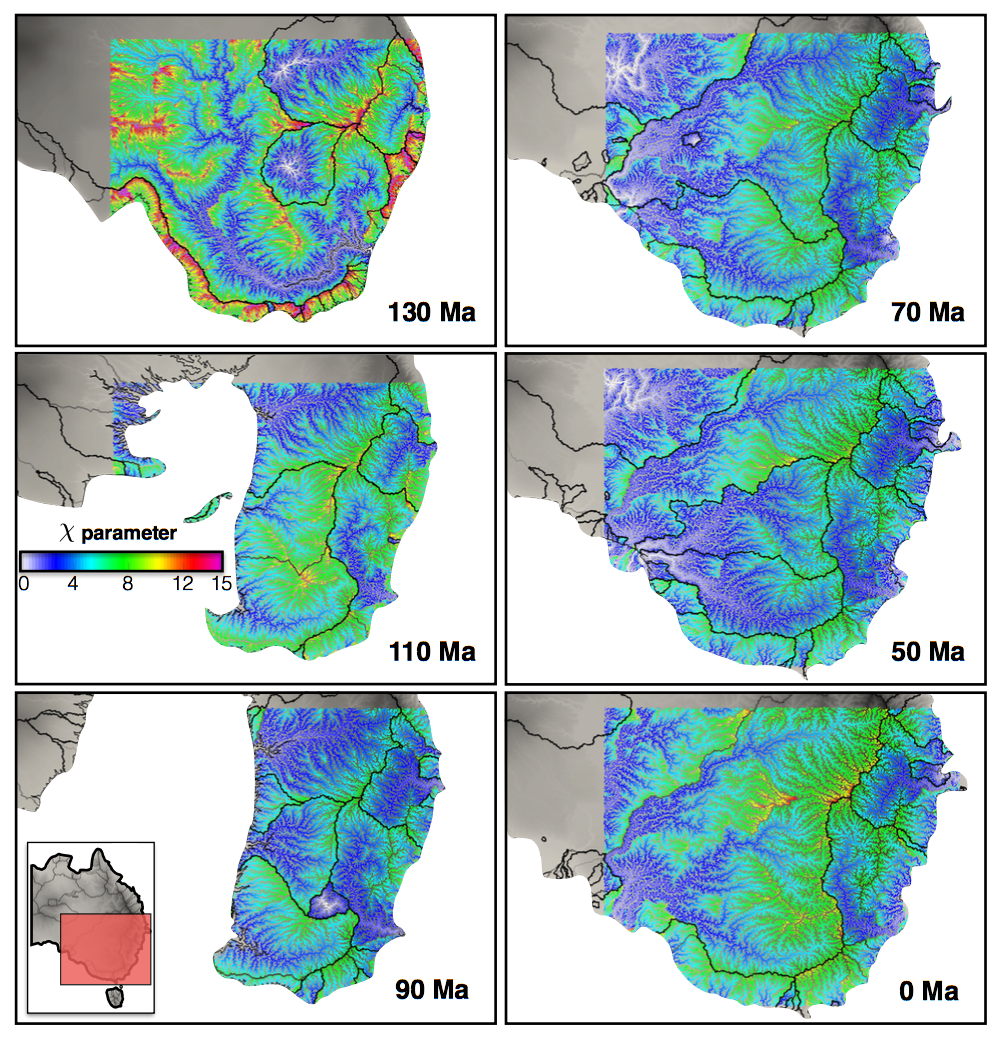
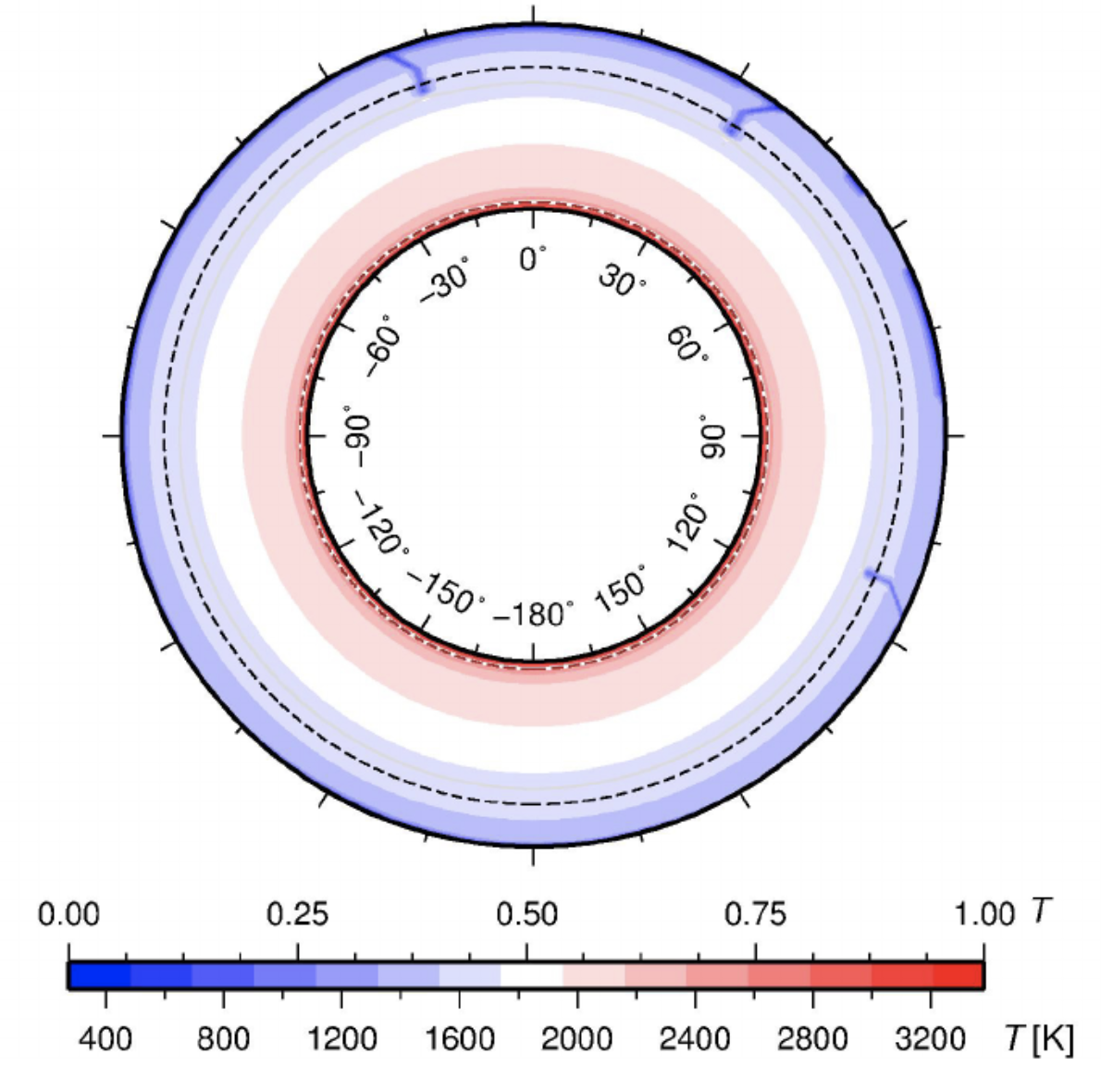
 Australia is an outstanding natural laboratory to study the influence of dynamic topography on landscape evolution, having been largely unaffected by tectonic deformation since the Jurassic. Recent studies of the past eastern Australian