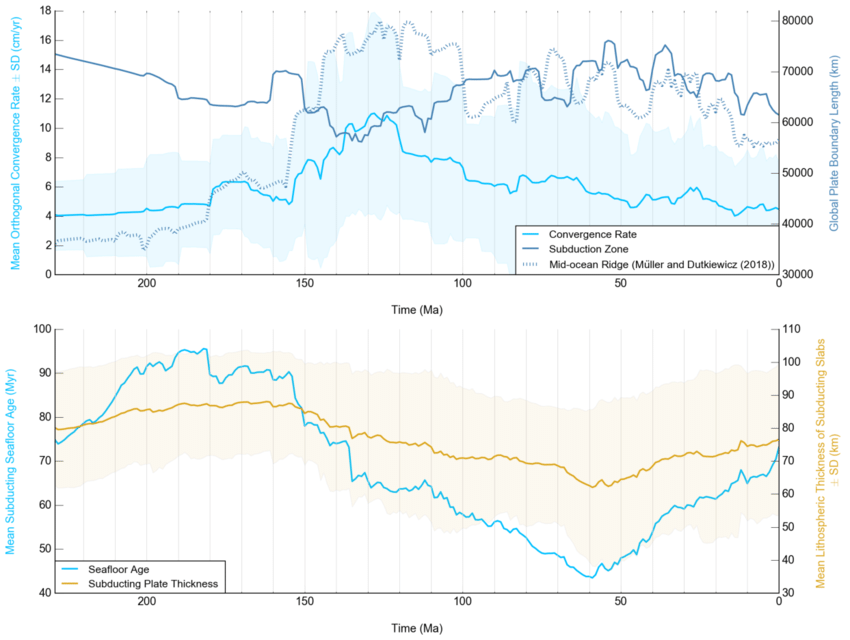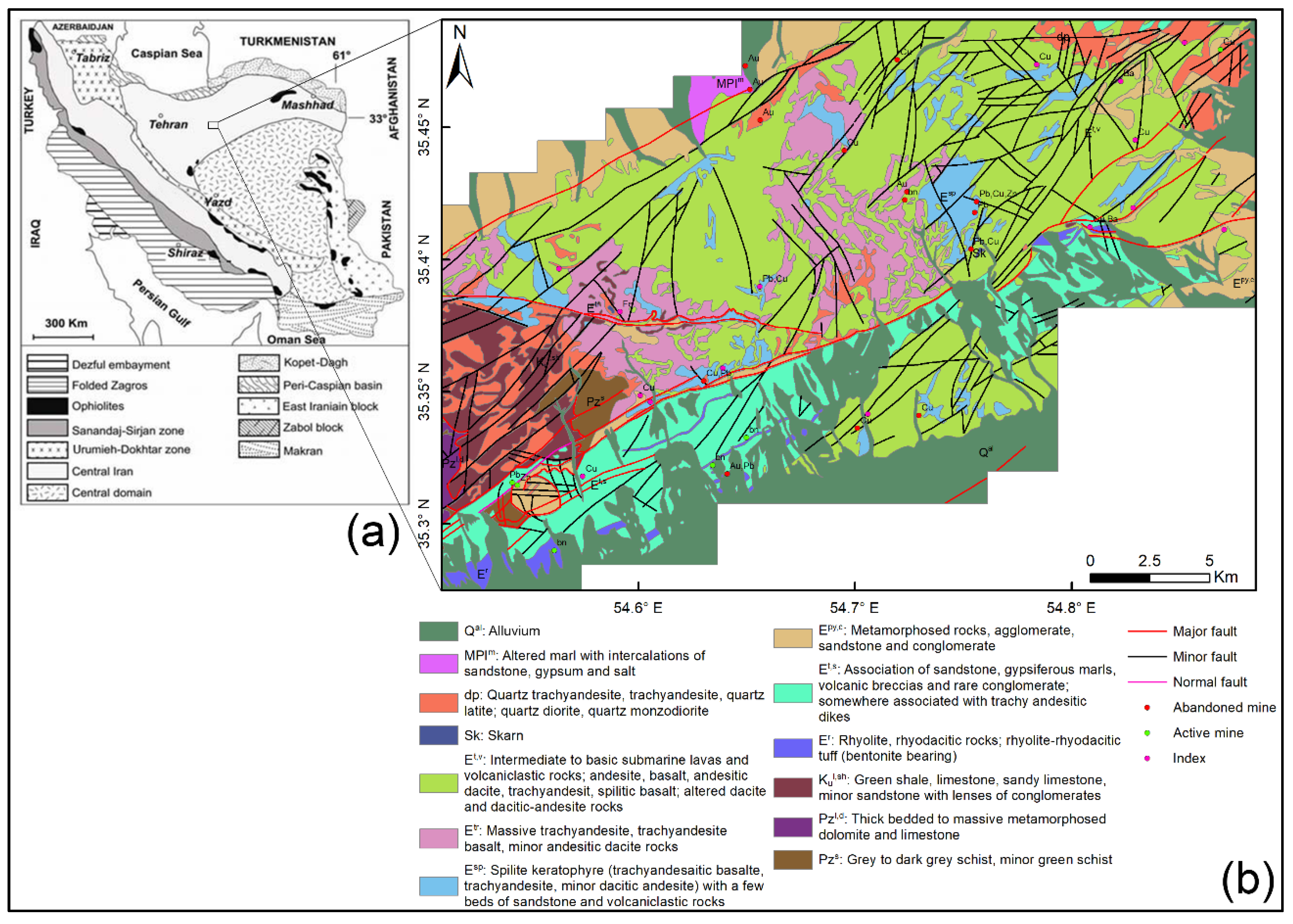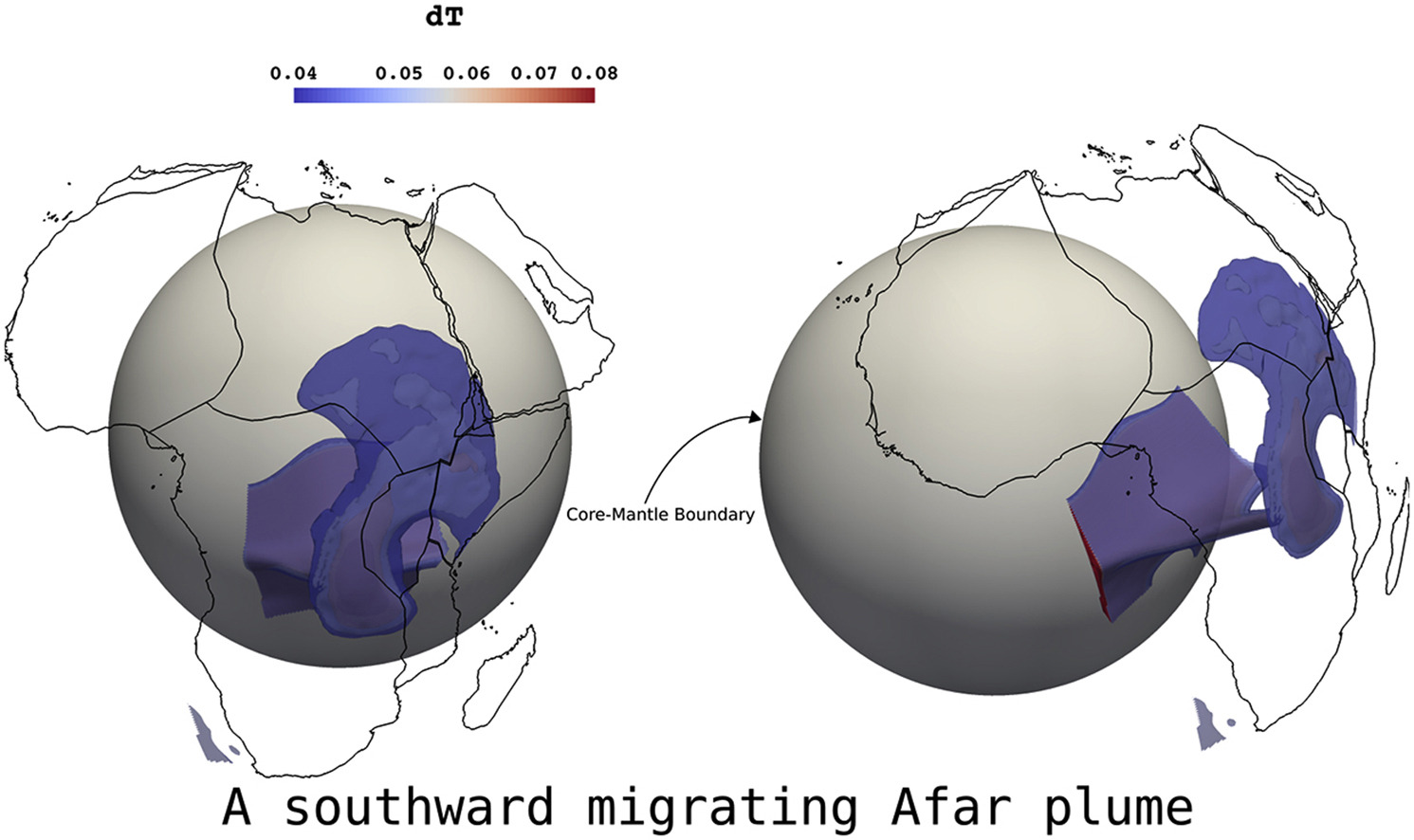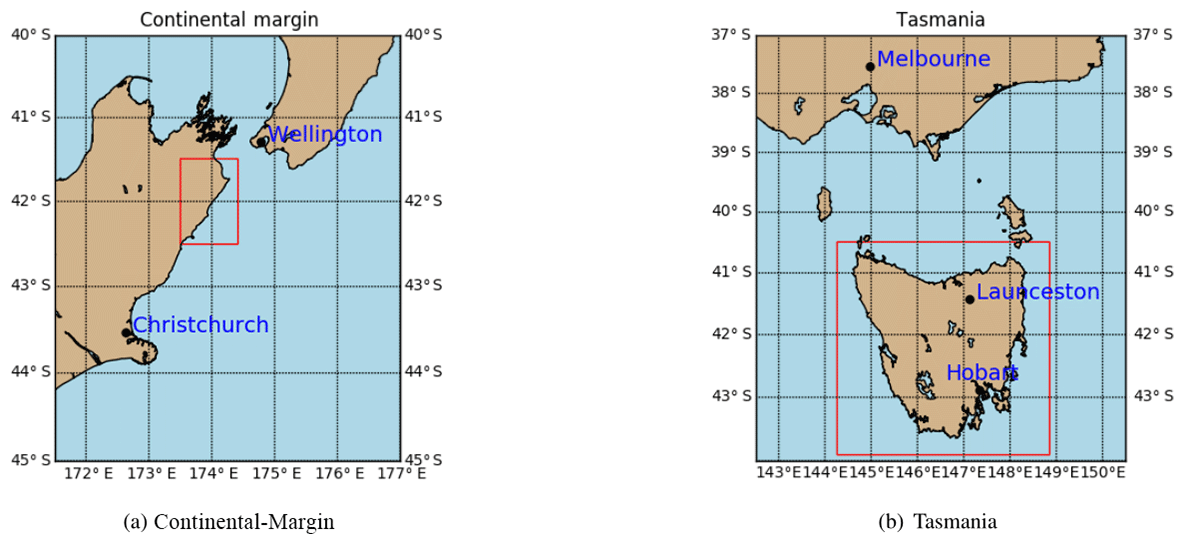