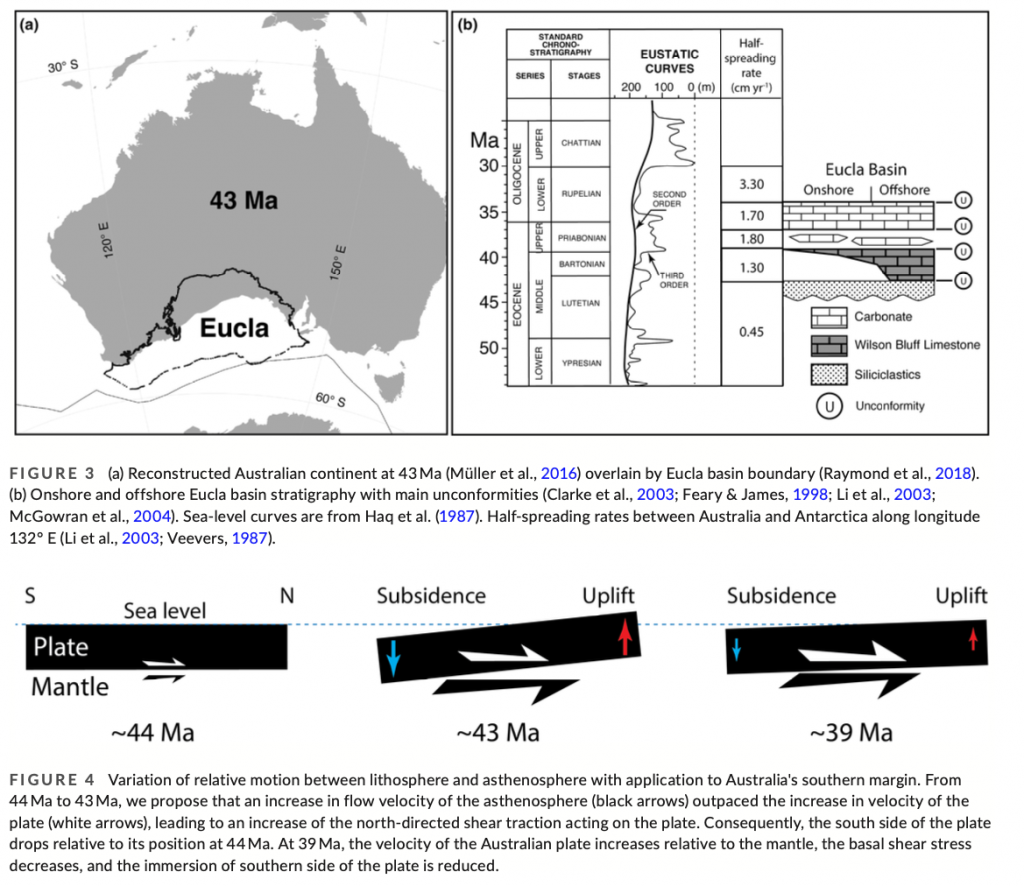
Dynamic subsidence and uplift of plates are often explained by the vertical motion of density anomalies in the mantle. Such models predict surface vertical motion rates of less than 100 m Myr−1 at long-wavelengths with a timespan of tens of Myr. However, during periods of relative sea-level stability, some of the phases of vertical motion on stable portions of plates have occurred at rates greater than 100 m Myr−1 during episodes that may last only a few Myr. Here, we show that vertical surface motions, with rates greater than 100 m Myr−1 and durations less than a few Myr, can be explained by changes in basal shear stress caused by variation in horizontal motion of a viscous plate relative to the asthenosphere. We apply our physical model to the short-lived mid-Eocene immersion of the southern margin of Australia.
![]()