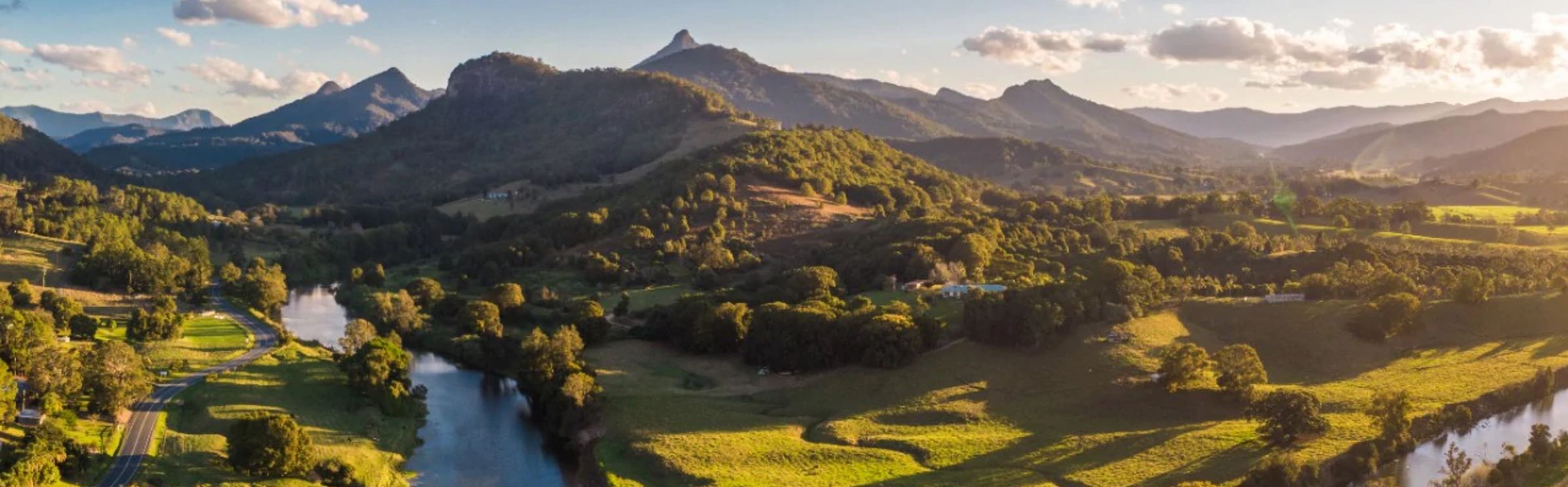
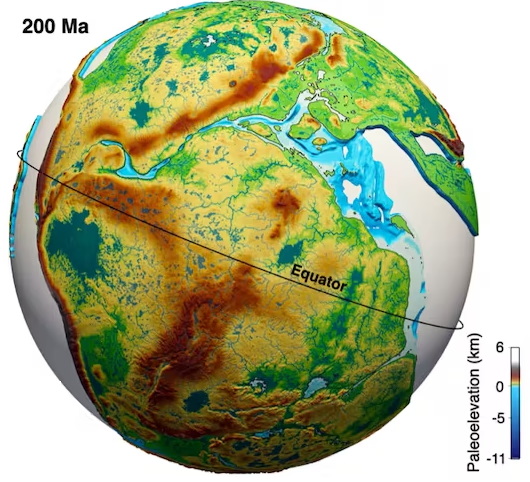
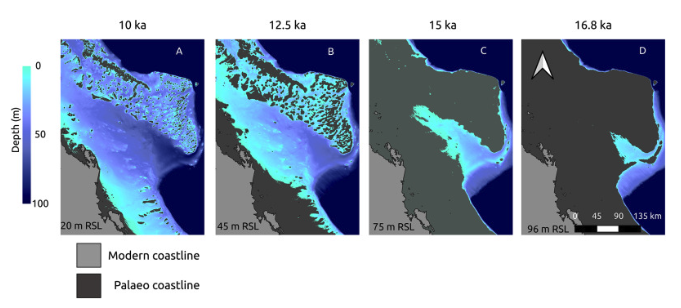
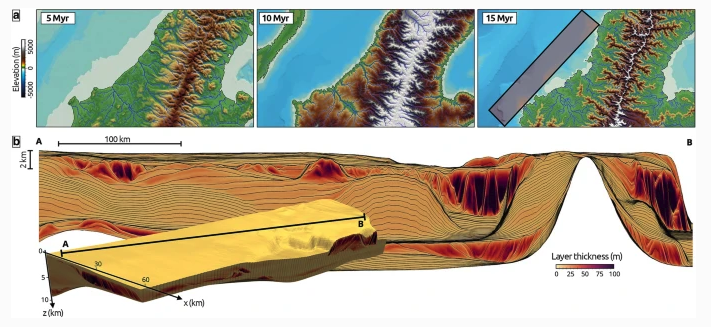
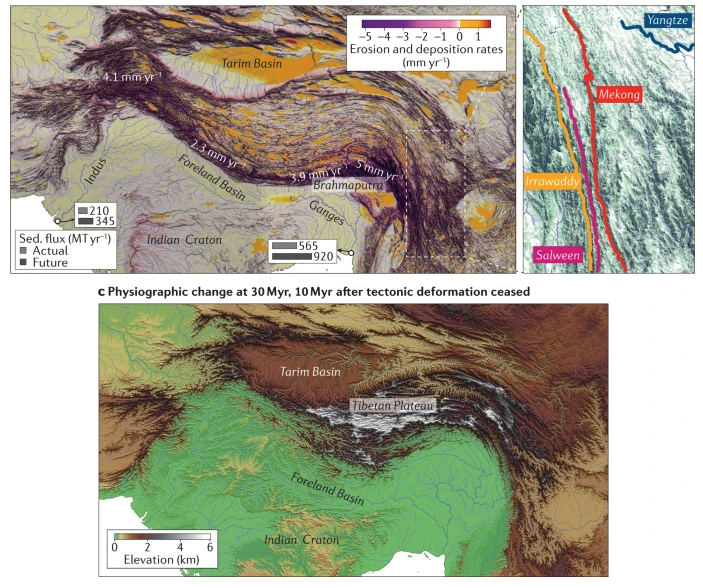
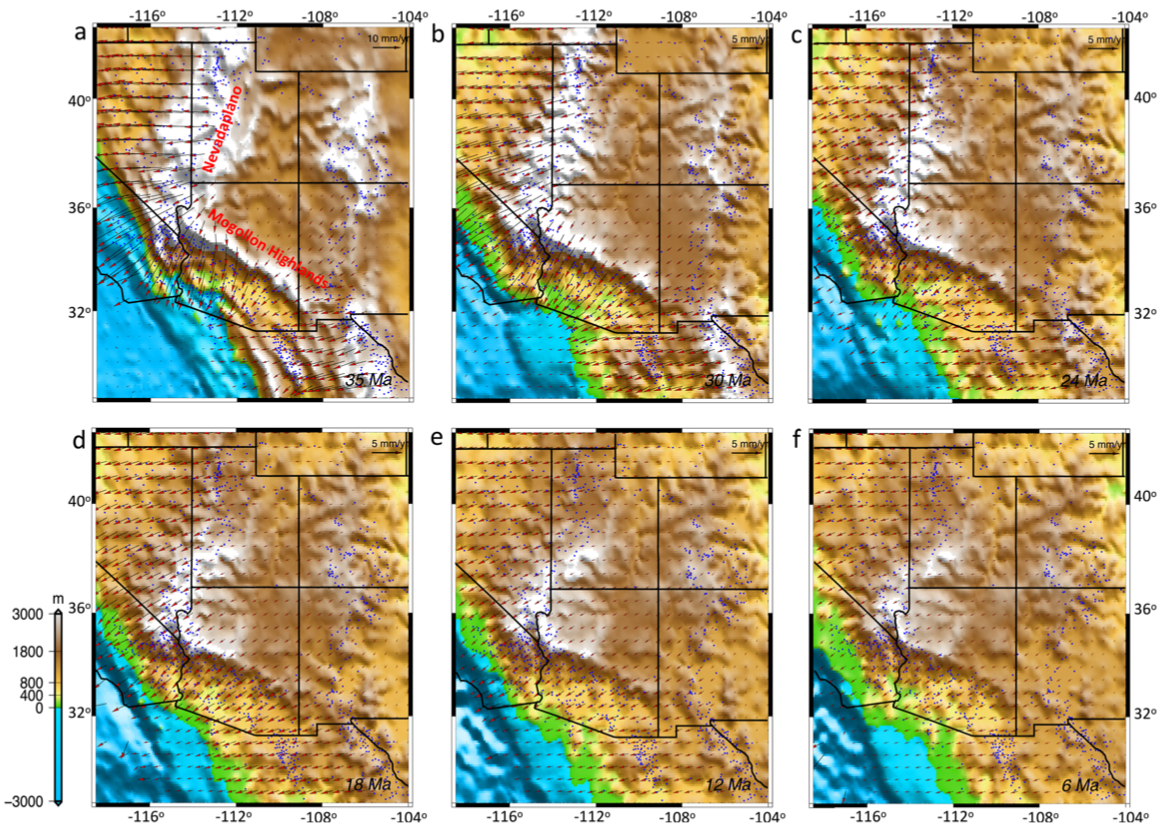
