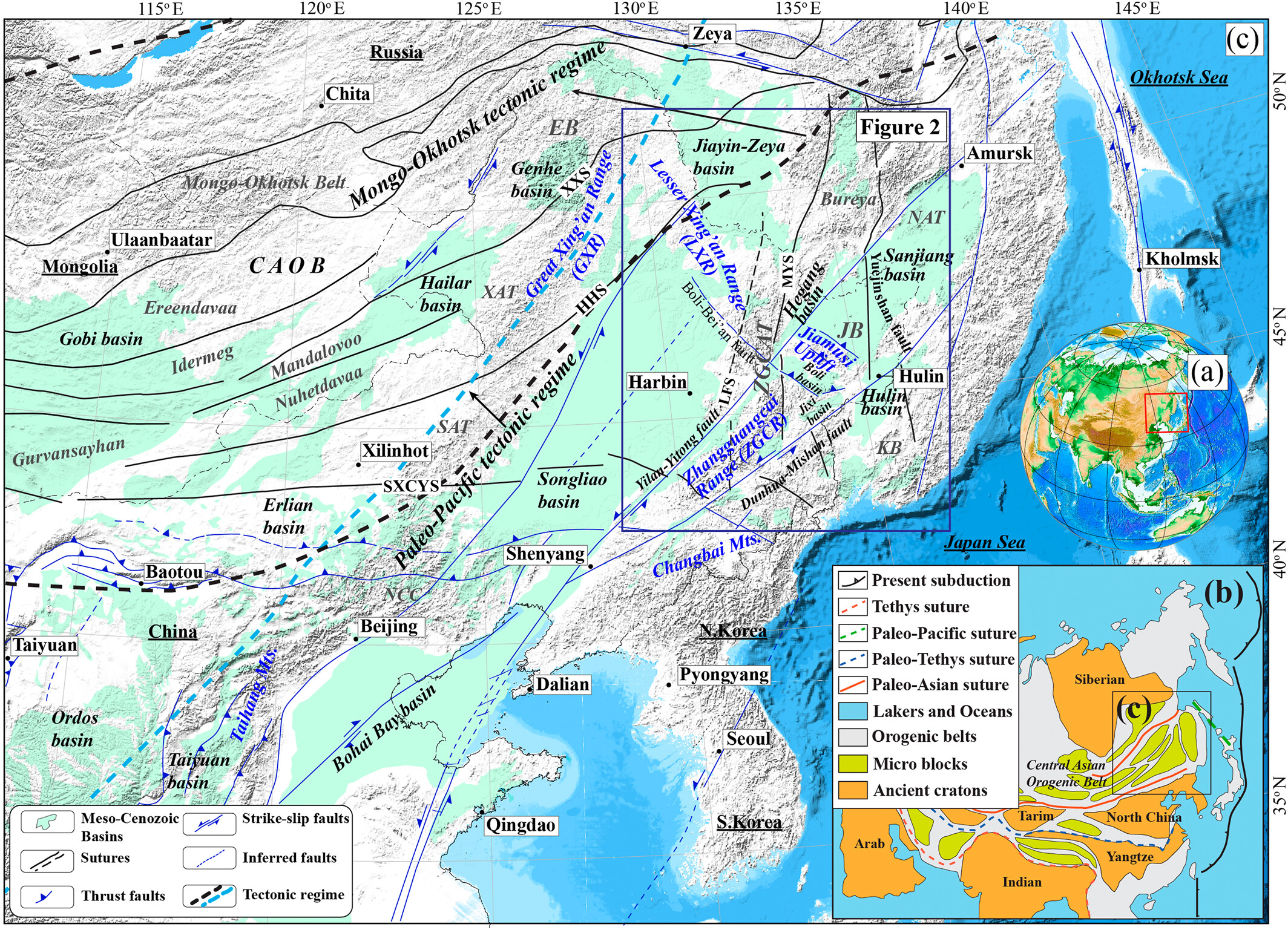
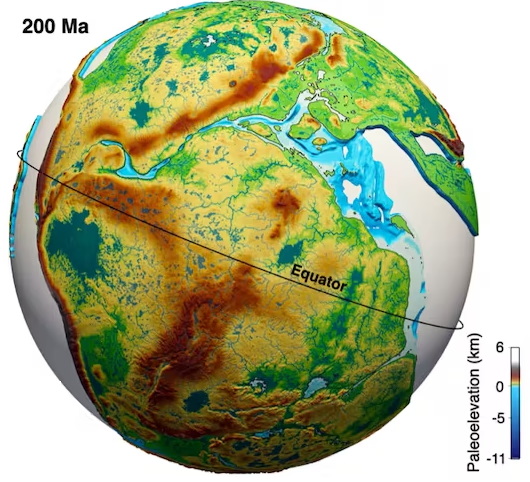
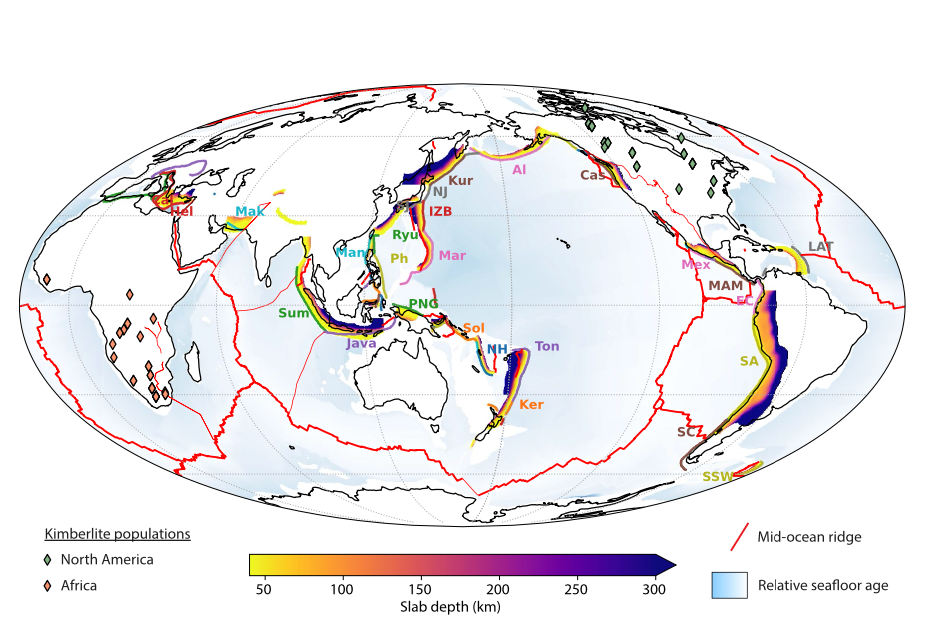
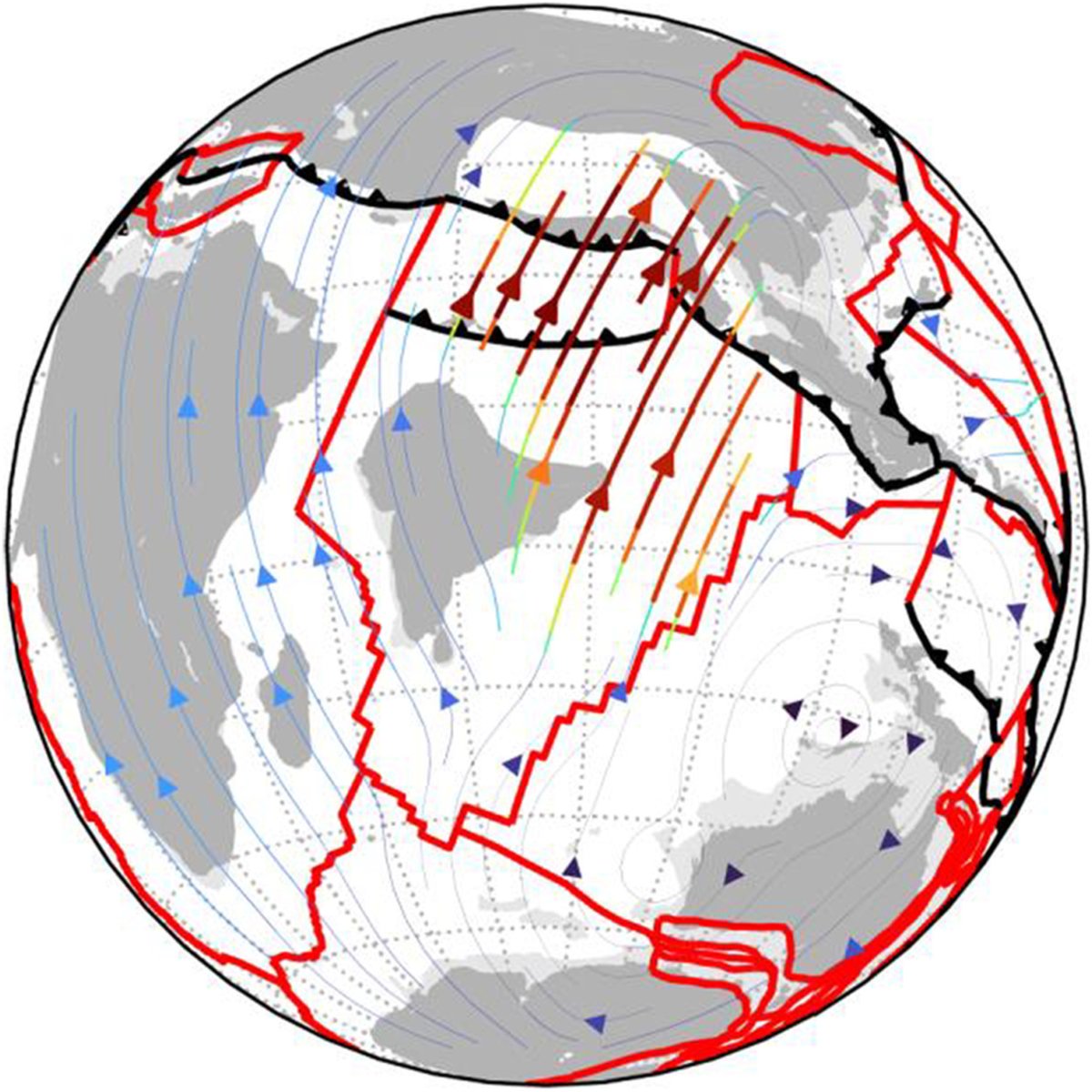
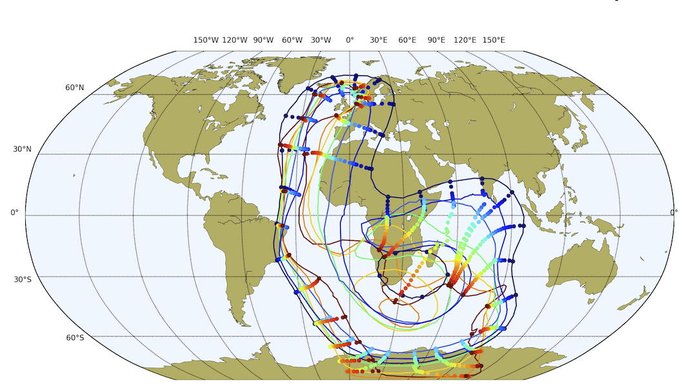
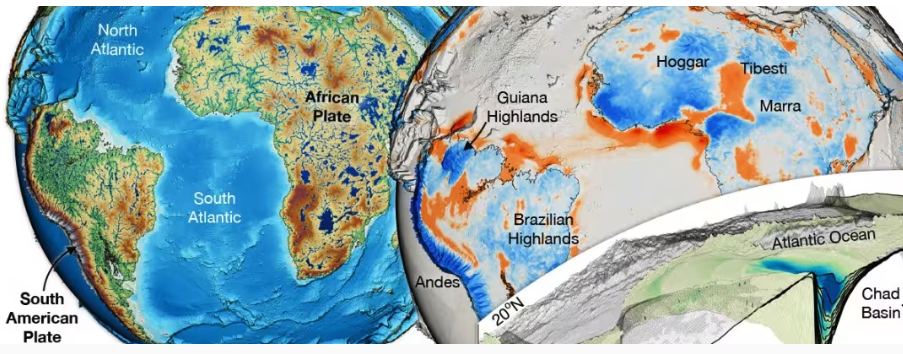
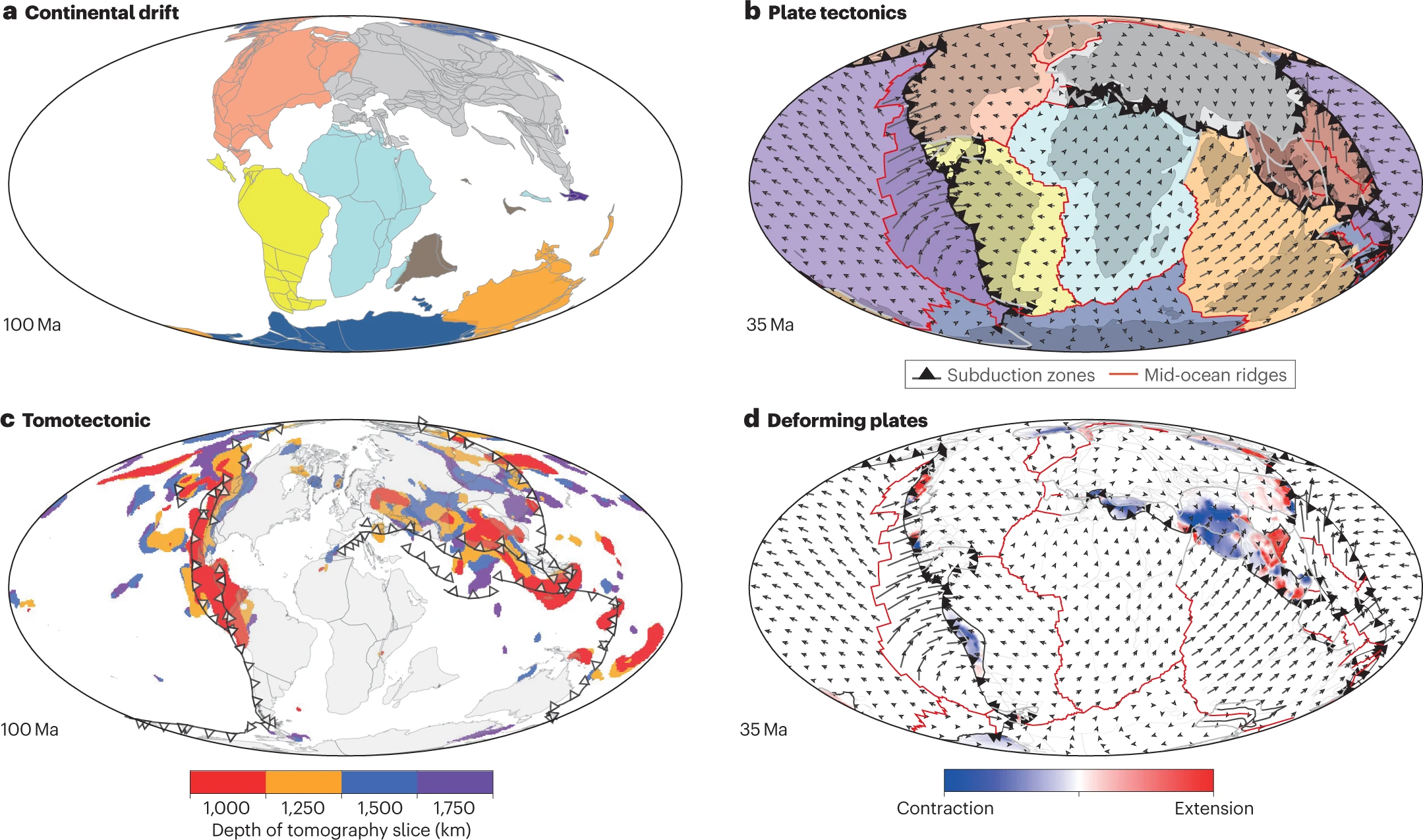
Understanding the intricate relationships between the solid Earth and its surface systems in deep time necessitates comprehensive full-plate tectonic reconstructions that include evolving plate boundaries and oceanic plates. In particular, a tectonic reconstruction that spans multiple supercontinent cycles is important to understand the long-term evolution of Earth’s interior, surface environments and mineral resources. Here, we present a new full-plate tectonic reconstruction from 1.8 Ga