landscape from present-day longitudinal river profiles and from mantle flow models suggest that the interaction of plate motion with mantle convection accounts for the two phases of large-scale uplift of the region since 120 Ma. … Read more…
Australia is an outstanding natural laboratory to study the influence of dynamic topography on landscape evolution, having been largely unaffected by tectonic deformation since the Jurassic. Recent studies of the past eastern Australian landscape from present-day longitudinal river profiles and from mantle flow models suggest that the interaction of plate motion with mantle convection accounts for the two phases of large-scale uplift of the region since 120 Ma. … Read more…
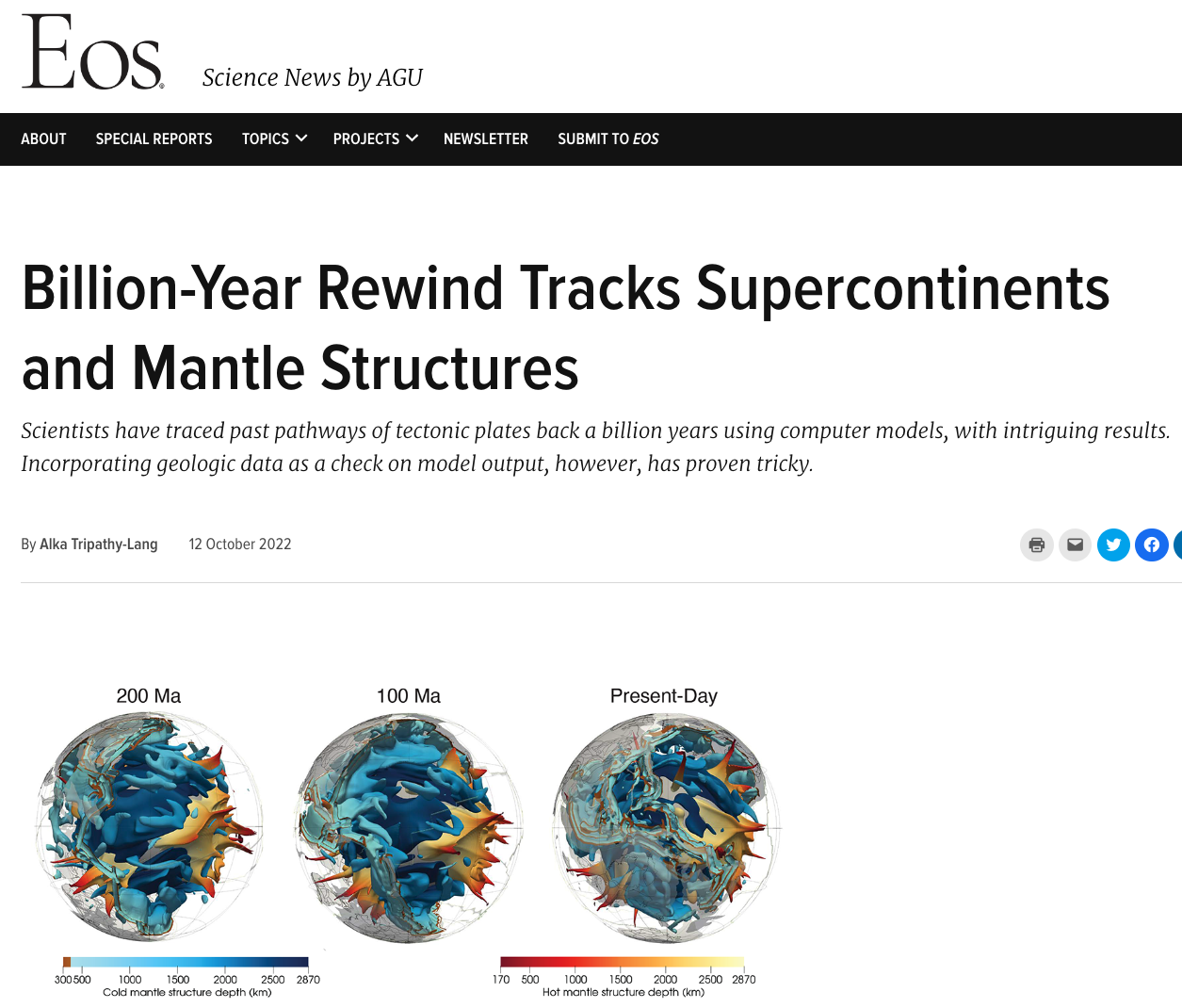
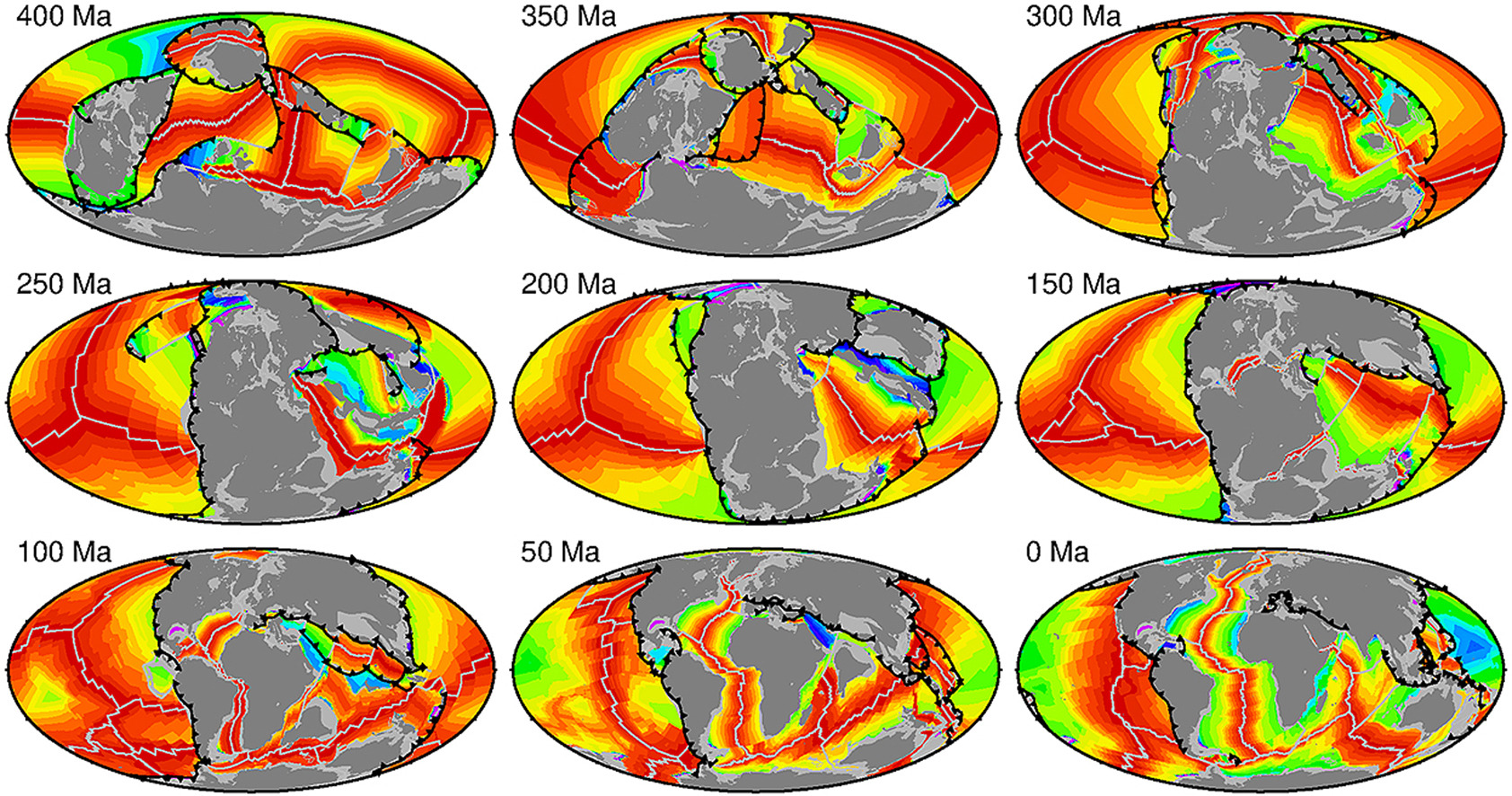
EOS: Billion-year rewind tracks supercontinents and mantle structures
AGU Science News: Billion-Year Rewind Tracks Supercontinents and Mantle