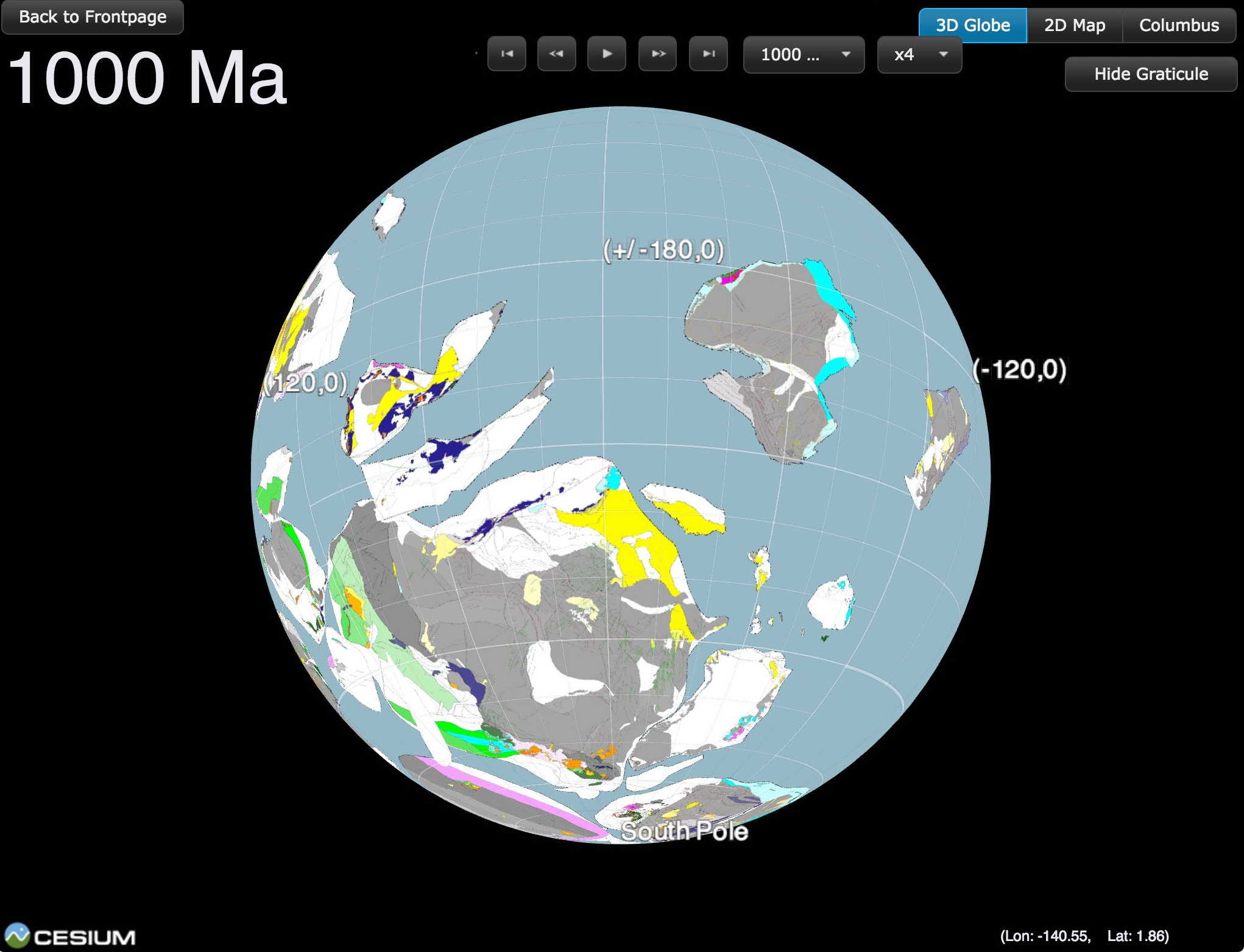
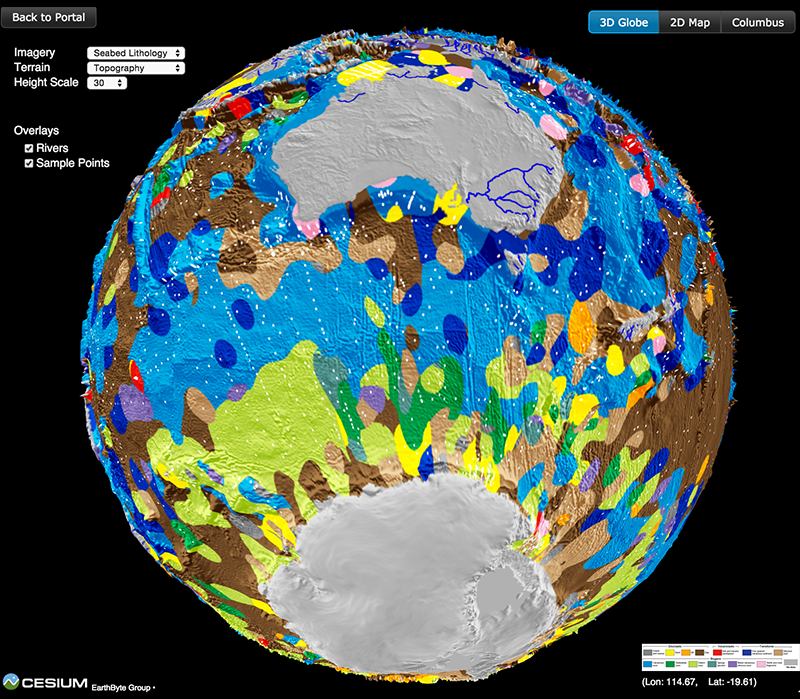
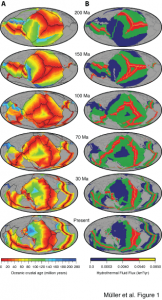
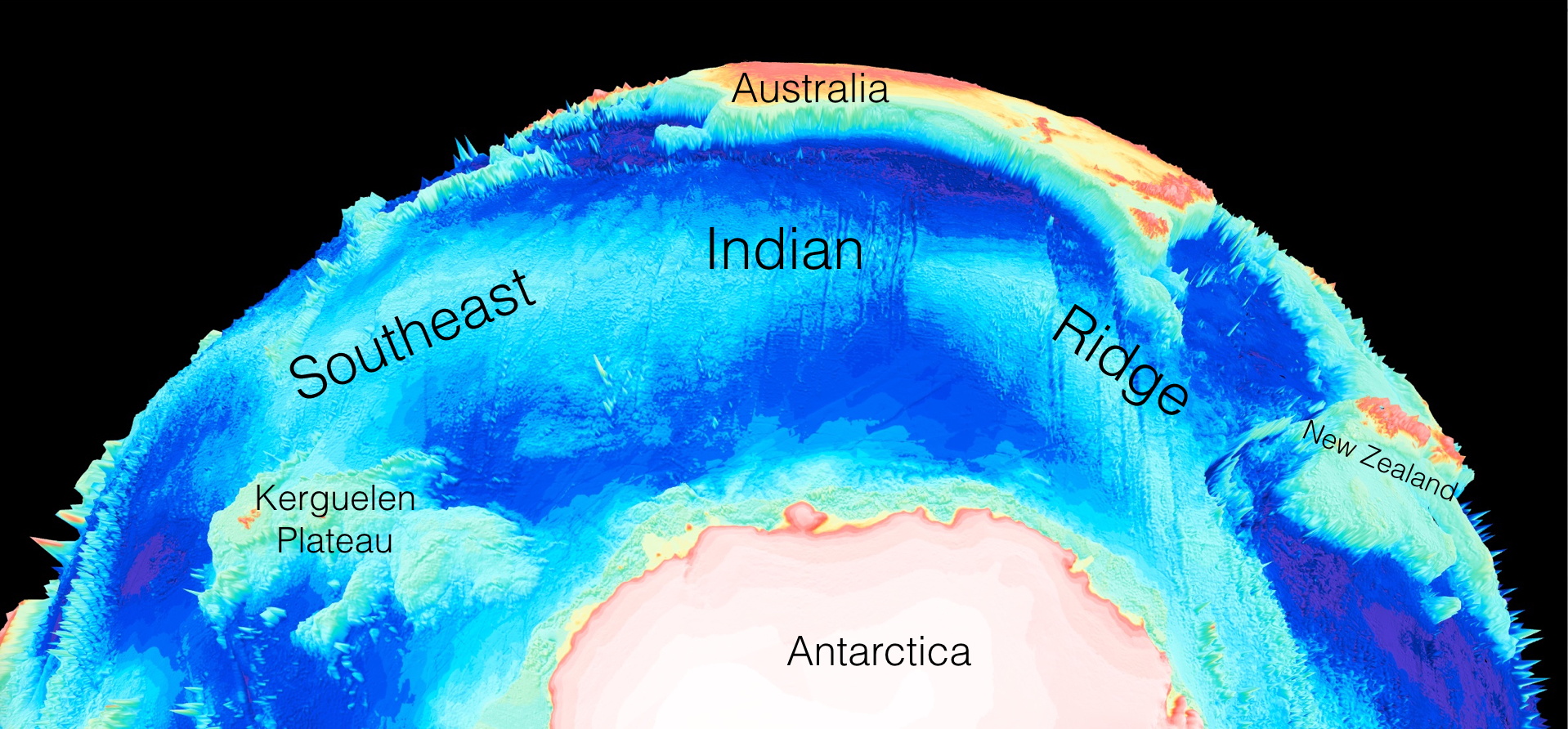
 When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
When organic particles sink from the surface ocean to the seafloor, a small but significant