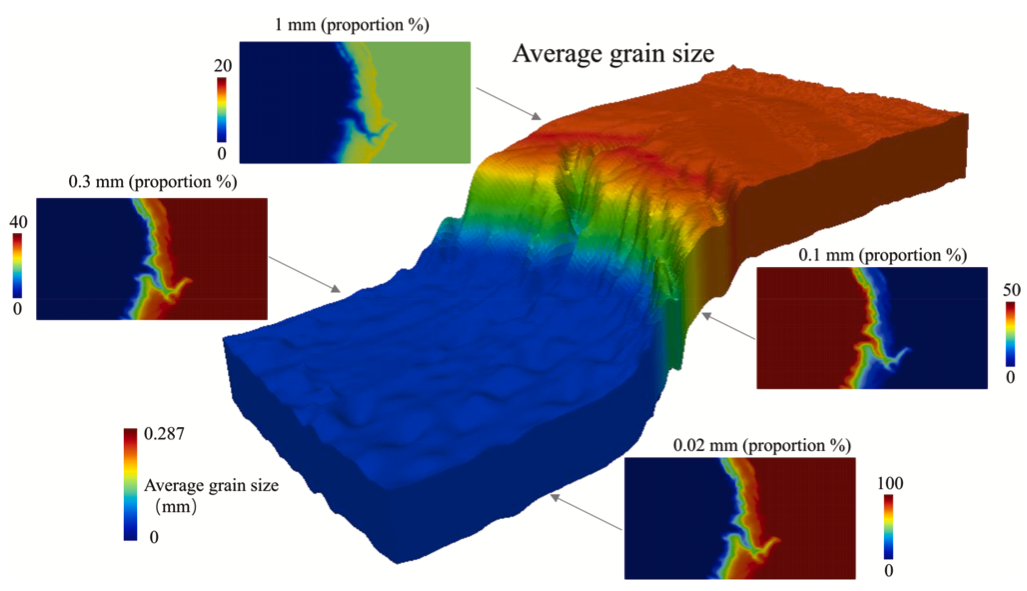
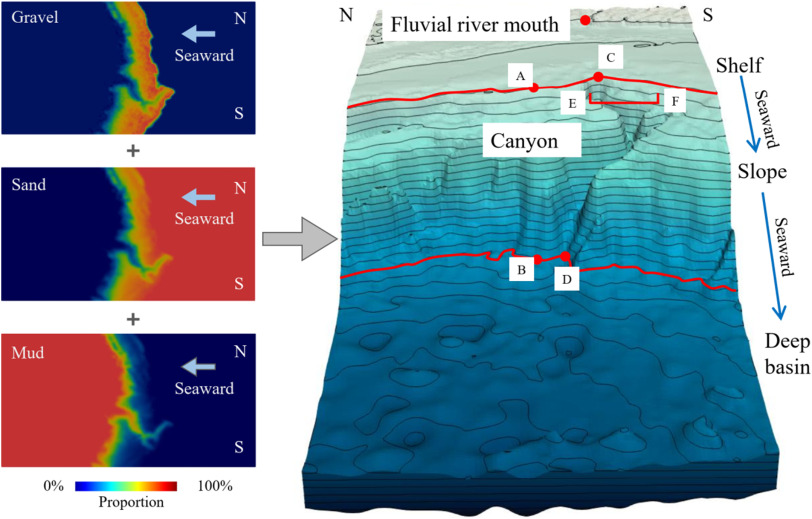
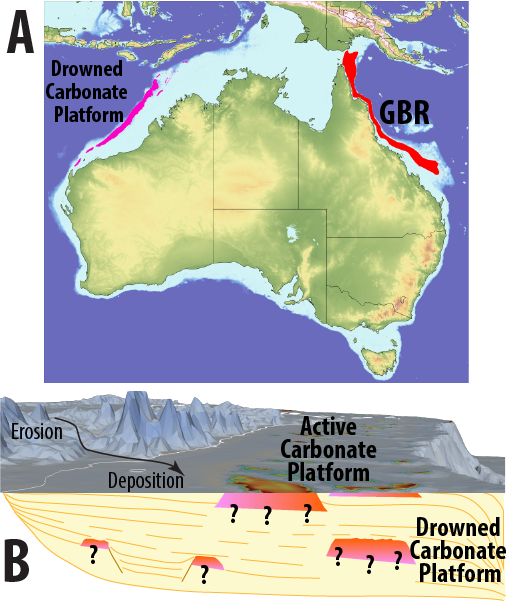
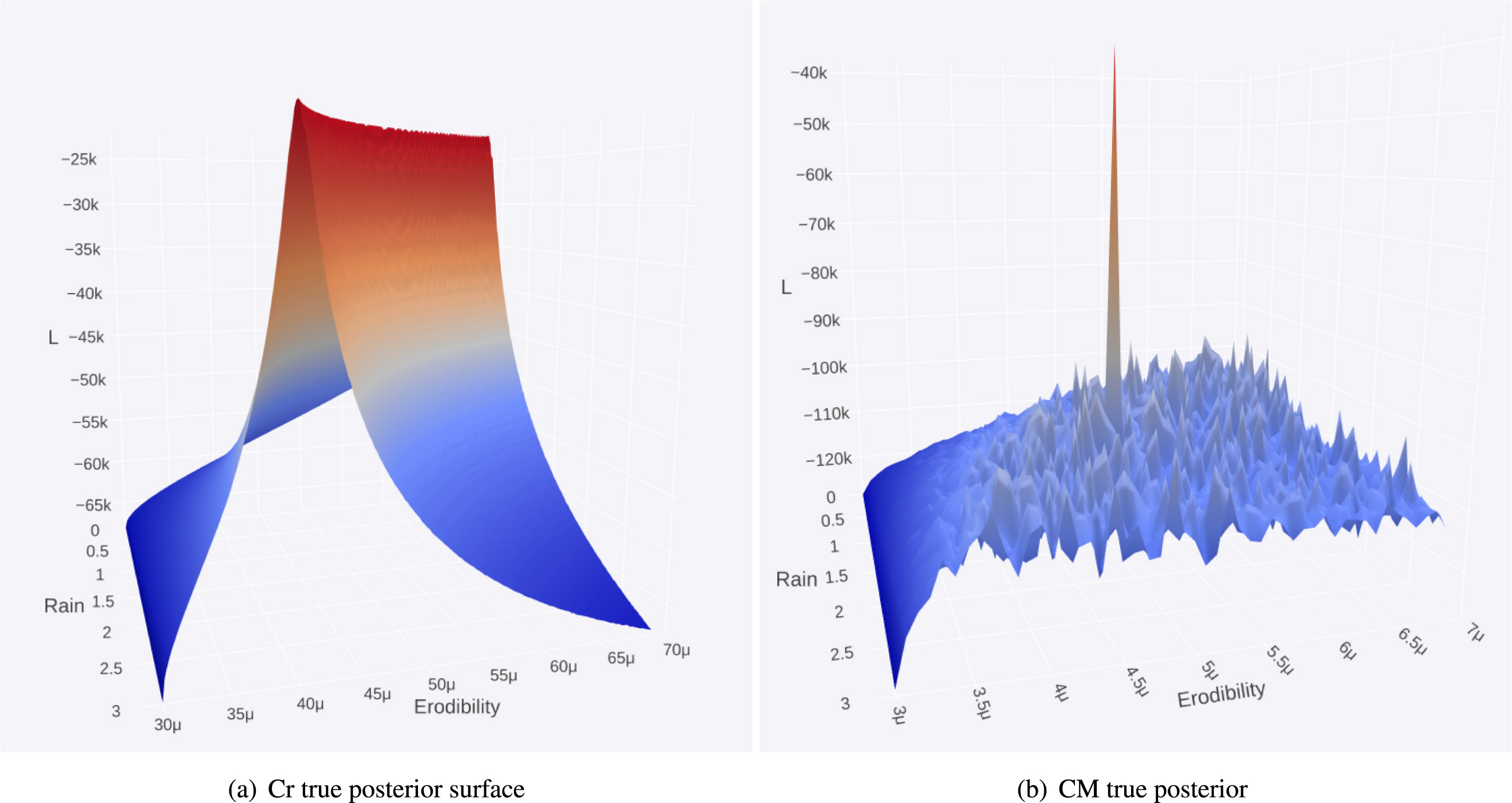
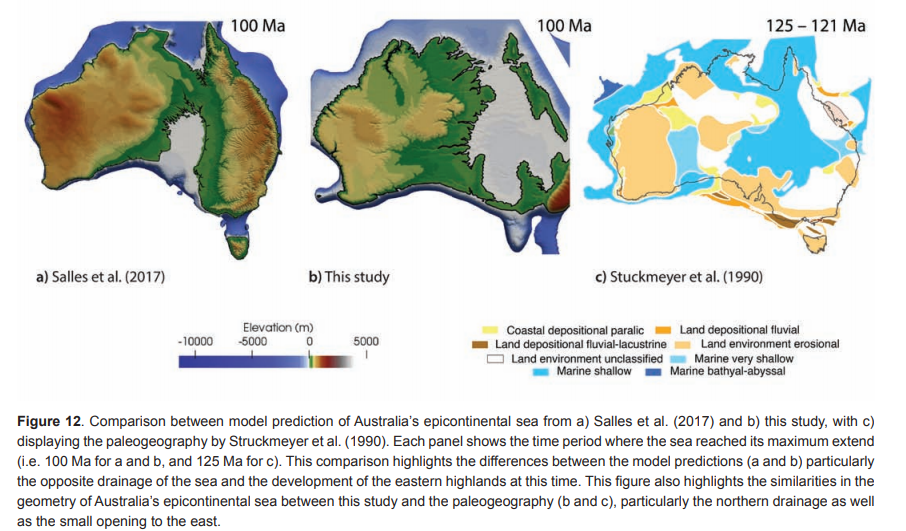
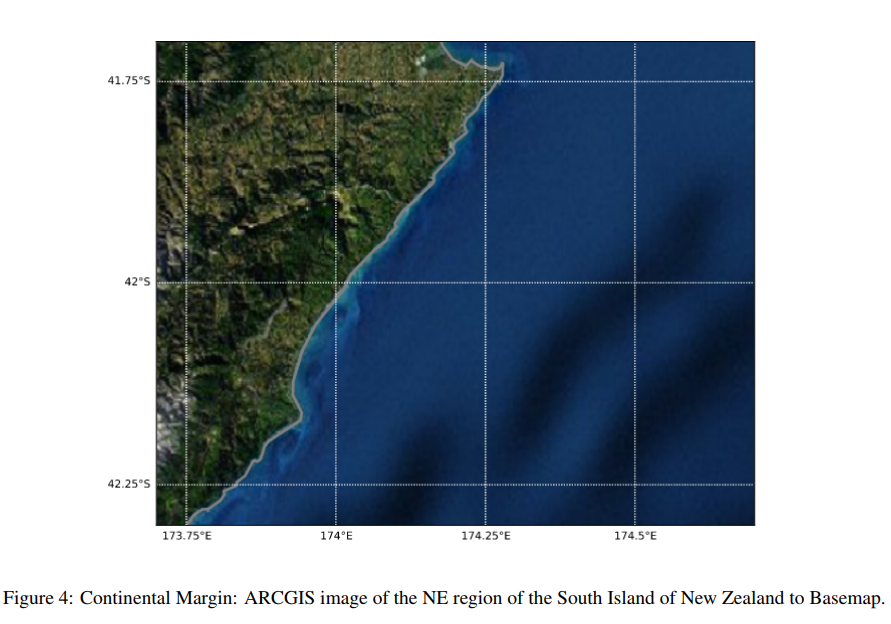