Structures – EOS has featured our recent paper on tracing past pathways of tectonic plates and their boundaries back a billion years. The article highlights how our work on solid Earth system evolution is driving “a second plate tectonic revolution”., inspiring future work to test and … Read more…


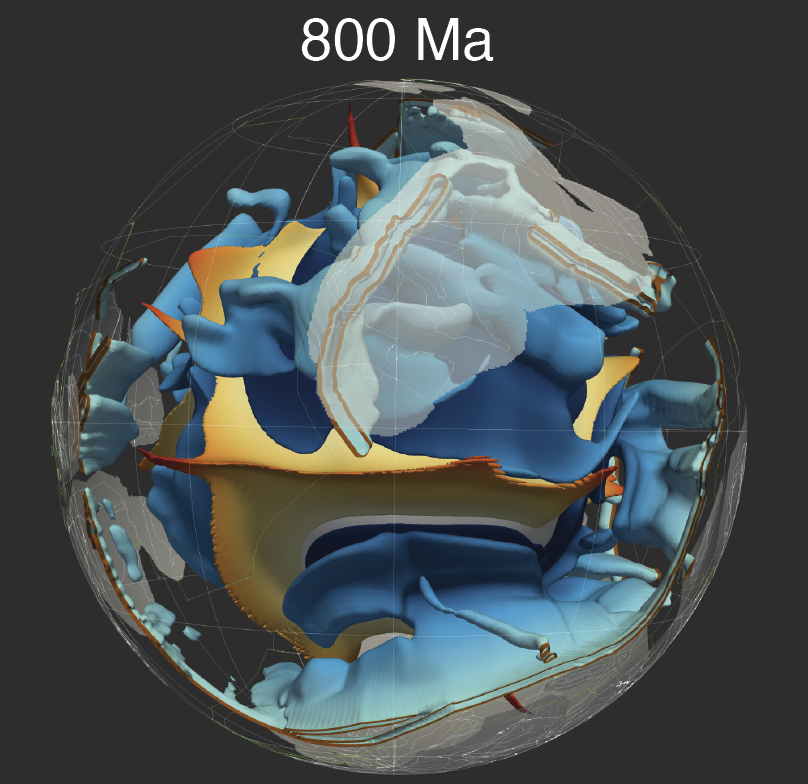