proportion of atmospheric carbon is stored away. Adriana Dutkiewicz and colleagues at the University of Sydney and Data61/CSIRO have now used global data sets collected over decades combined with cutting-edge big data analysis to understand how this process depends on surface ocean environments. … Read more…
How seafloor weathering drives the slow carbon cycle
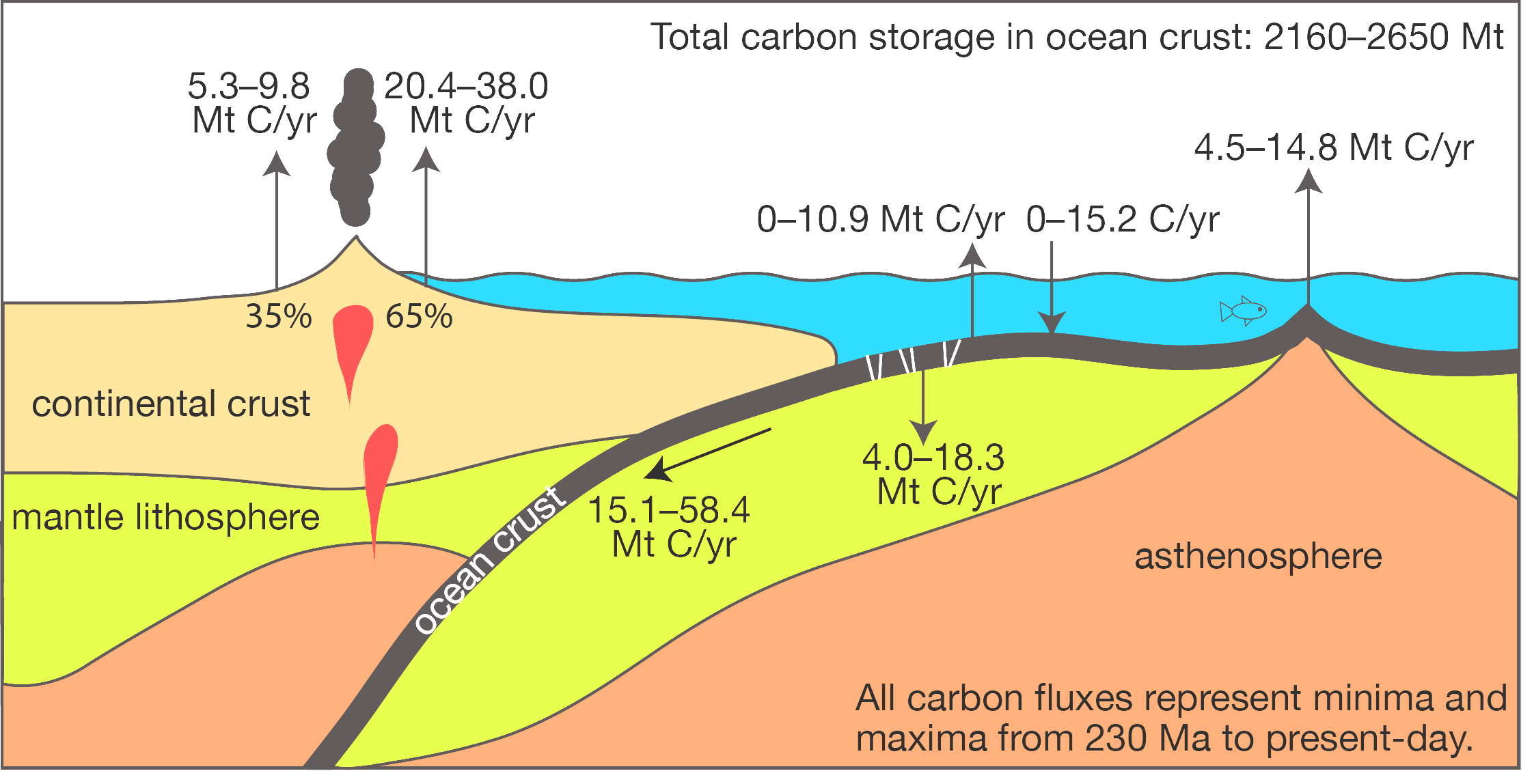
A previously unknown connection between geological atmospheric carbon dioxide cycles and the fluctuating capacity of the ocean crust to store carbon dioxide has been uncovered by two geoscientists from the University