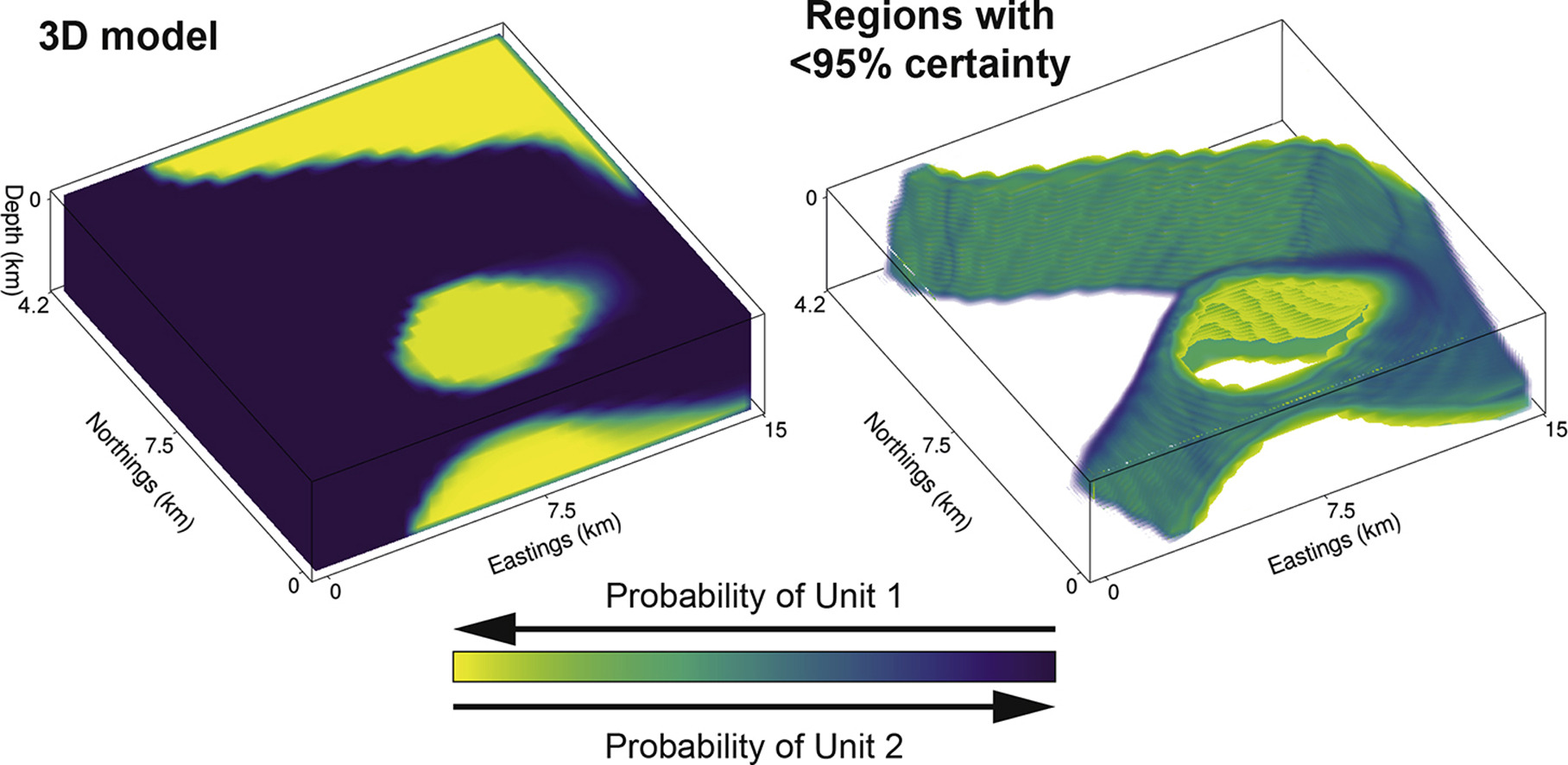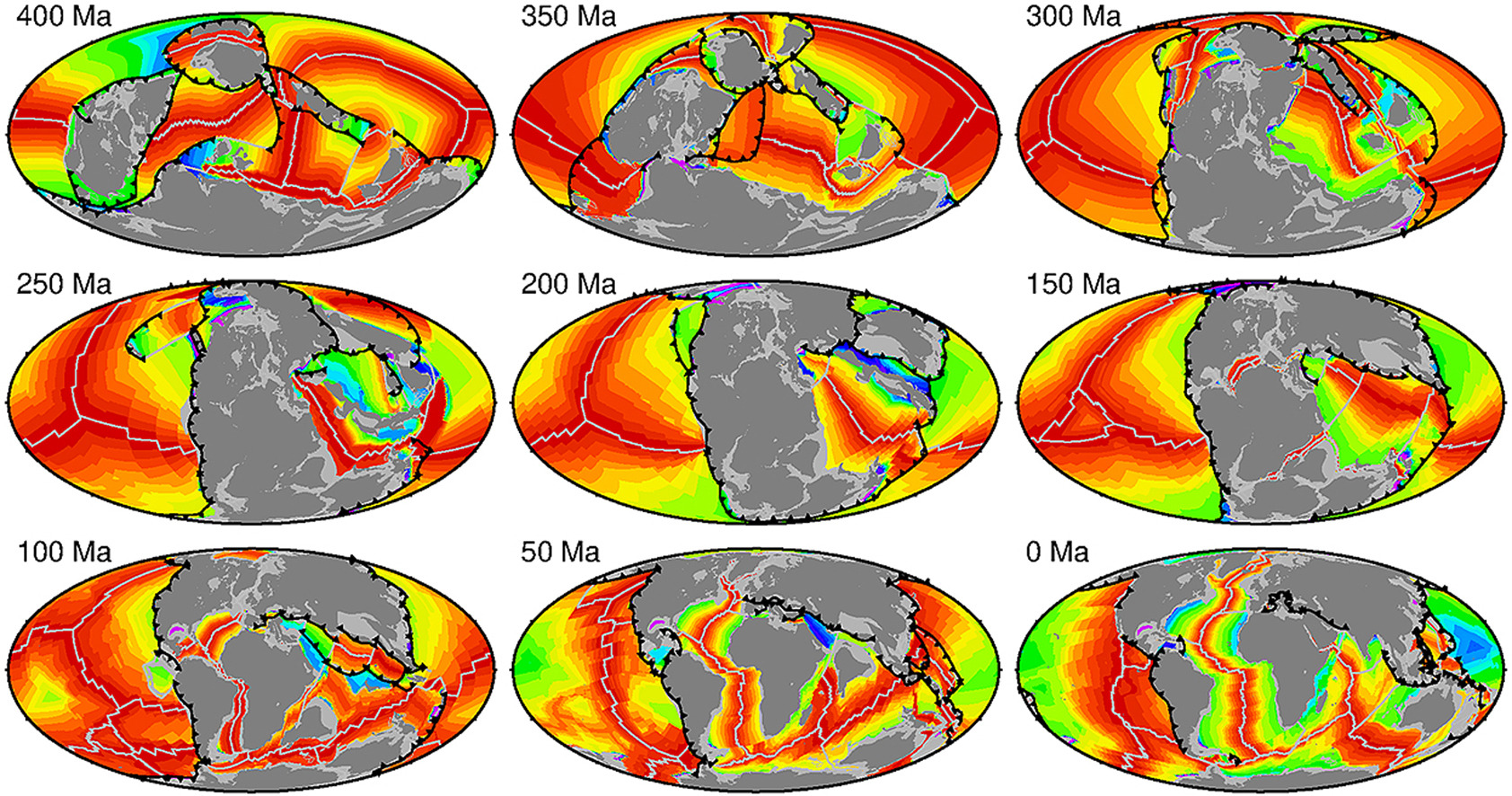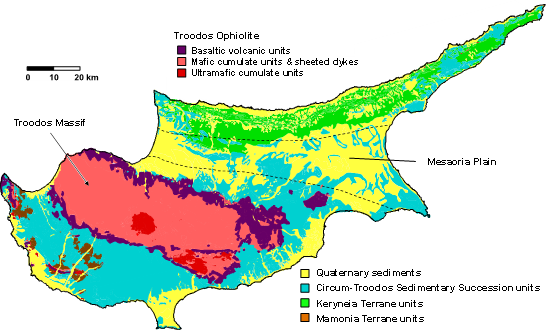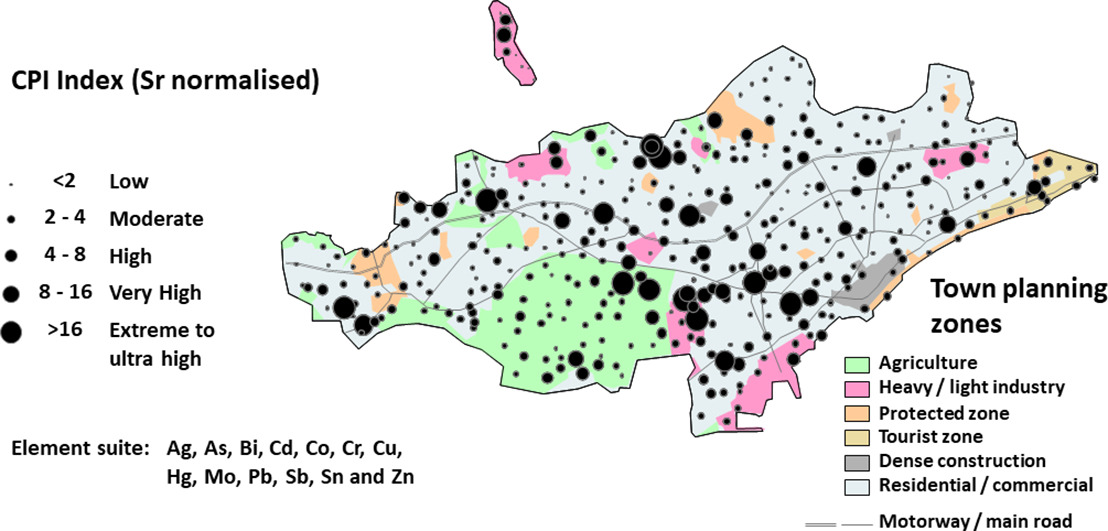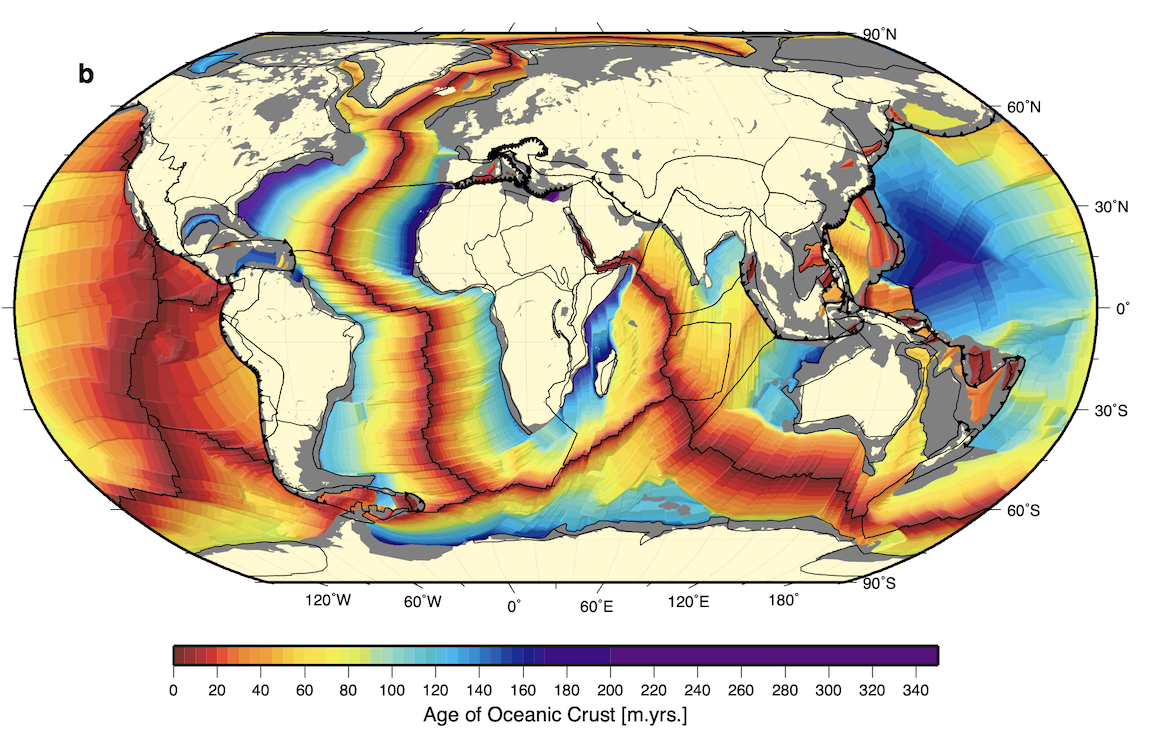