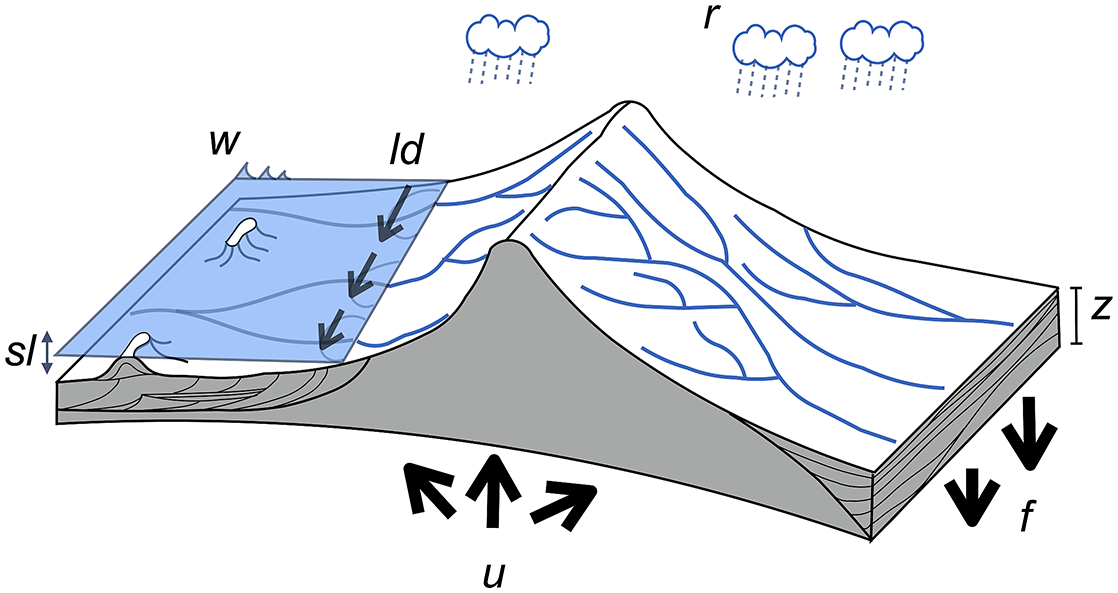
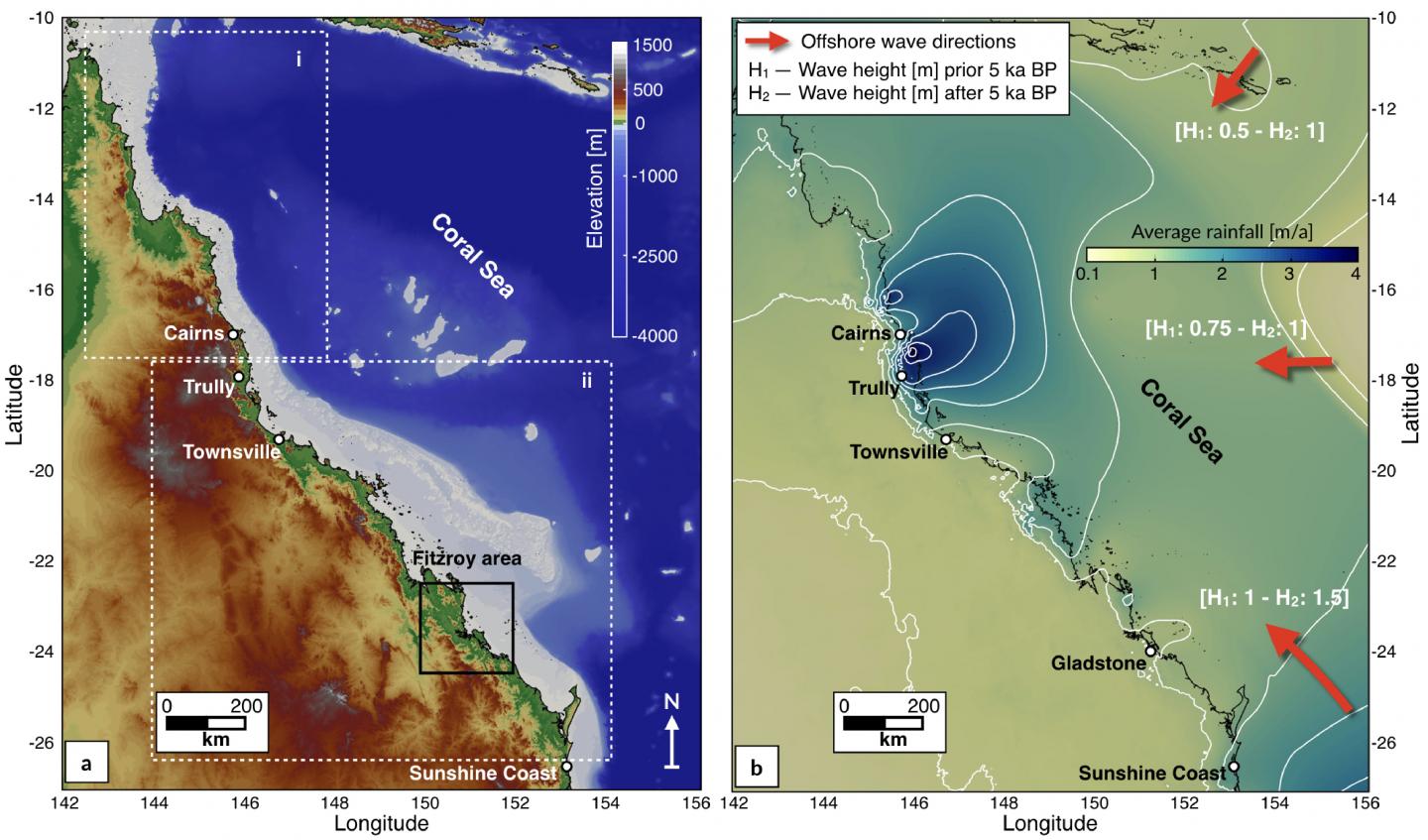
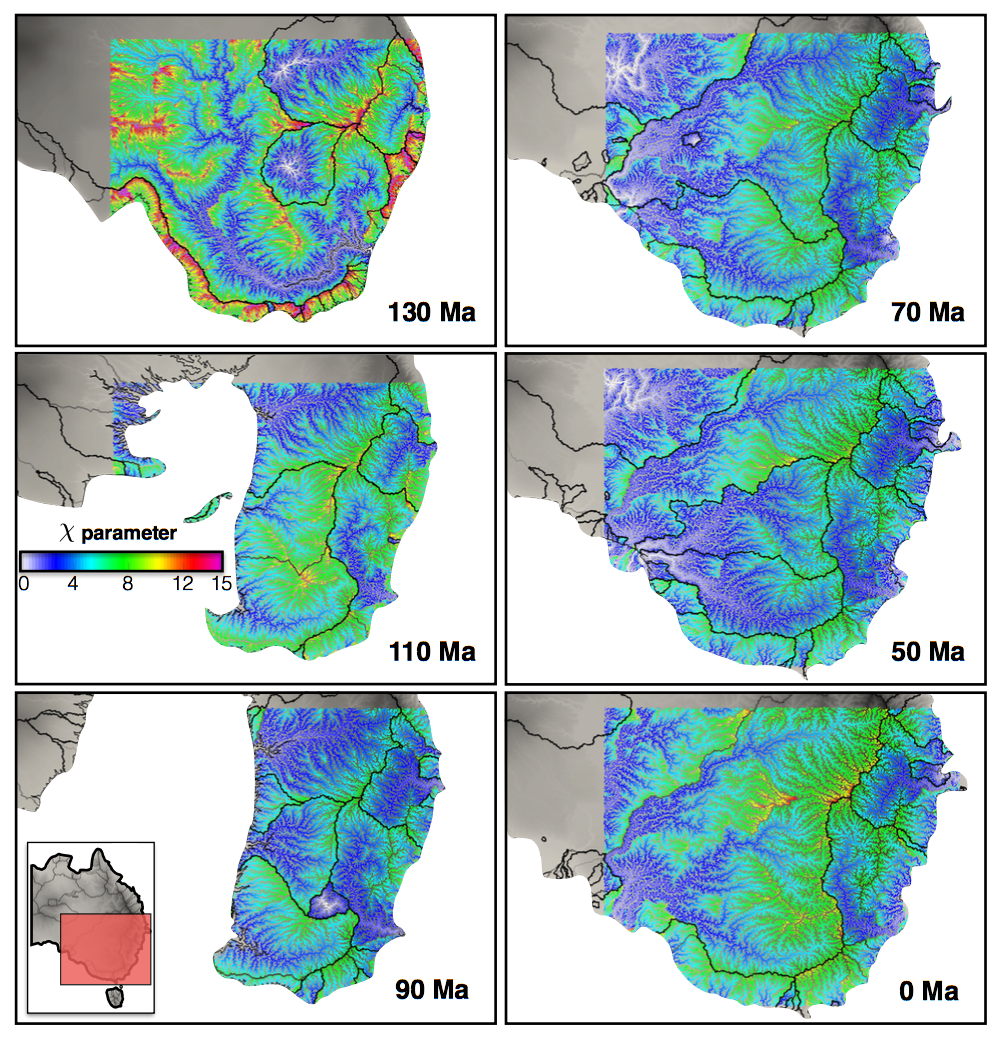
 Australia is an outstanding natural laboratory to study the influence of dynamic topography on landscape evolution, having been largely unaffected by tectonic deformation since the Jurassic. Recent studies of the past eastern Australian landscape from present-day longitudinal river profiles and from mantle flow models suggest that the interaction of plate motion with mantle convection accounts for the two phases of large-scale uplift of the region since 120 Ma. … Read more…
Australia is an outstanding natural laboratory to study the influence of dynamic topography on landscape evolution, having been largely unaffected by tectonic deformation since the Jurassic. Recent studies of the past eastern Australian landscape from present-day longitudinal river profiles and from mantle flow models suggest that the interaction of plate motion with mantle convection accounts for the two phases of large-scale uplift of the region since 120 Ma. … Read more…
Nature: Landscape dynamics and the Phanerozoic diversification of the biosphere
The long-term diversification of the biosphere responds to changes in the physical environment. Yet, over the continents, the nearly monotonic expansion of life started later in the early part of the Phanerozoic eon1 than the expansion in the marine realm, where instead the number of genera waxed and waned over time2. A comprehensive evaluation of … Read more…