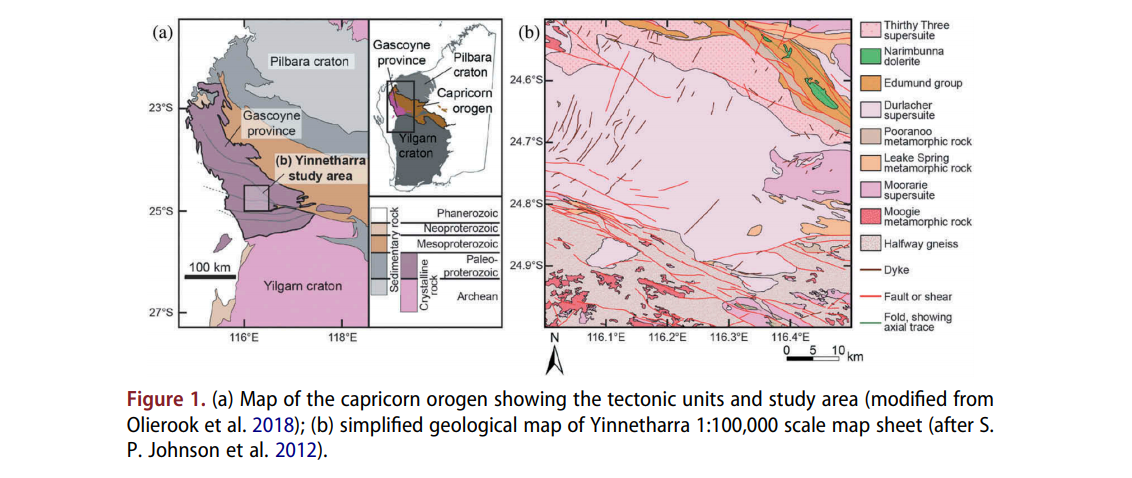
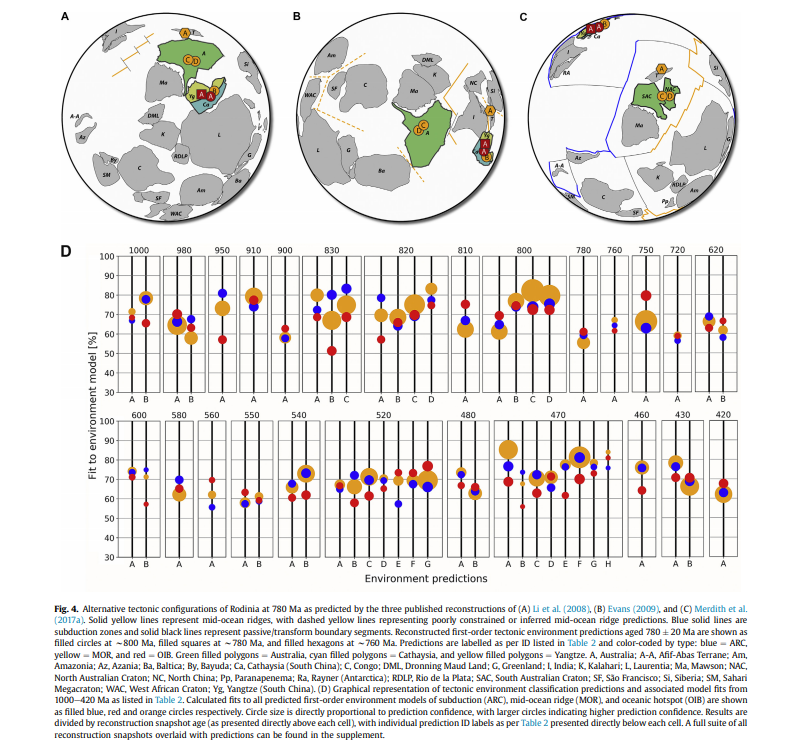
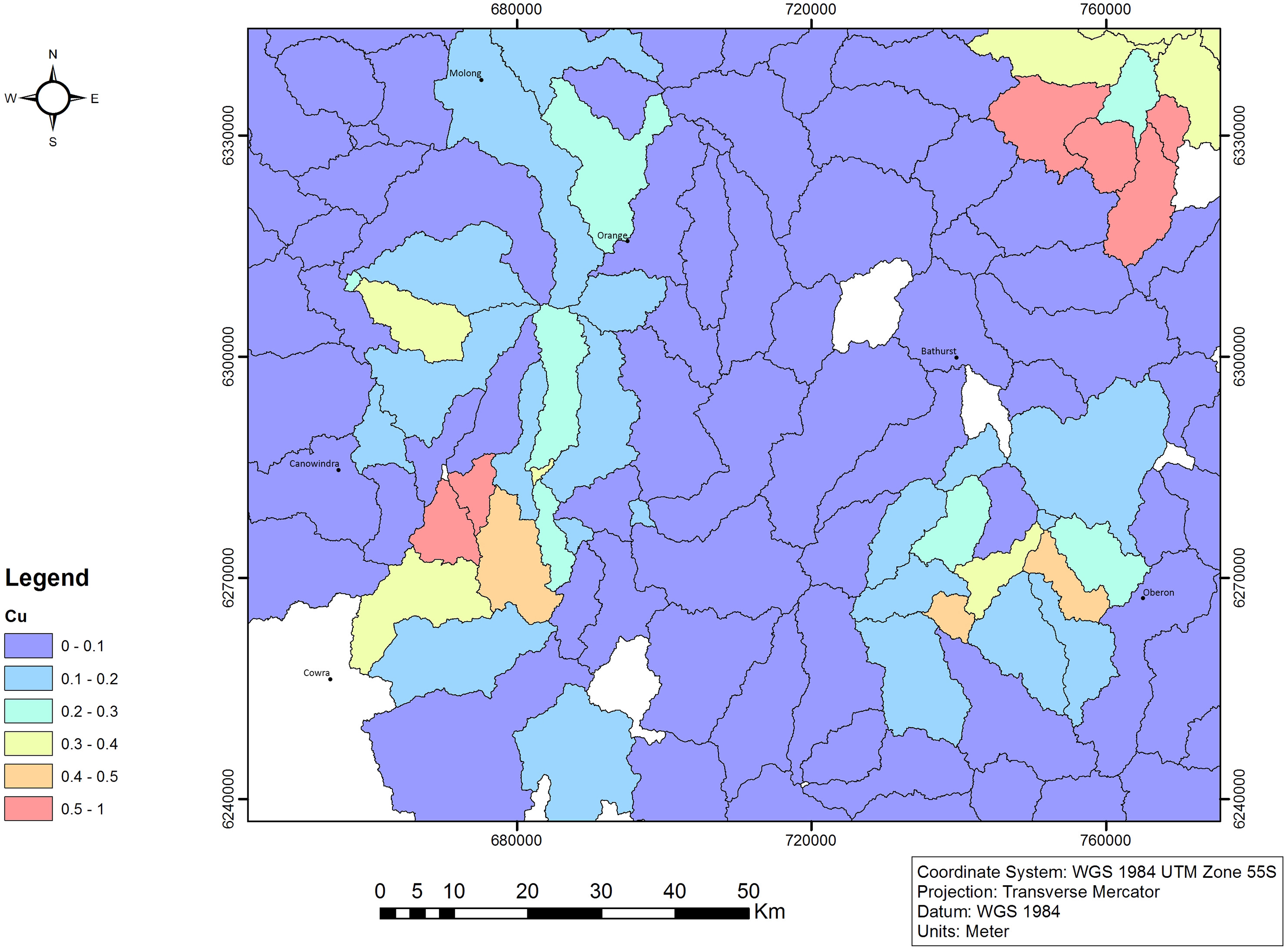
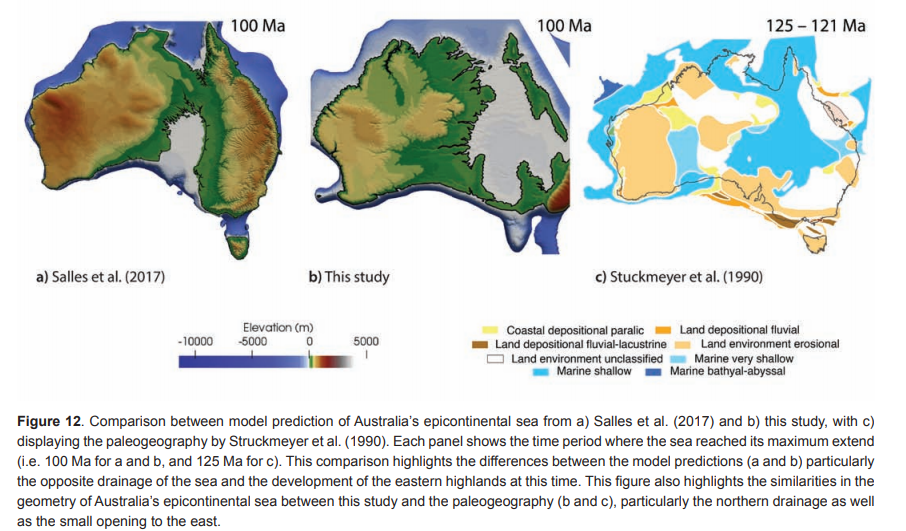