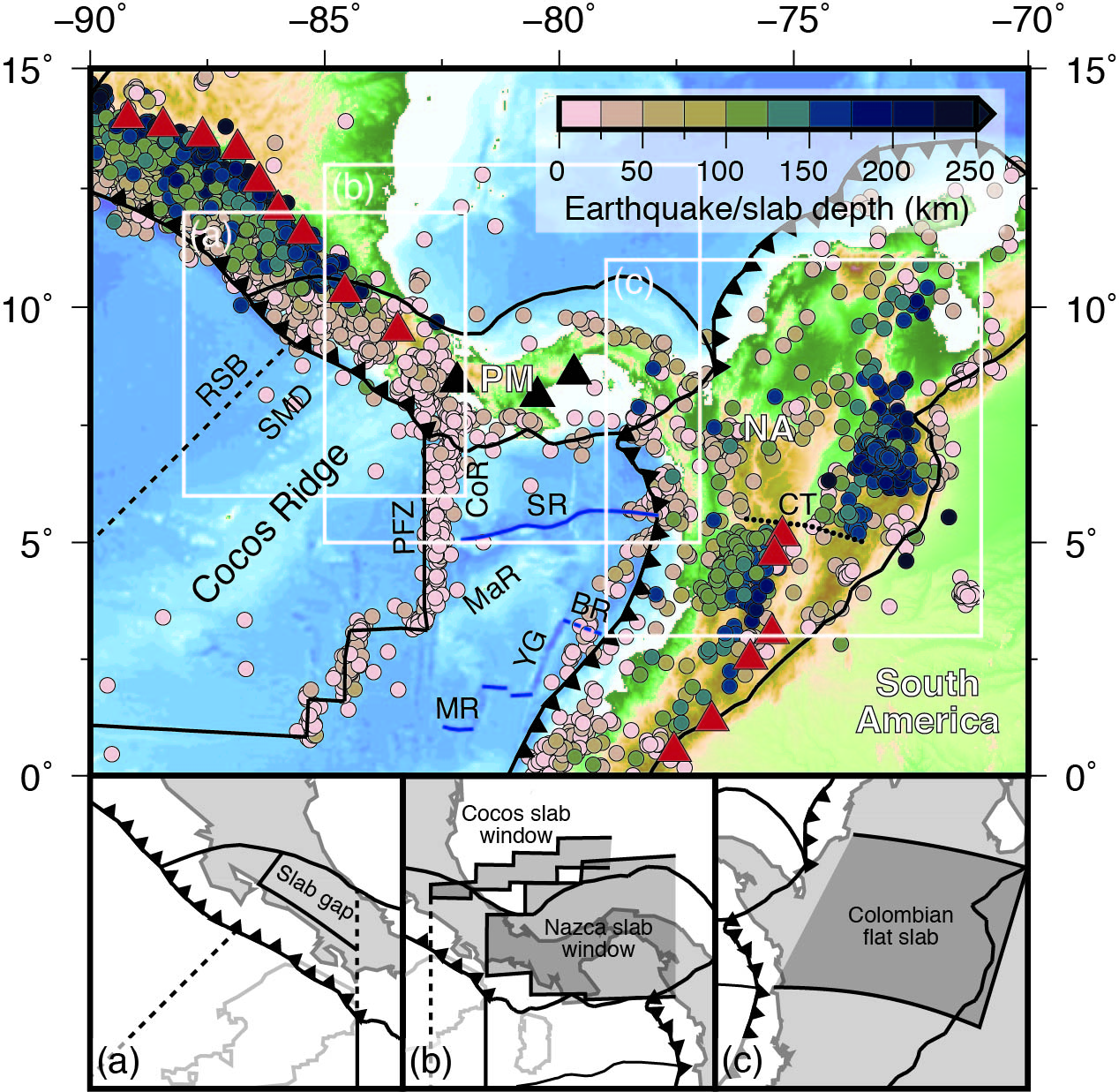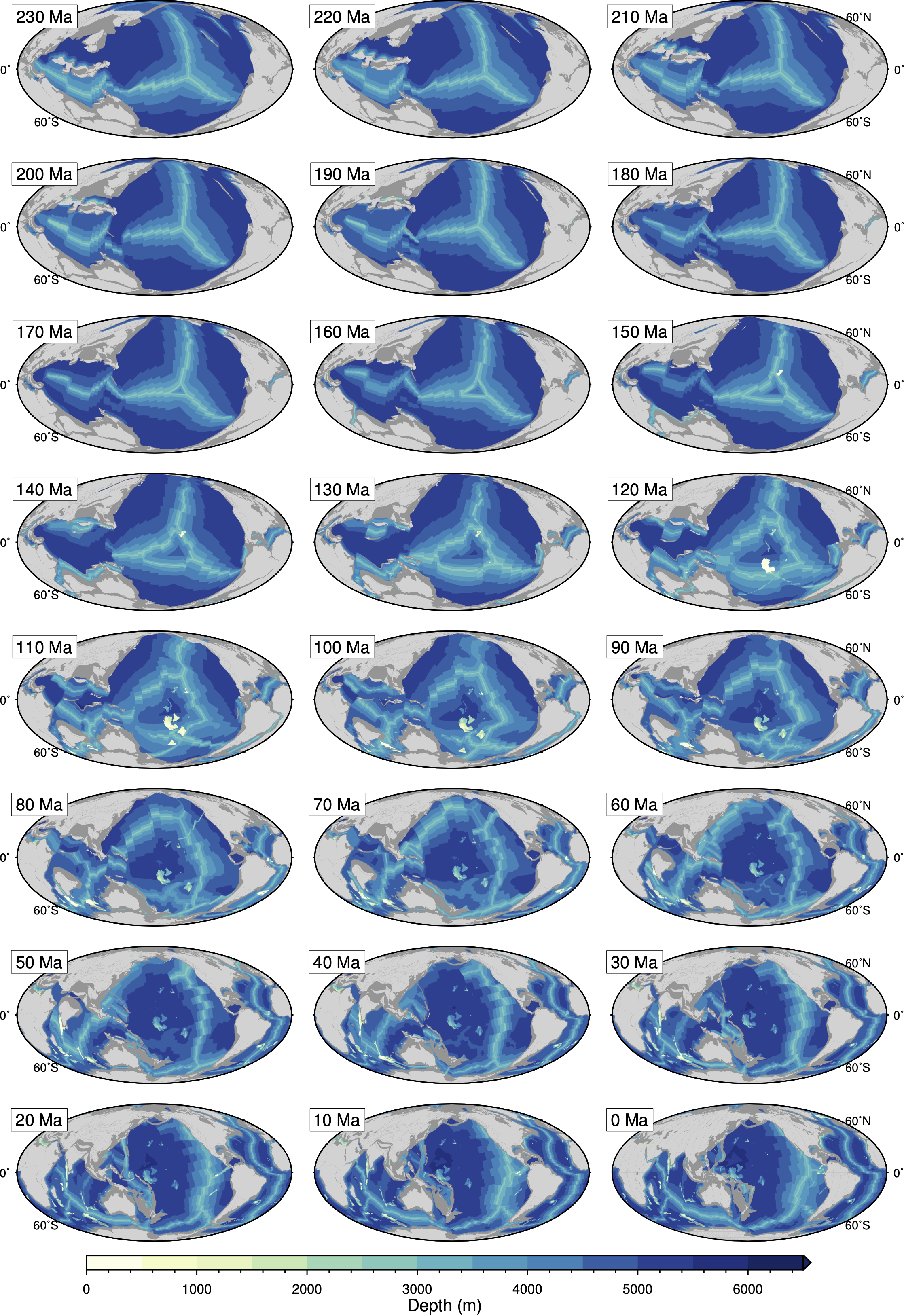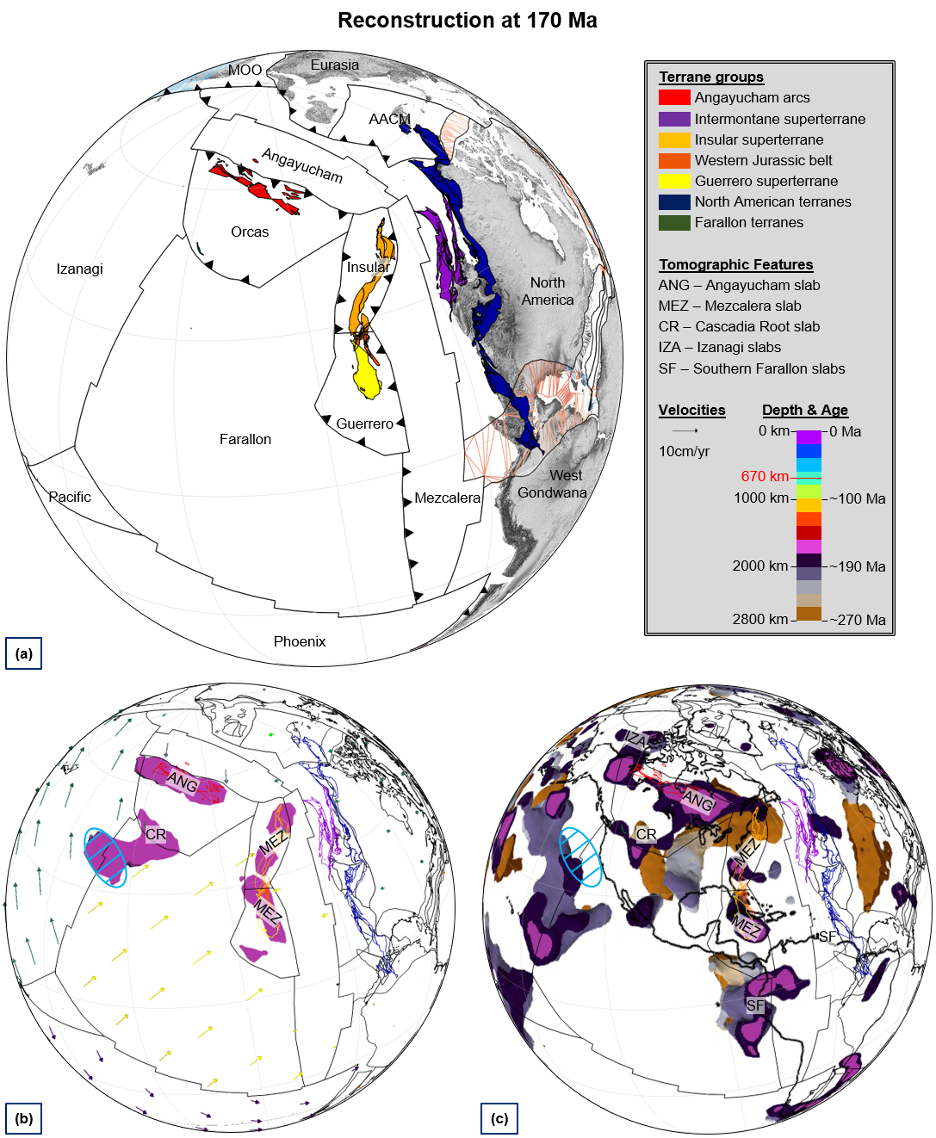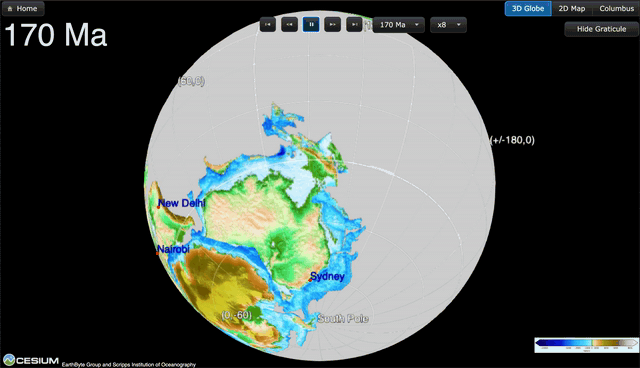