The influence of carbonate platform interactions with subduction zone volcanism on palaeo-atmospheric CO2 since the Devonian
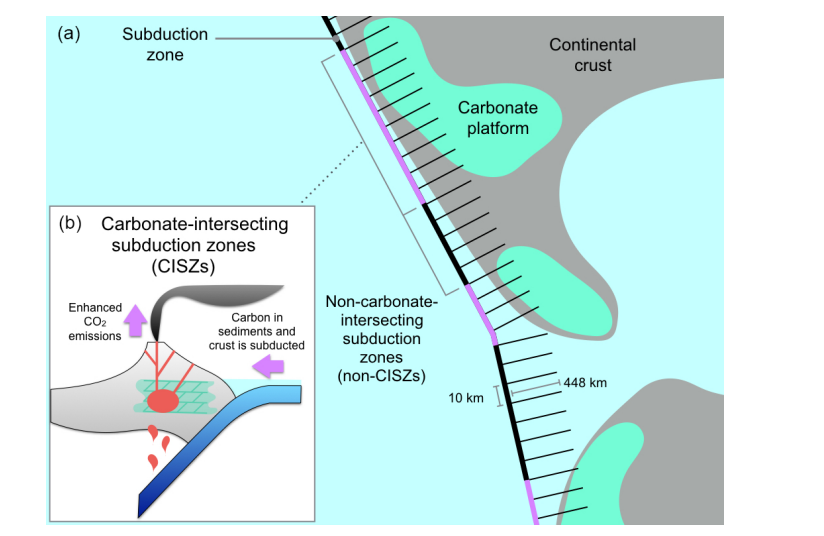
Abstract: The CO2 liberated along subduction zones through intrusive/extrusive magmatic activity and the resulting active and diffuse outgassing influences global atmospheric CO2. However, when melts derived from subduction zones intersect buried carbonate platforms, decarbonation reactions may cause the contribution to atmospheric CO2 to be far greater than segments of the active margin that lacks buried carbon-rich rocks and … Read more…