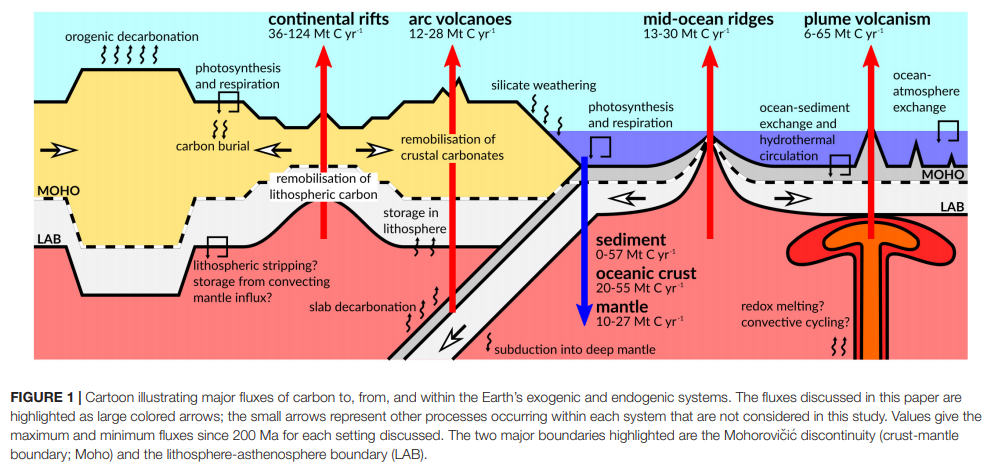
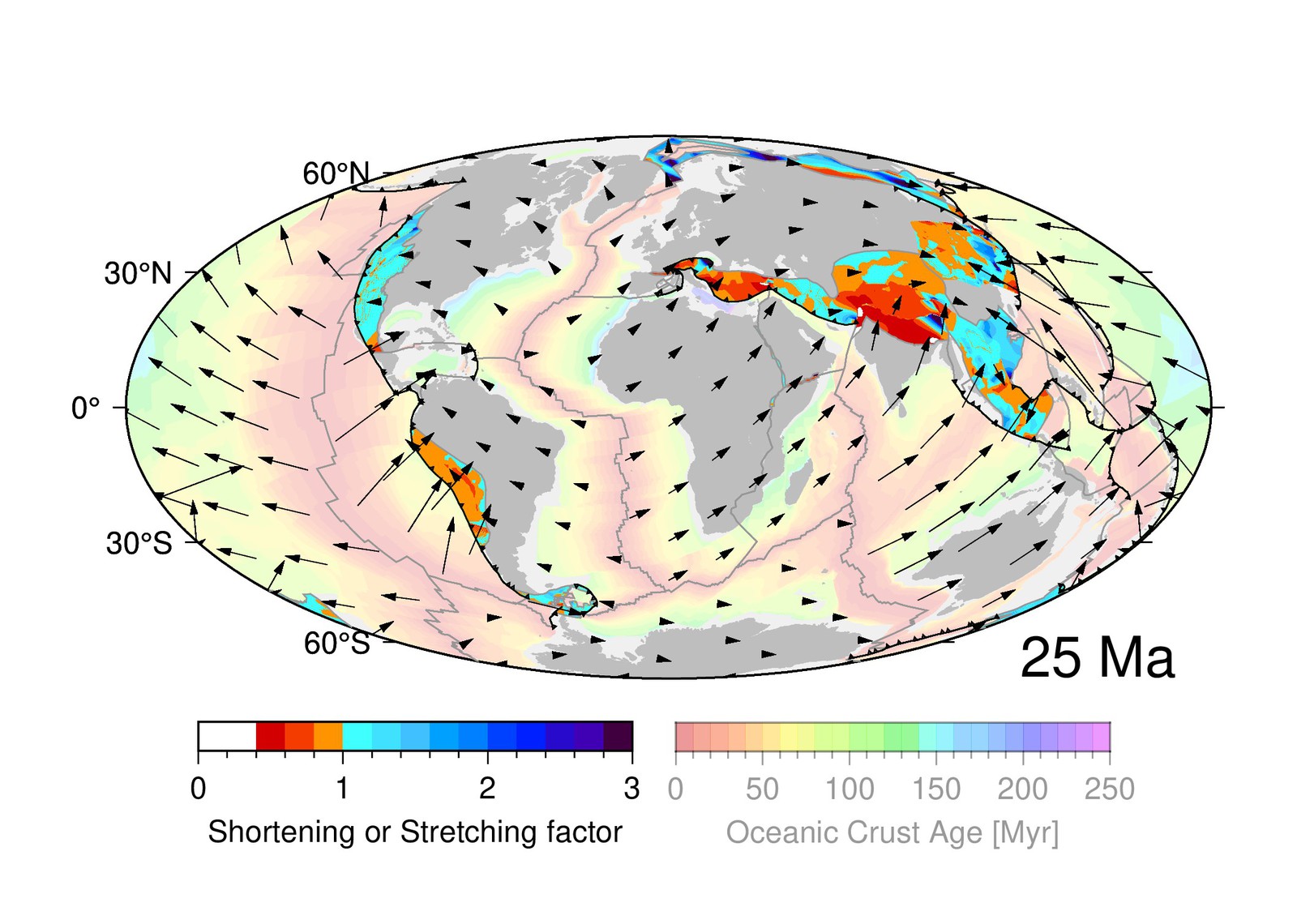
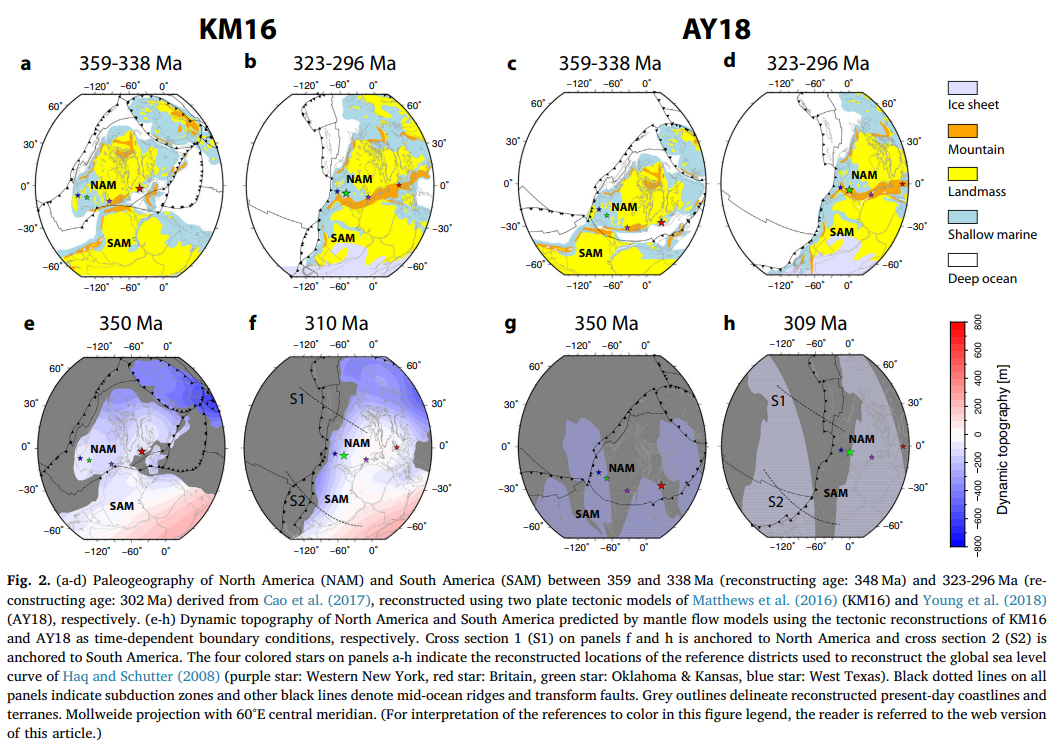
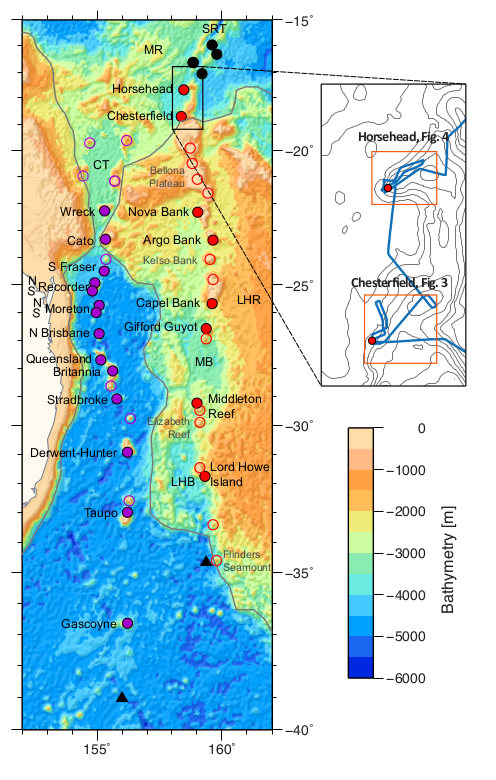