to present that combines and refines three published models: one full-plate tectonic model spanning 1 Ga to present and two continental-drift models focused on the late Paleoproterozoic to Mesoproterozoic eras. Our model is constrained by geological and geophysical data, and presented as a relative plate motion model in a paleomagnetic reference frame. The model encompasses three supercontinents, Nuna (Columbia), Rodinia, and Gondwana/Pangea, and more than two complete supercontinent cycles, covering ~40% of the Earth’s history. Our refinements to the base models are focused on times before 1.0 Ga, with minor changes for the Neoproterozoic. For times between 1.8 Ga and 1.0 Ga, the root mean square speeds for all plates generally range between 4 cm/yr and 7 cm/yr (despite short-term fast motion around 1.1 Ga), which are kinematically consistent with post-Pangean plate tectonic constraints. The time span of the existence of Nuna is updated to between 1.6 Ga (1.65 Ga in the base model) and 1.46 Ga based on geological and paleomagnetic data. We follow the base models to leave Amazonia/West Africa separate from Nuna (as well as Western Australia, which only collides with the remnants of Nuna after initial break-up), and South China/India separate from Rodinia. Contrary to the concept of a “boring billion”, our model reveals a dynamic geological history between 1.8 Ga and 0.8 Ga, characterized by supercontinent assembly and breakup, and continuous accretion events. The model is publicly accessible, providing a framework for future refinements and facilitating deep time studies of Earth’s system. We suggest that the model can serve as a valuable working hypothesis, laying the groundwork for future hypothesis testing.

Click on the image to watch the video on youtube
Lateritic Ni-Co prospectivity modelling in eastern Australia using an enhanced generative adversarial network and positive-unlabelled bagging
The surging demand for nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co), driven by the acceleration of clean energy transitions, has sparked interest in the Lachlan Orogen of New South Wales for its potential lateritic Ni-Co resources. Despite recent discoveries, a substantial knowledge gap exists in understanding the full scope of these critical metals in this geological province. … Read more…