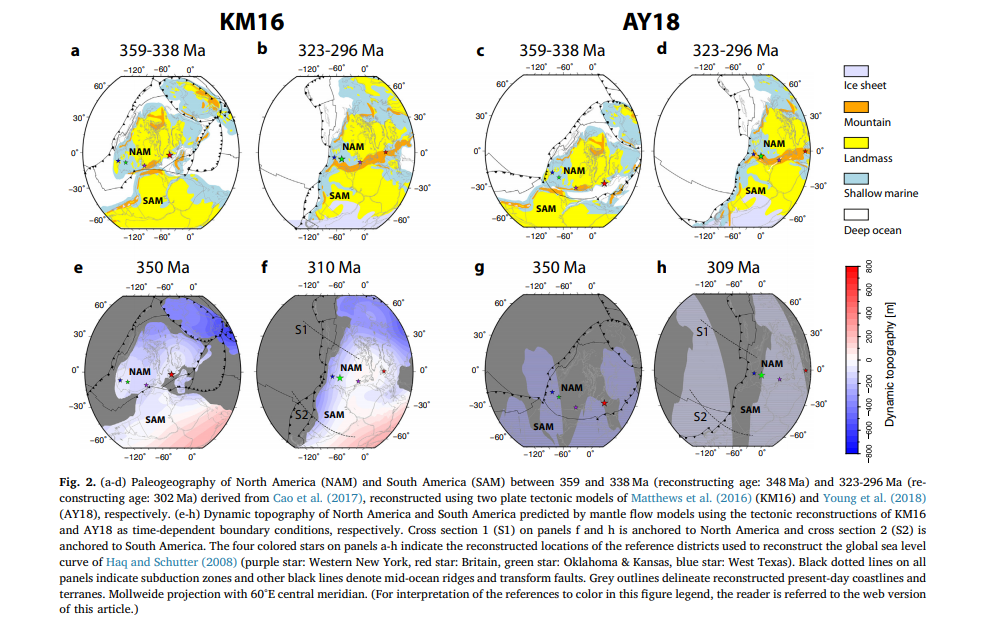
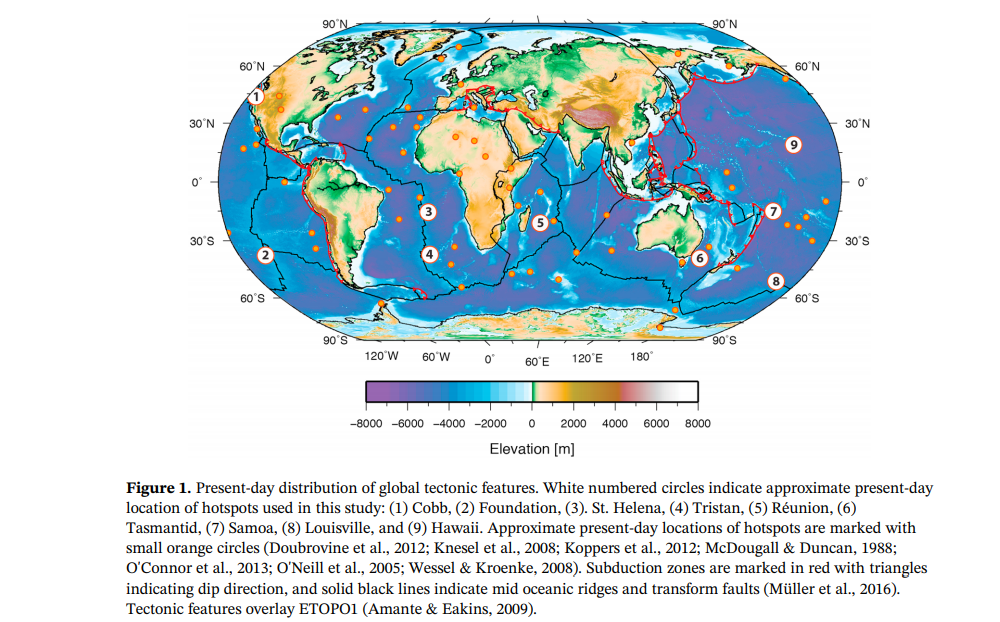
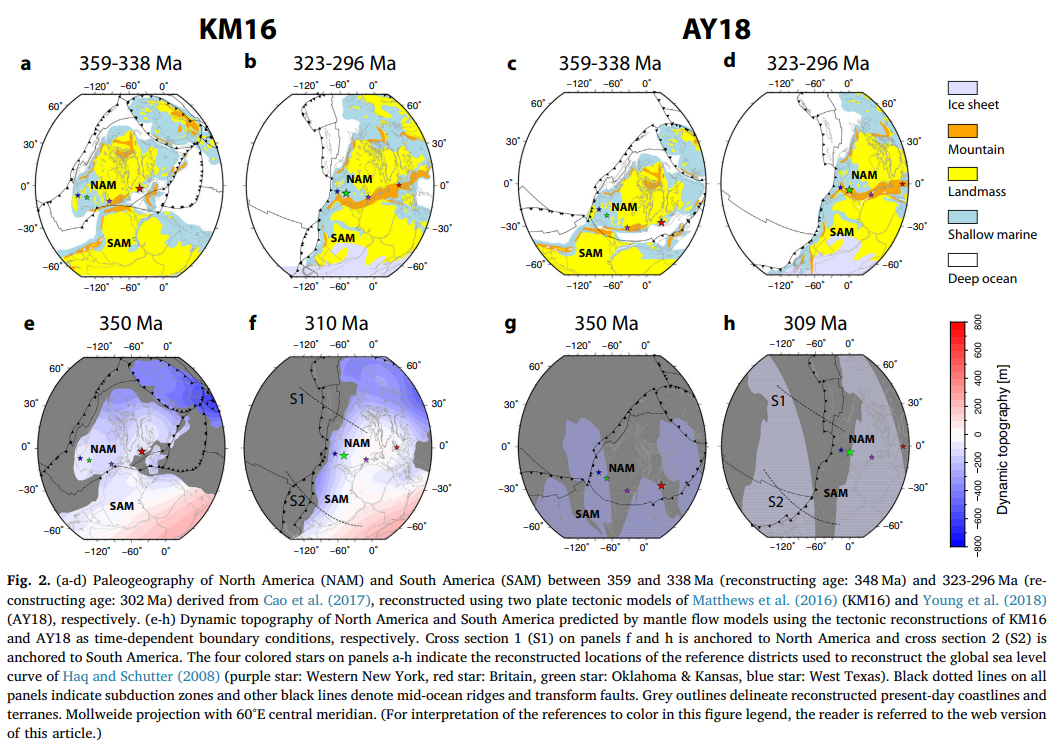
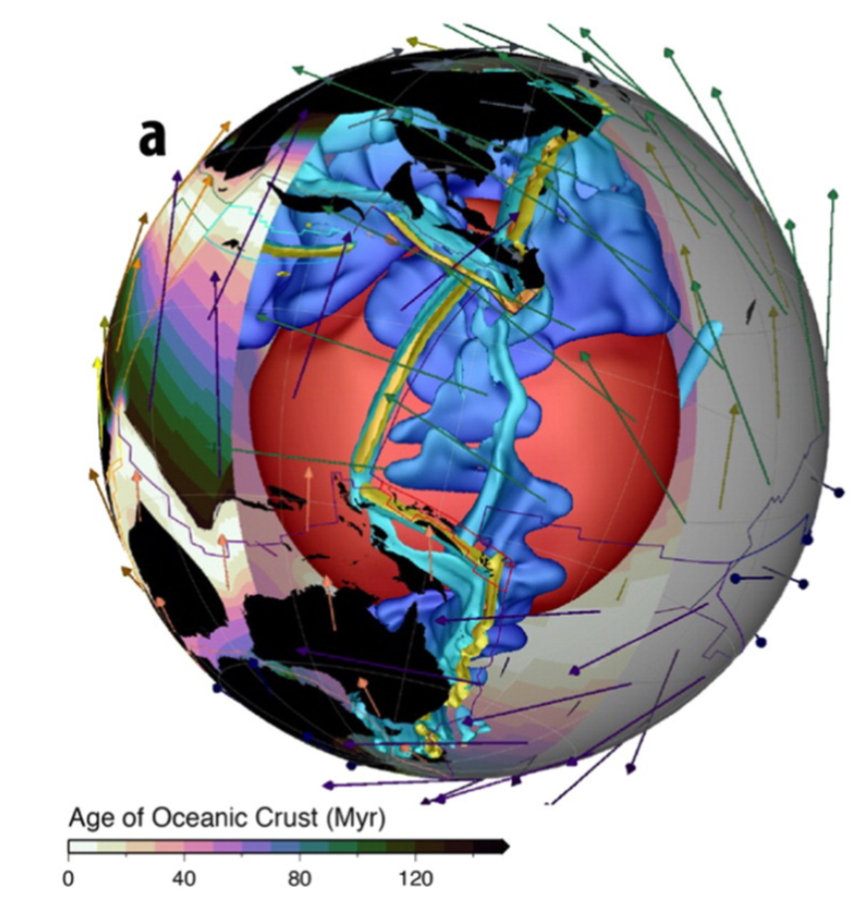
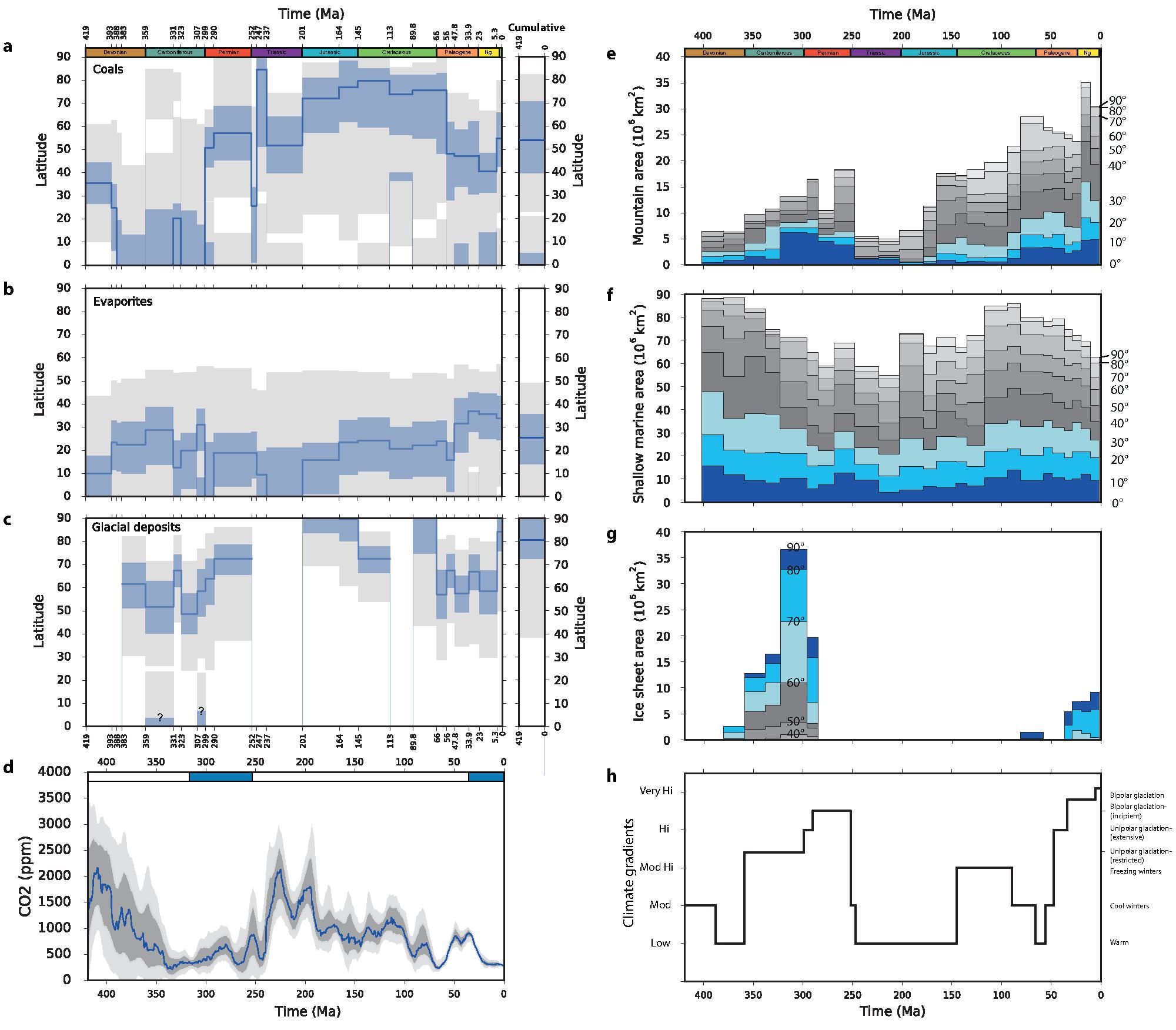
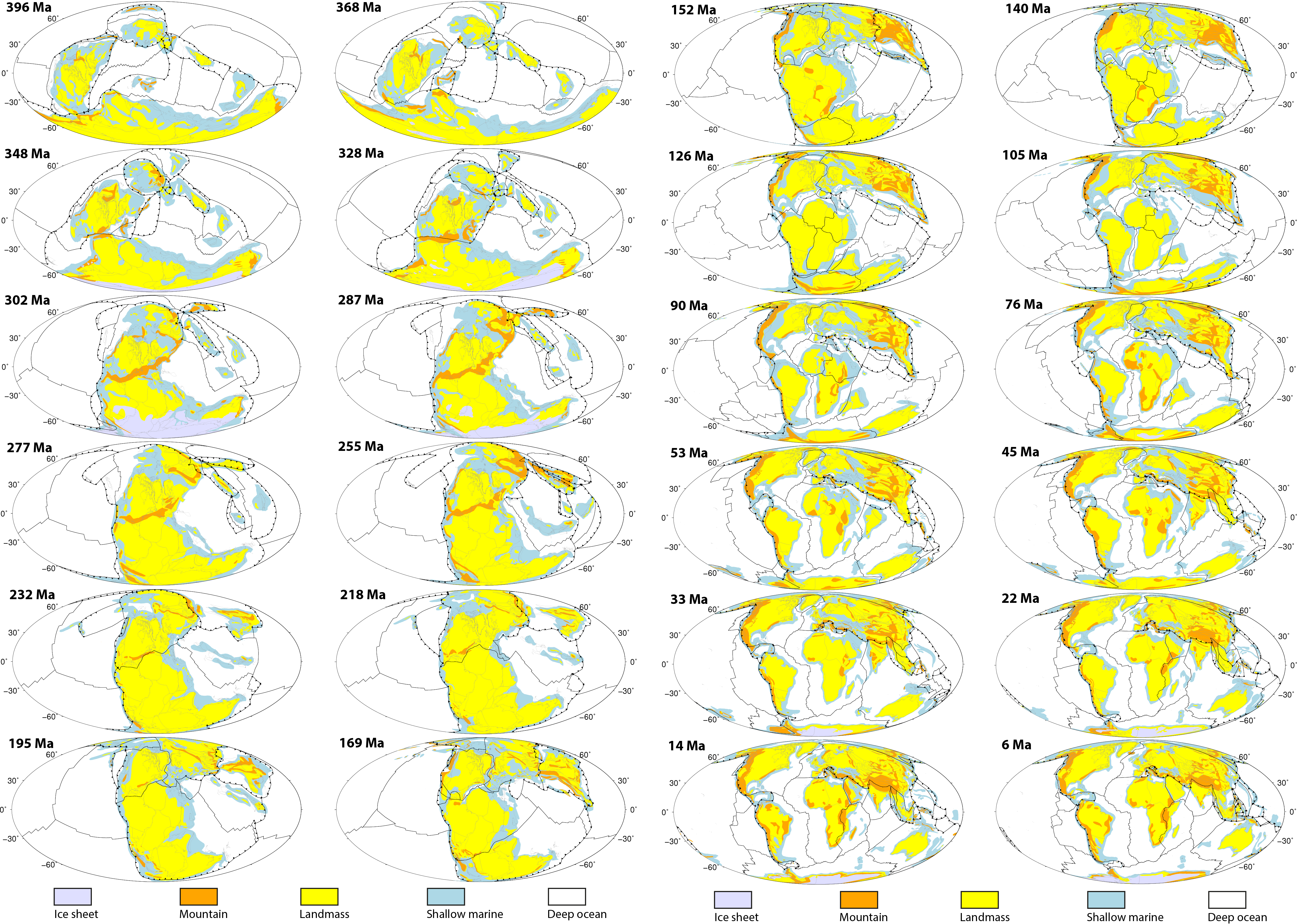
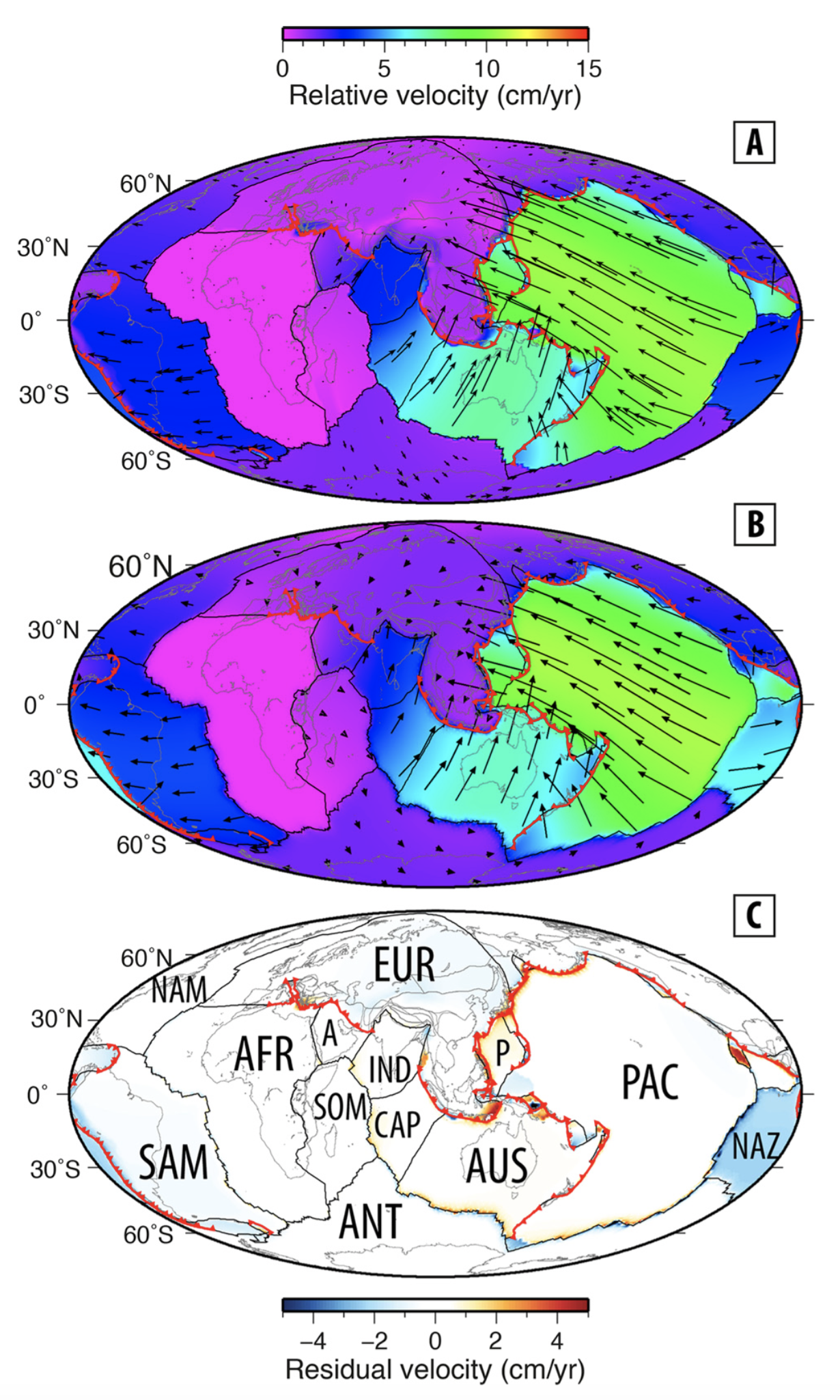