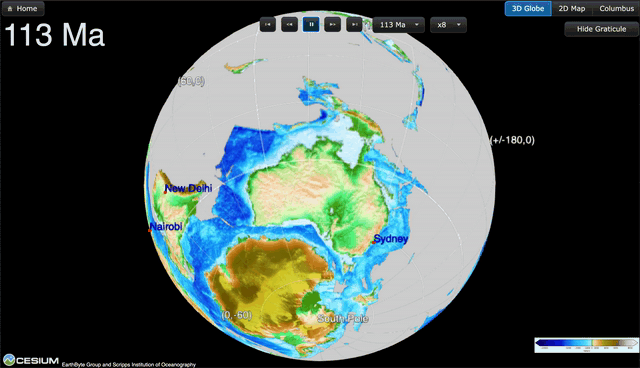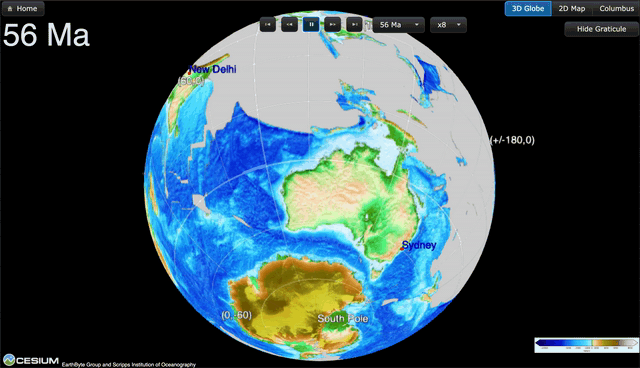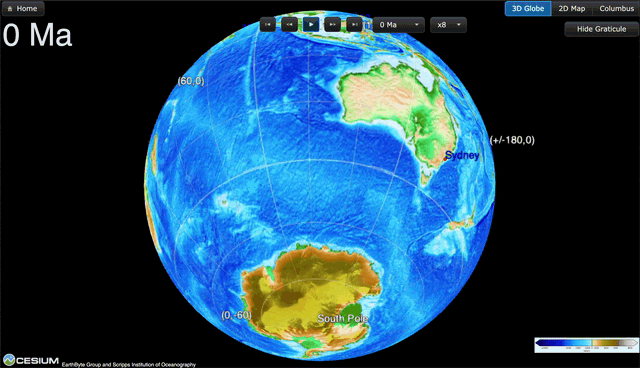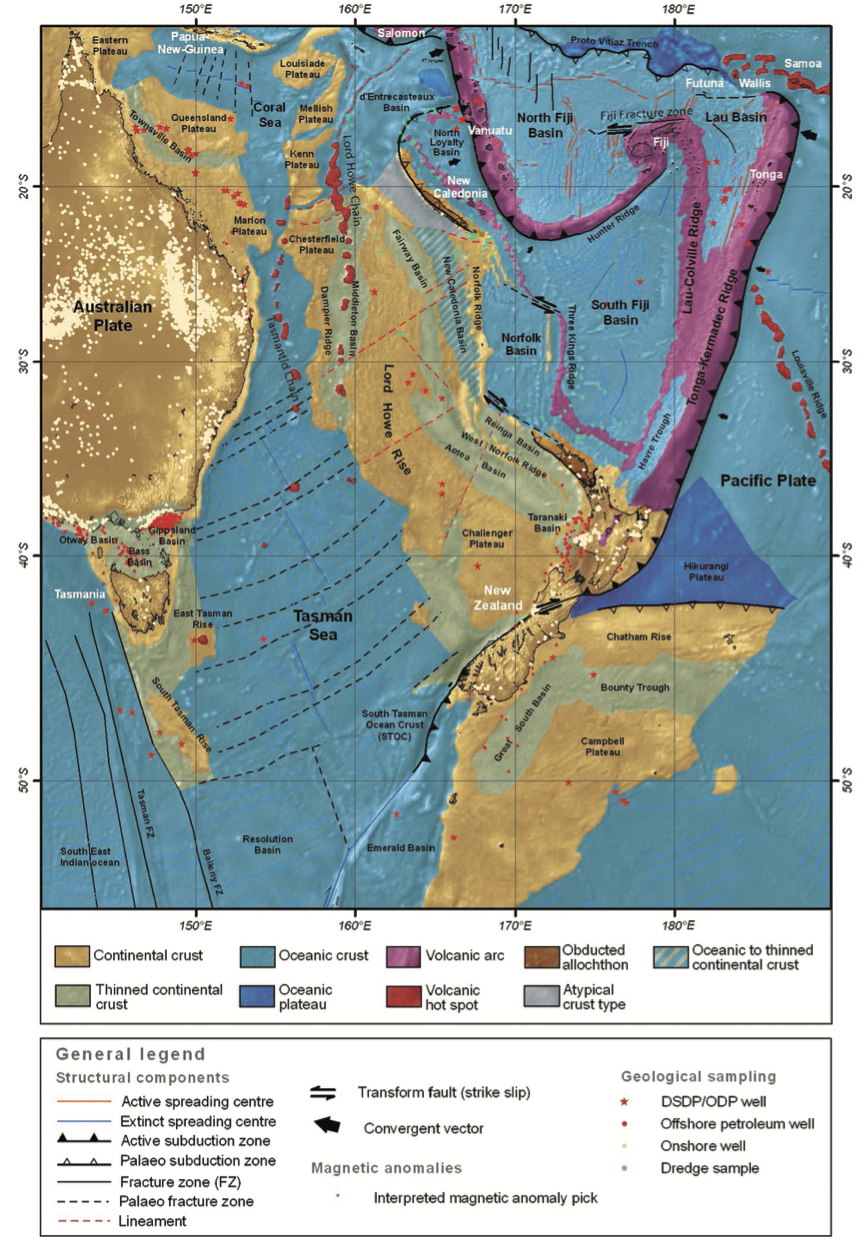