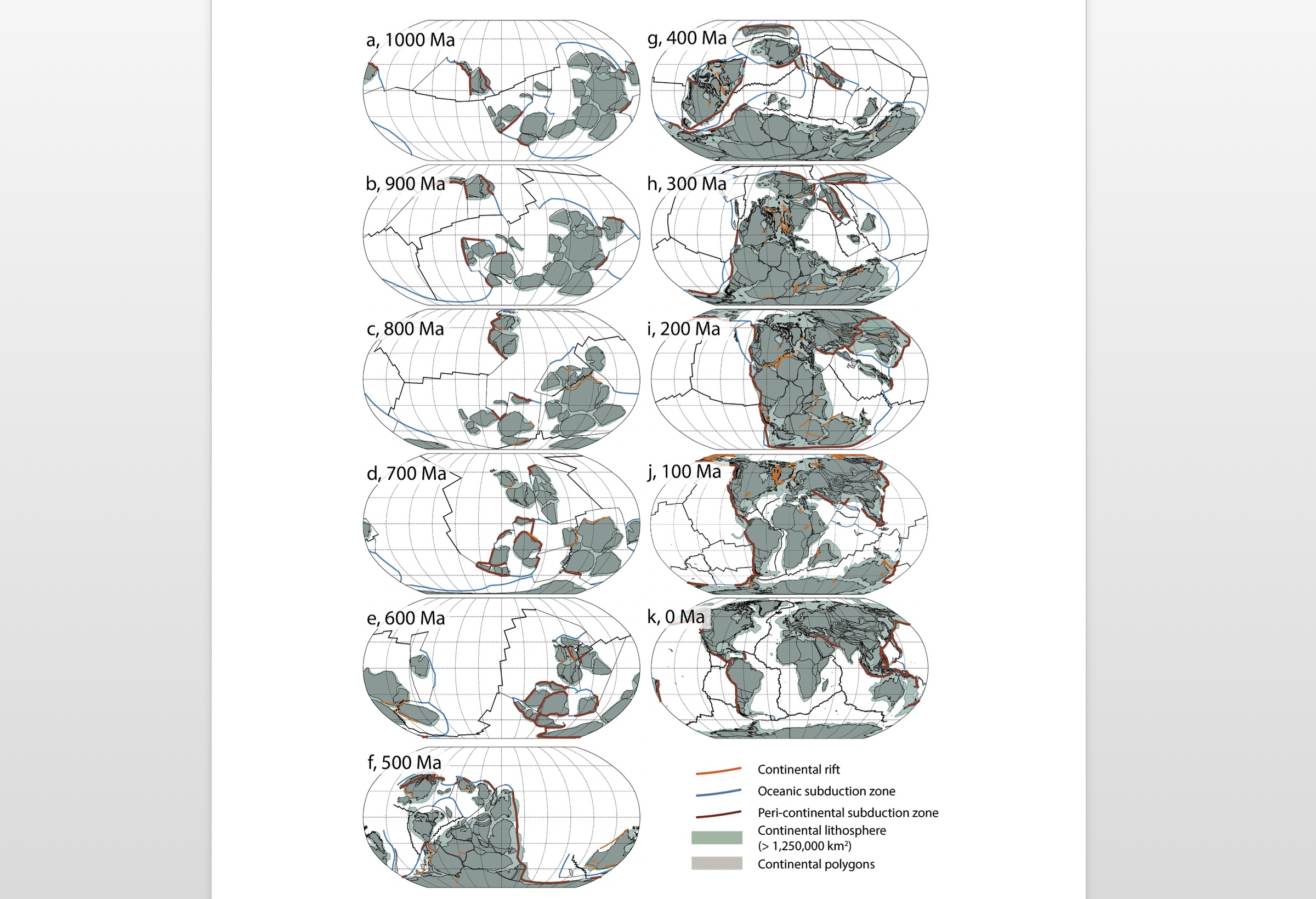
Computer vision-based framework for extracting tectonic lineaments from optical remote sensing data
Abstract: The extraction of tectonic lineaments from digital satellite data is a fundamental application in remote sensing. The location of tectonic lineaments such as faults and dykes are of interest for a range of applications, particularly because of their association with hydrothermal mineralization. Although a wide range of applications have utilized computer vision techniques, a … Read more…