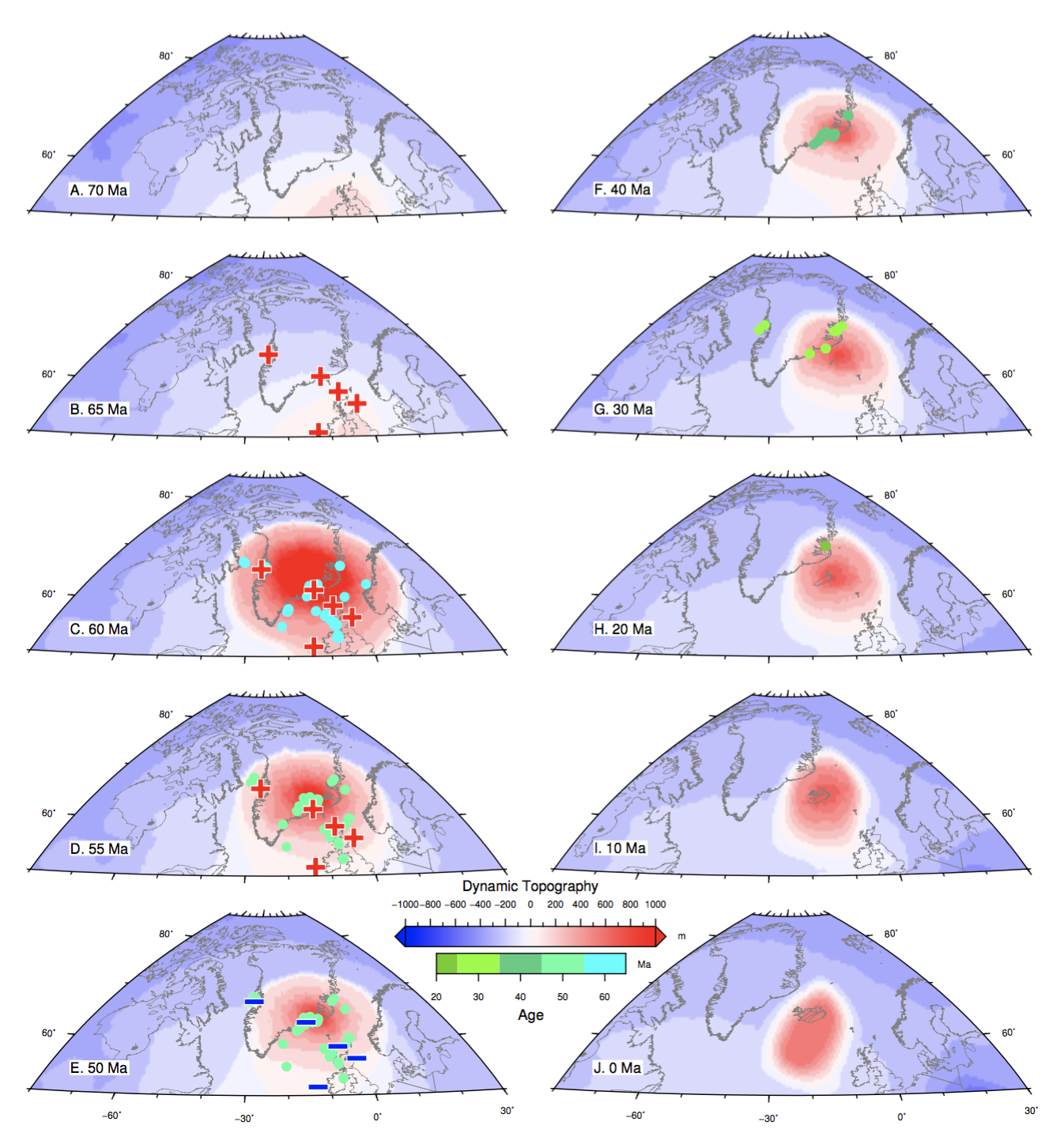
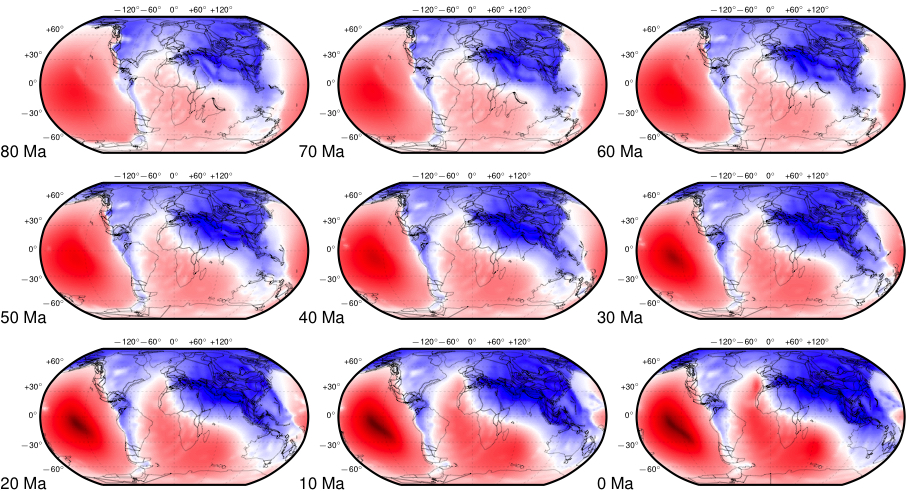

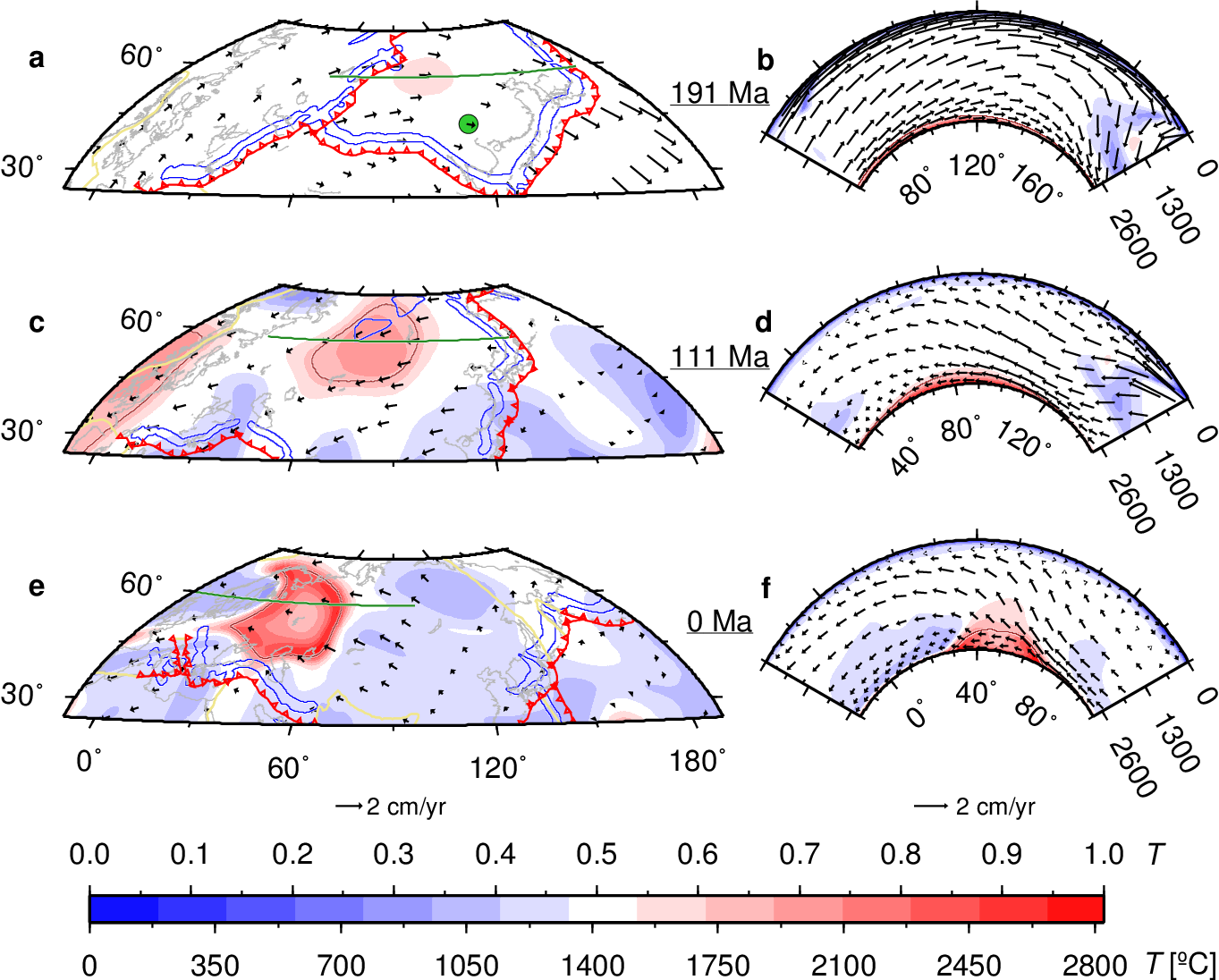
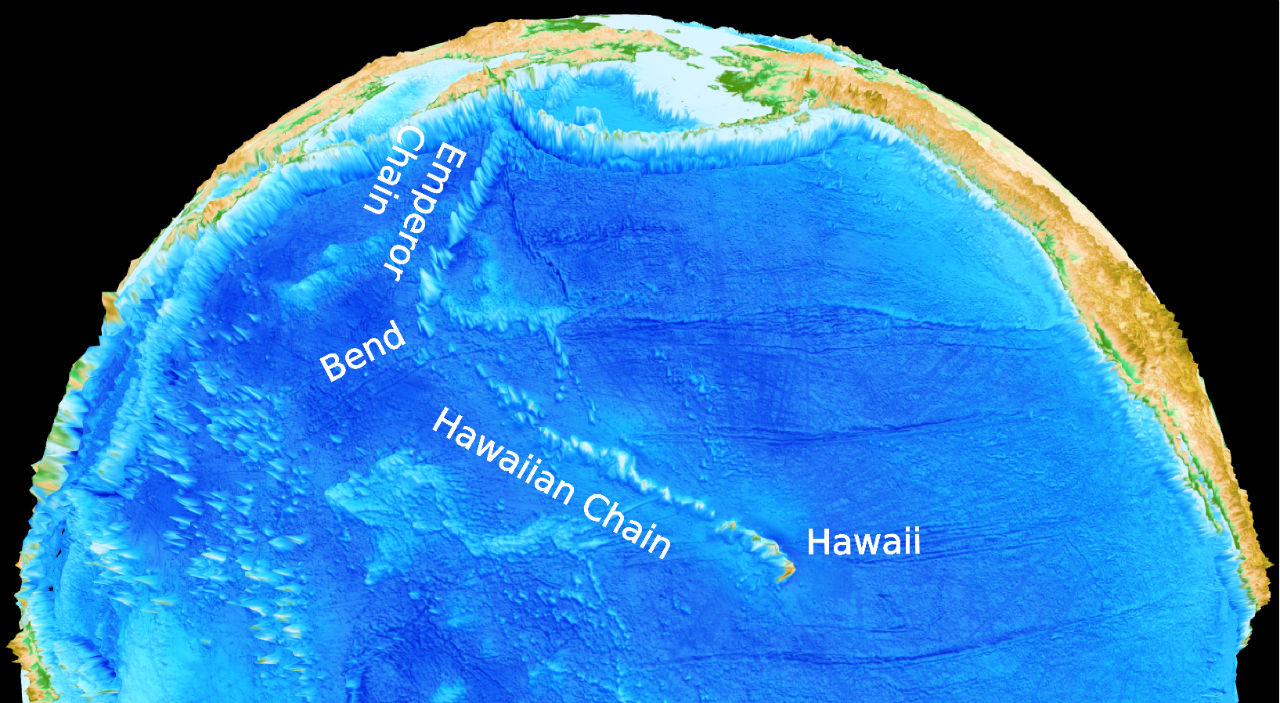
 Congratulations to Prof Dietmar Müller, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Kara Matthews, Dr Simon Williams, and Prof Michael Gurnis on their paper recently published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters. Their paper,
Congratulations to Prof Dietmar Müller, Dr Nicolas Flament, Dr Kara Matthews, Dr Simon Williams, and Prof Michael Gurnis on their paper recently published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters. Their paper,