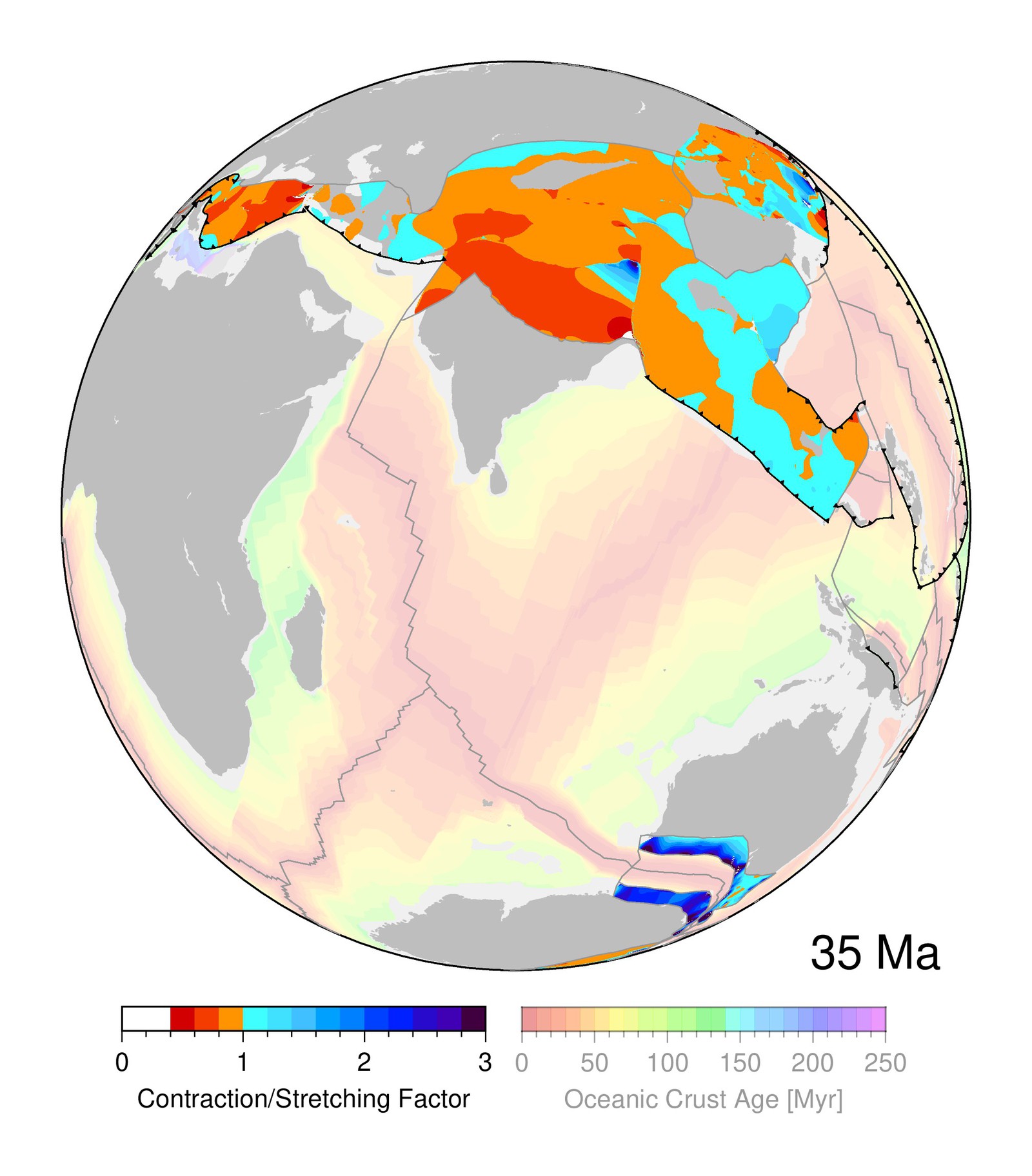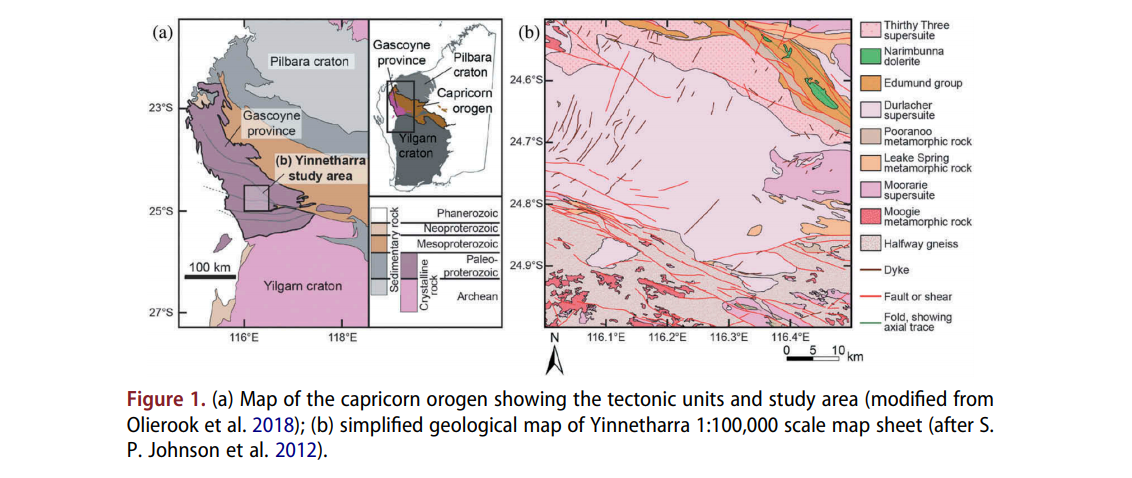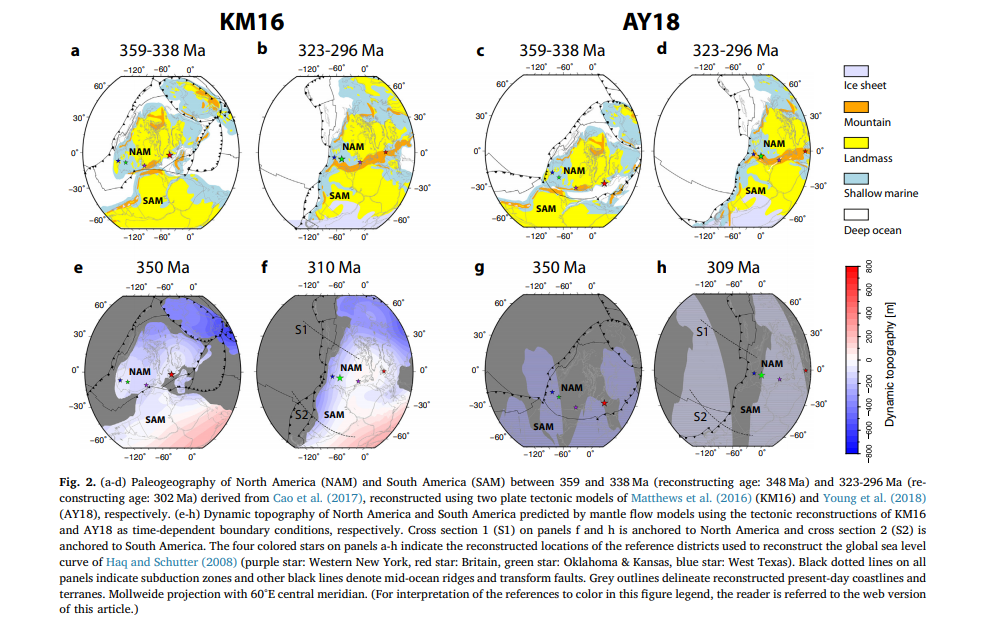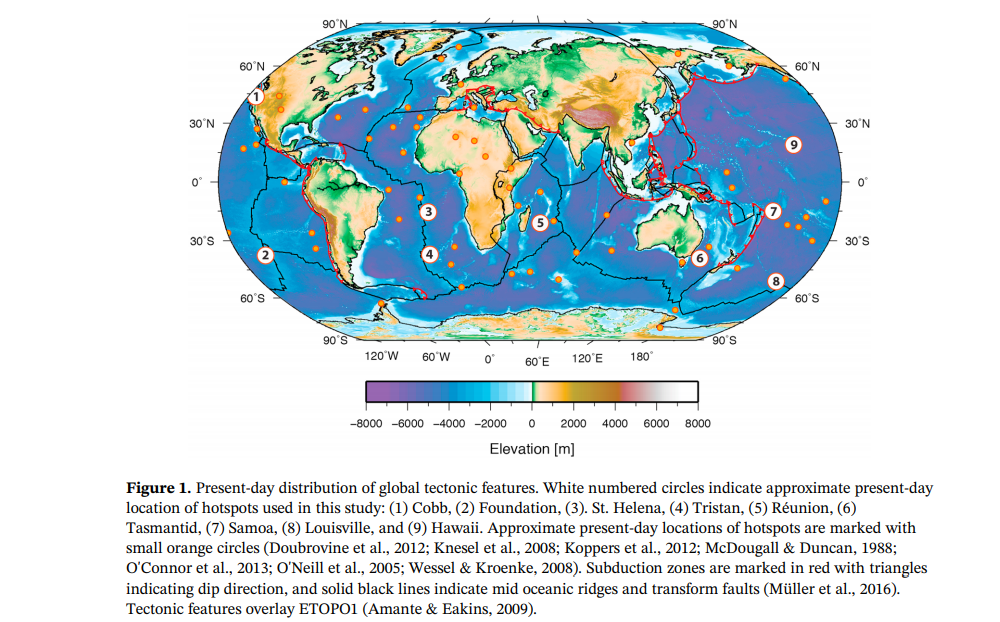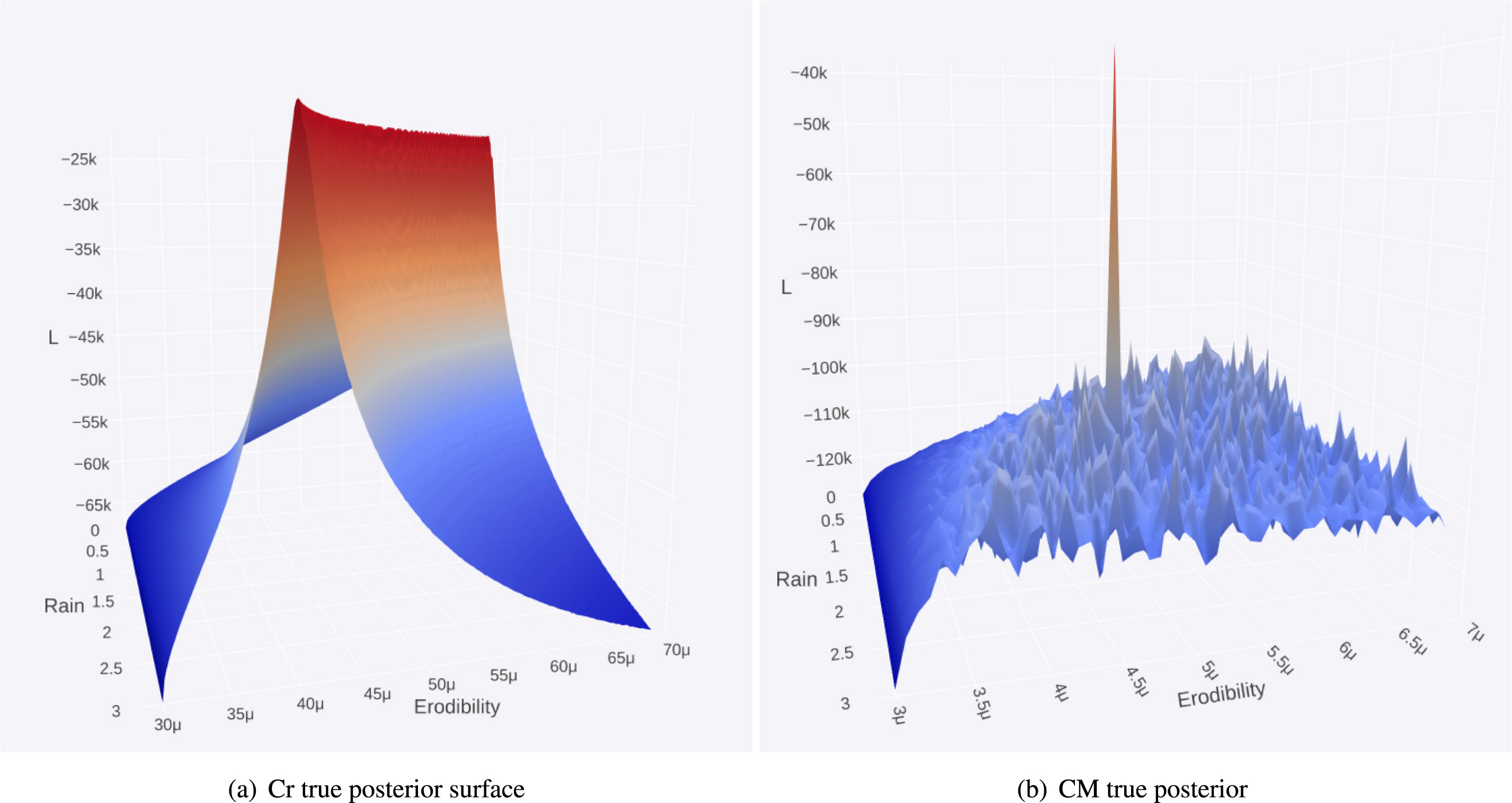