of Sydney. Prof Dietmar Müller and Dr Adriana Dutkiewicz from the Sydney Informatics Hub and the School of Geosciences report their discovery in the … Read more…

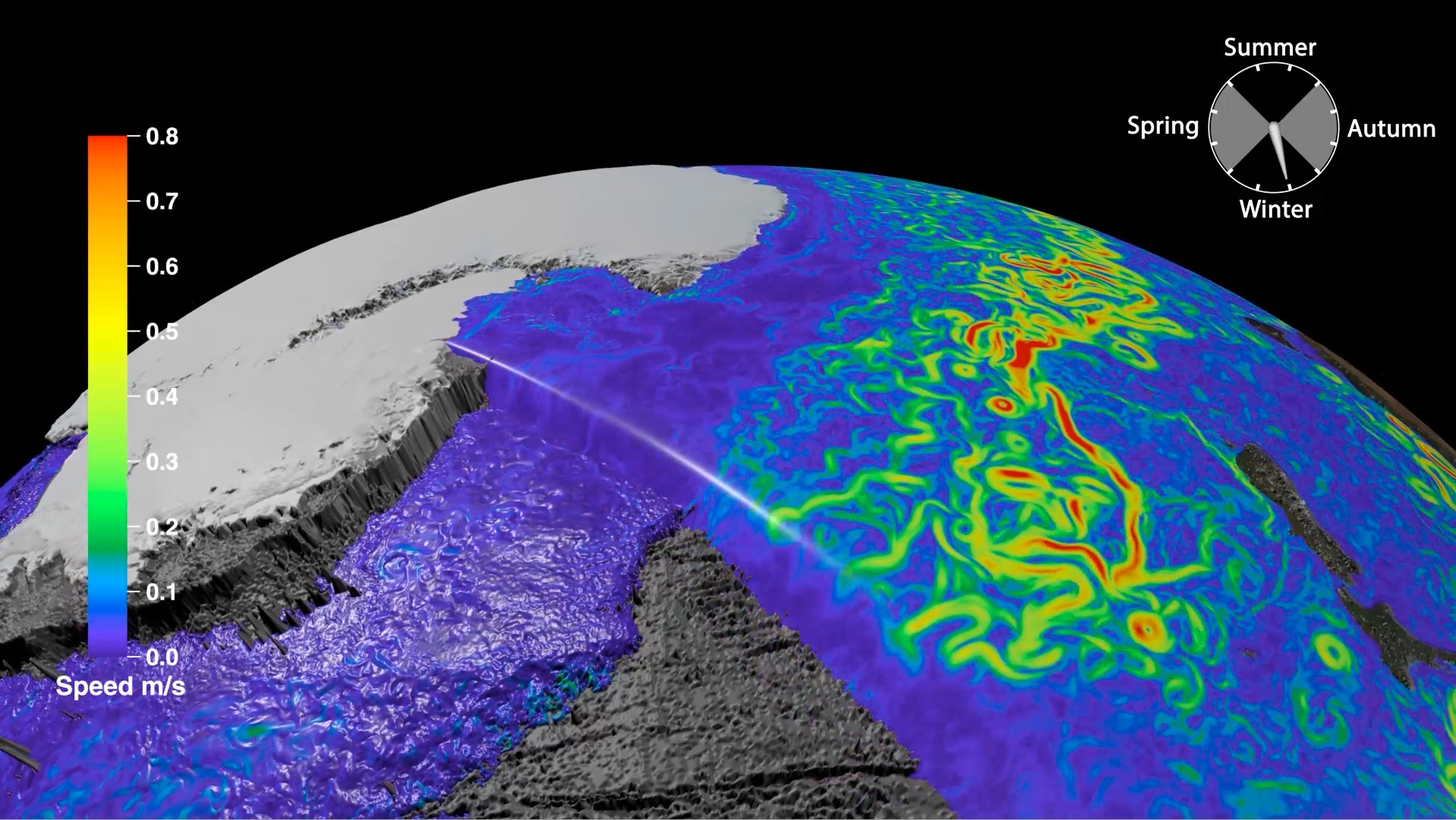
 The recent article on the GPlates Portal published in
The recent article on the GPlates Portal published in