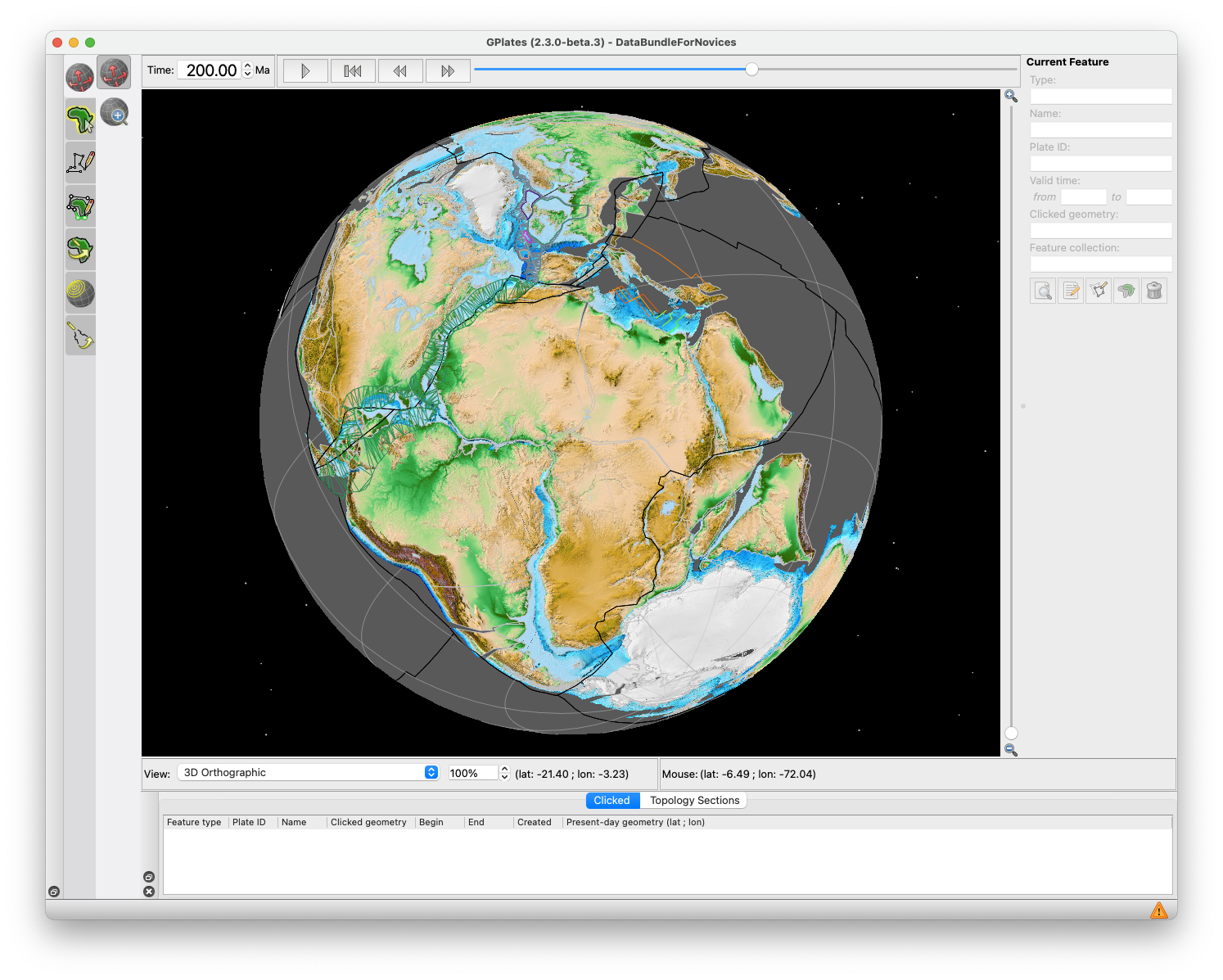
GPlates is a free desktop software for the interactive visualisation of plate-tectonics. The compilation and documentation of GPlates 2.3 data was primarily funded by AuScope National Collaborative Research Infrastructure (NCRIS).
GPlates is developed by the EarthByte Group (part of AuScope NCRIS) at the University of Sydney and the Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences (GPS) at California Institute of Technology (CalTech). … Read more…